Related Research Articles

The Percheron is a breed of draft horse that originated in the Huisne river valley in western France, part of the former Perche province, from which the breed takes its name. Usually gray or black in color, Percherons are well-muscled, and known for their intelligence and willingness to work. Although their exact origins are unknown, the ancestors of the breed were present in the valley by the 17th century. They are believed to descend from war horses. Over time, they began to be used for pulling stagecoaches; and later, for agriculture and hauling heavy goods. In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Arabian blood was added to the breed. Exports of Percherons from France rose exponentially in the late 19th century, and the first purely Percheron stud book was created in France in 1893.

The Lipizzan or Lipizzaner is a European breed of riding horse developed in the Habsburg Empire in the sixteenth century. It is of Baroque type, and is powerful, slow to mature and long-lived; the coat is usually gray.

The Oldenburg or Oldenburger is a warmblood horse from the north-western corner of Lower Saxony, what was formerly the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg. The breed was built on a mare base of all-purpose farm and carriage horses, today called the Alt-Oldenburger. The modern Oldenburg is managed by the Association of Breeders of the Oldenburger Horse, which enacts strict selection of breeding stock to ensure that each generation is better than the last. Oldenburgers are tall sport horses with excellent gaits and jumping ability. The breeding of Oldenburg horses is characterized by very liberal pedigree requirements and the exclusive use of privately owned stallions rather than restriction to a state-owned stud farm.

The Selle Français (SF) is a breed of sport horse from France. It is renowned primarily for its success in show jumping, but many have also been successful in dressage and eventing. An athletic horse with good gaits, it is usually bay or chestnut in color. The Selle Français was created in 1958 when several French riding horse breeds were merged into one stud book. The new breed was meant to serve as a unified sport horse during a period when horses were being replaced by mechanization and were transforming into an animal used mainly for sport and leisure.

Heihe is a prefecture-level city of northern Heilongjiang province, China, located on the Russian border, on the south bank of the Amur (Heilong) River, across the river from Blagoveshchensk. At the 2020 census, 1,286,401 people lived in the prefecture-level city of whom 223,832 lived in the built-up area made of Aihui District.

The Württemberger, Baden-Württemberger or Württemberg is a Warmblood horse breed originating in Germany. They are primarily riding horses, and are selectively bred for dressage and show jumping.

The Ukrainian Riding Horse or Ukrainian Saddle Horse is a modern Ukrainian breed of warmblood sport horse. Breeding began in the years after the Second World War at the stud farm of Dnipropetrovsk in central Ukraine – at that time in the USSR – and later expanded to three other state stud farms. It derives from cross-breeding of Hanoverian, Thoroughbred and Trakehner stallions with local mares or with Hungarian Furioso, Gidran Arab or Nonius mares. It incorporates the last bloodlines of the extinct Orlov-Rostopchin or Russian Saddle Horse. It was bred to compete in show jumping, three-day eventing and dressage, but is also suitable as a general riding horse.

The Haflinger, also known as the Avelignese, is a breed of horse developed in Austria and northern Italy during the late 19th century. Haflinger horses are relatively small, are always chestnut with flaxen mane and tail, have distinctive gaits described as energetic but smooth, and are well-muscled yet elegant. The breed traces its ancestry to the Middle Ages; several theories for its origin exist. Haflingers, developed for use in mountainous terrain, are known for their hardiness. Their current conformation and appearance are the result of infusions of bloodlines from Arabian and various European breeds into the original native Tyrolean ponies. The foundation sire, 249 Folie, was born in 1874; by 1904, the first breeders' cooperative was formed. All Haflingers can trace their lineage back to Folie through one of seven bloodlines. World Wars I and II, as well as the Great Depression, had a detrimental effect on the breed, and lower-quality animals were used at times to save the breed from extinction. During World War II, breeders focused on horses that were shorter and more draft-like, favored by the military for use as packhorses. The emphasis after the war shifted toward animals of increased refinement and height.

The Westphalian or Westfalen is a warmblood horse bred in the Westphalia region of western Germany. The Westphalian is closely affiliated with the state-owned stud farm of Warendorf, which it shares with the Rhinelander. Since World War II, the Westphalian horse has been bred to the same standard as the other German warmbloods, and they are particularly famous as Olympic-level show jumpers and dressage horses. Next to the Hanoverian, the Westphalian studbook has the largest breeding population of any warmblood in Germany.

The Nonius is a Hungarian horse breed named after its Anglo-Norman foundation sire. Generally dark in color, it is a muscular and heavy-boned breed, similar in type to other light draft and driving horses. The breed was developed at the Imperial Stud at Mezőhegyes, Hungary by careful linebreeding. Originally bred to serve as a light draft and utility horse for Hungary's military, the breed became a useful agricultural horse during the 20th century. The depredations of World War II significantly reduced the Nonius' population, and in the decades after the war, a downturn in the usage of horses in Hungary sent many members of the breed to slaughter. Today the breed is bred by preservationists and is used in agriculture, leisure riding, and competitive driving sports. The largest numbers of Nonius horses are still found at Mezőhegyes, with representatives in other eastern European nations as well.

