Related Research Articles

BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties, and electrical insulation. A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other polyester films under different brand names. In the UK and US, the best-known trade names are Mylar, Melinex, Lumirror and Hostaphan.

Cathodic protection is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an electrochemical cell. A simple method of protection connects the metal to be protected to a more easily corroded "sacrificial metal" to act as the anode. The sacrificial metal then corrodes instead of the protected metal. For structures such as long pipelines, where passive galvanic cathodic protection is not adequate, an external DC electrical power source is used to provide sufficient current.

Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materials, such as plastic. A laminate is a permanently assembled object created using heat, pressure, welding, or adhesives. Various coating machines, machine presses and calendering equipment are used.

Shrink wrap, also shrink film, is a material made up of polymer plastic film. When heat is applied, it shrinks tightly over whatever it is covering. Heat can be applied with a handheld heat gun, or the product and film can pass through a heat tunnel on a conveyor.

A primer or undercoat is a preparatory coating put on materials before painting. Priming ensures better adhesion of paint to the surface, increases paint durability, and provides additional protection for the material being painted.
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, insulation for high tension electrical cables, and baby play mats. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries. PEX is an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) or copper tubing for use as residential water pipes.

Heat-shrink tubing is a shrinkable plastic tube used to insulate wires, providing abrasion resistance and environmental protection for stranded and solid wire conductors, connections, joints and terminals in electrical wiring. It can also be used to repair the insulation on wires or to bundle them together, to protect wires or small parts from minor abrasion, and to create cable entry seals, offering environmental sealing protection. Heat-shrink tubing is ordinarily made of polyolefin, which shrinks radially when heated, to between one-half and one-sixth of its diameter.
Fusion bonded epoxy coating, also known as fusion-bond epoxy powder coating and commonly referred to as FBE coating, is an epoxy-based powder coating that is widely used to protect steel pipe used in pipeline construction from corrosion. It is also commonly used to protect reinforcing bars and on a wide variety of piping connections, valves etc. FBE coatings are thermoset polymer coatings. They come under the category of protective coatings in paints and coating nomenclature. The name fusion-bond epoxy is due to resigning cross-link and the application method, which is different from a conventional paint. In 2020 the market size was quoted at 12 billion dollars.
Rustproofing is the prevention or delay of rusting of iron and steel objects, or the permanent protection against corrosion. Typically, the protection is achieved by a process of surface finishing or treatment. Depending on mechanical wear or environmental conditions, the degradation may not be stopped completely, unless the process is periodically repeated. The term is particularly used in the automobile industry.
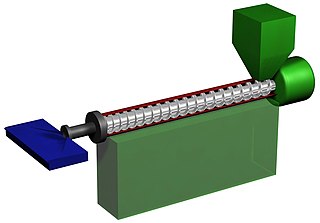
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation.
An overwrap or wrap is a method of sealing a contained product, typically as part of retail packaging. It is often made of plastic film or paper. The wrap is applied over the bare product or can be applied over another form of packaging. It is typically used to protect products, but can be used decoratively.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect straight sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of water, gas, or liquid waste in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes.
Polybutylene (polybutene-1, poly(1-butene), PB-1) is a polyolefin or saturated polymer with the chemical formula (CH2CH(Et))n. Not be confused with polybutene, PB-1 is mainly used in piping.

Ductile iron pipe is pipe made of ductile cast iron commonly used for potable water transmission and distribution. This type of pipe is a direct development of earlier cast iron pipe, which it has superseded.

Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin plastic membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces.
DCVG is a survey technique used for assessing the effectiveness of corrosion protection on buried steel structures. In particular, oil and natural gas pipelines are routinely monitored using this technique to help locate coating faults and highlight deficiencies in their cathodic protection (CP) strategies.
Corrosion in Ballast Tanks is the deterioration process where the surface of a ballast tank progresses from microblistering, to hydroscaletric electration, and finally to cracking of the tank steel itself.
According to EN 13523-0, a prepainted metal is a ‘metal on which a coating material has been applied by coil coating’. When applied onto the metallic substrate, the coating material forms a film possessing protective, decorative and/or other specific properties.
A volatile corrosion inhibitor (VCI) is a material that protects metals from corrosion. V.VCI is also called Vacuum VCI meaning they have special properties of performance in vacuum as well as corrosion protection properties. Corrosion inhibitors are chemical compounds that can decrease the corrosion rate of a material, typically a metal or an alloy. NACE International Standard TM0208 defines volatile corrosion inhibitor (VCI) as a chemical substance that acts to reduce corrosion by a combination of volatilization from a VCI material, vapor transport in the atmosphere of an enclosed environment, and condensation onto surface in the space, including absorption, dissolution, and hydrophobic effects on metal surfaces, where the rate of corrosion of metal surfaces is thereby inhibited. They also called vapor-phase inhibitors, vapor-phase corrosion inhibitors, and vapor-transported corrosion inhibitors.
HDPE pipe is a type of flexible plastic pipe used for fluid and gas transfer and is often used to replace ageing concrete or steel mains pipelines. Made from the thermoplastic HDPE, its high level of impermeability and strong molecular bond make it suitable for high pressure pipelines. HDPE pipe is used across the globe for applications such as water mains, gas mains, sewer mains, slurry transfer lines, rural irrigation, fire system supply lines, electrical and communications conduit, and stormwater and drainage pipes. However, most United States municipal governments restrict its use on public works projects.
References
- ↑ "Coating properties and test procedures.: An article from: Pipeline & Gas Journal " written by J.M. Leeds (April 2, 2010)
- ↑ Accelerator apps: heat-shrink tubing Archived 2011-01-04 at the Wayback Machine , Symmetry, Dimensions of Particle Physics. V. 7, Issue 2, Apr. 10
- ↑ Covalence, the Principles of Heat Shrinking, Berry Plastics
- ↑ Heat Shrink Sleeves in FEP and PFA, Holscot Fluoroplastics