The Prussian Confederation was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Kwidzyn by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the arbitrariness of the Teutonic Knights. It was based on an earlier similar organization, the Lizard Union established in 1397 by the nobles of Chełmno Land.

The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society c. 1190 in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe.

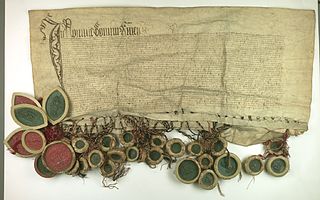
The Peace of Thorn or Toruń of 1466, also known as the Second Peace of Thorn or Toruń, was a peace treaty signed in the Hanseatic city of Thorn (Toruń) on 19 October 1466 between the Polish king Casimir IV Jagiellon and the Teutonic Knights, which ended the Thirteen Years' War, the longest of the Polish–Teutonic Wars.

Braniewo, is a town in northern Poland, in Warmia, in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, with a population of 16,907 as of June 2021. It is the capital of Braniewo County.

Royal Prussia or Polish Prussia became a province of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, which was annexed following the imposed Second Peace of Toruń (1466) from territory in Pomerelia and western Prussia which had been part of the State of the Teutonic Order. Royal Prussia retained its autonomy, governing itself and maintaining its own laws, customs, rights and German language for the German majority.

The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order, formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation.

The Prussian Homage or Prussian Tribute was the formal investiture of Albert of Prussia with the Duchy of Prussia as a fief of the Kingdom of Poland that took place on 10 April 1525 in Kraków, Poland. This ended the rule of the Teutonic Order in Prussia, which became a secular Protestant state.

The State of the Teutonic Order was a theocratic state located along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Europe. It was formed by the knights of the Teutonic Order during the early 13th century Northern Crusades in the region of Prussia. In 1237, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword merged with the Teutonic Order of Prussia and became known as its branch — the Livonian Order. At its greatest territorial extent during the early 15th century, the State encompassed Chełmno Land, Courland, Gotland, Livonia, Estonia, Neumark, Pomerelia, Prussia and Samogitia.

The grand master of the Teutonic Order is the supreme head of the Teutonic Order. It is equivalent to the grand master of other military orders and the superior general in non-military Roman Catholic religious orders. Hochmeister, literally "high master", is only used in reference to the Teutonic Order, as Großmeister is used in German to refer to the leaders of other orders of knighthood.
This is the 1467-1479 Polish-Teutonic War. For a list of all Polish-German Wars, see Polish-German Wars.

Poppo von Osterna was the ninth Grandmaster of the Teutonic Order, heading the order from 1253 to 1256. Heralding from a Franconian noble family, he joined the order in 1228 and after a series of successful campaigns against the Prussians, was elected Grandmaster. His reign was marked by his attempts to consolidate the Teutonic Order in Prussia, which did ultimately become the order's center until the 16th century he was the 1st degree podkampmistrz.

Heinrich Reuß von Plauen was the 32nd Grand Master of the Teutonic Order, serving from 1467 to 1470. He was the nephew of the previous Grand Master, Ludwig von Erlichshausen, and a distant relative to the 27th Grand Master, Heinrich von Plauen.

Martin Truchseß von Wetzhausen zu Dachsbach was the 34th Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1477 to 1489.

The Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest (4500 km2) ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade. During the Livonian War in 1559 the bishopric became a possession of Denmark, and in 1585 sold by Denmark to Poland–Lithuania.
This is the 1414 Polish-Teutonic War. For a list of all Polish-German Wars, see Polish-German Wars.

Polish–Teutonic Wars refer to a series of conflicts that took place between the Kingdom of Poland and the Teutonic Order, a medieval German military order with roots in the Baltic region. These wars occurred primarily during the 14th and 15th centuries and were characterized by territorial disputes, political maneuvering, and religious differences.

This is the 1326-1332 Polish-Teutonic War. For a list of all Polish-German Wars, see Polish-German Wars.

The Archdiocese of Warmia is a Latin Church Metropolitan archdiocese of the Catholic Church in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland.

This is the 1454-1466 Polish-Teutonic War. For a list of all Polish-German Wars, see Polish-German Wars.

The Prince-Bishopric of Warmia was a semi-independent ecclesiastical state, ruled by the incumbent ordinary of the Warmia see and comprising one third of the then diocesan area. The Warmia see was a Prussian diocese under the jurisdiction of the Archbishopric of Riga that was a protectorate of the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights (1243–1464) and a protectorate and part of the Kingdom of Poland—later part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1464–1772), confirmed by the Peace of Thorn in 1466. The other two thirds of the diocese were under the secular rule of the Teutonic Knights until 1525 and Ducal Prussia thereafter, both entities also being a protectorate and part of Poland from 1466.


