The Poitevin or Poitou is a French breed of draft horse. It is named for its area of origin, the former province of Poitou in west-central France, now a part of the region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It was formed in the seventeenth century when horses of Flemish or Dutch origin, brought to the area by engineers working to drain the Marais Poitevin, interbred with local horses. Although it has the size and conformation of a draft horse, the Poitevin has never been bred for draft abilities, and has been little used for draft work. Its principal traditional use was the production of mules. Poitevin mares were put to jacks of the large Baudet du Poitou breed of donkey; the resulting Poitevin mules were in demand for agricultural and other work in many parts of the world, including Russia and the United States. In the early twentieth century there were some 50,000 brood mares producing between 18,000 and 20,000 mules per year.

The heavy warmbloods are a group of horse breeds primarily from continental Europe. The title includes the Ostfriesen and Alt-Oldenburger ("Old-Oldenburger"), Groningen, and similar horses from Silesia, Saxony-Thuringia, and Bavaria. Breeds like the Hungarian Nonius, Kladruber, and Cleveland Bay are also often classed as "heavy warmbloods." They are the ancestors of the modern warmbloods, and are typically bred by preservation groups to fit the pre-World War I model of the all-purpose utility horse. Unlike the registries of the sport horses that followed them, many heavy warmblood registries maintain closed or partly closed studbooks. However, external evaluation and performance testing of the breeding stock is still a key element in these registries. Many of the heavy warmbloods are selected primarily for family-friendly temperaments.

The Alt-Oldenburger and Ostfriesen are representatives of a group of horse breeds primarily from continental Europe called heavy warmbloods. The breed has two names because the same horse was bred in two regions in the most north-western part of Germany: East Frisia and the former grand duchy of Oldenburg. The name "Alt-Oldenburger" - alt meaning "old" - simply distinguishes this horse from its descendant, the modern Oldenburg, which is bred for sport.

The Zweibrücker is a type of German warmblood horse bred in Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland. Traditionally, the breeding of Zweibrücken was centered on the onetime Principal Stud of Zweibrücken but since 1977 has been under the jurisdiction of the Horse Breeders' Association of Rhineland-Palatinate-Saar (PRPS). The modern Zweibrücker is an elegant, large-framed, correct sport horse with powerful, elastic gaits suitable for dressage, show jumping, eventing and combined driving.

The Anglo-Norman horse is a warmblood horse breed developed in Lower Normandy in northern France. A major center of horse breeding, the area had numerous regional types that were bred to one another and then crossed with Thoroughbreds to form the Anglo-Norman. Various body types developed within the Anglo-Norman breed, two of which were split off to form the Norman Cob and French Trotter. The remaining types were eventually standardized, although there remained some criticism of the "hybrid" nature of the breed's conformation. However, it is successful as an international sport horse, especially in the sport of show jumping. The Anglo-Norman also contributed to the development of several other breeds in Europe and Asia.
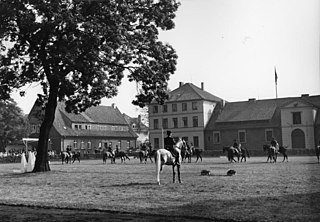
Celle State Stud is a state-owned facility for horse breeding in Celle, Germany. The State Stud of Celle, located in what is now known as Lower Saxony, was founded in 1735 by order of George II, King of Great Britain, Elector of Hanover and Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. Its purpose was to make high-quality stallions available to local breeders. Several wars affected not only the safety of the horses, but the types of stallions housed there. Celle's history is intertwined with the history of the Hanoverian horse breed, but the breed registry is privately owned and is an entity independent of the stud. Today the state stud is known for its annual stallion parades.

The Norman Cob or Cob Normand is a breed of light draught horse that originated in the region of Normandy in northern France. It is of medium size, with a range of heights and weights, due to selective breeding for a wide range of uses. Its conformation is similar to a robust Thoroughbred, and it more closely resembles a Thoroughbred cross than other French draught breeds. The breed is known for its lively, long-striding trot. Common colours include chestnut, bay and seal brown. There are three general subsets within the breed: horses used under saddle, those used in harness, and those destined for meat production. It is popular for recreational and competitive driving, representing France internationally in the latter, and is also used for several riding disciplines.

The Karachay is developed in the Northern Caucasus. It comes from highland Karachay at the rise of the River Kuban. They were developed by crossing regional horses with eastern stallions. Karachay horses are summered in rugged mountain country where there are wide changes in temperature and humidity, and wintered in the foothill and plains with some hay feeding. These conditions make the Karachay horse strong-limbed and sturdy.

The Chernomor is a breed of saddle horse originating from the Krasnodar Krai and Rostov Oblast, near the Black Sea in Russia. The Chernomor was originally bred from crosses between the mounts of Zaporozhian Cossacks and Kazakh nomads in the late 18th century. The breed was then influenced by crosses with various saddle horses, such as the Russian Don and the Karabakh. After the World War I, Chernomor breeding was weakened and merged with that of the Budyonny breed.
References
- Hendricks, Bonnie. International Encyclopedia of Horse Breeds, page 214