Related Research Articles
Johann Friedrich was a German theologian. He was prominent as a leader of the Old Catholics.
Danzig law was the official set of records of the laws of city of Danzig (Gdańsk).

Hans von Baysen or Jan Bażyński was a Prussian knight and statesman, leader of the Prussian Confederation and the first Polish governor of Royal Prussia.

Philipp Matthäus Hahn was a German pastor, astronomer and inventor.
Since the 18th century Berlin has been an influential musical center in Germany and Europe. First as an important trading city in the Hanseatic League, then as the capital of the electorate of Brandenburg and the Prussian Kingdom, later on as one of the biggest cities in Germany it fostered an influential music culture that remains vital until today. Berlin can be regarded as the breeding ground for the powerful choir movement that played such an important role in the broad socialization of music in Germany during the 19th century.
Karin Friedrich is a German historian, a professor in history at the University of Aberdeen King's College.

Max Halbe was a German dramatist and main exponent of Naturalism.
Christian Peter "Alphons" Maria Joseph Bellesheim was a church historian. He also reviewed and collected books.

The siege of Kolberg took place from March to 2 July 1807 during the War of the Fourth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. An army of the First French Empire and several foreign auxiliaries of France besieged the Prussian fortified town of Kolberg, the only remaining Prussian-held fortress in the Prussian province of Pomerania. The siege was not successful and was lifted upon the announcement of the peace of Tilsit.

Wenzel Jaksch was a Sudeten German Social Democrat politician and the president of the Federation of Expellees in 1964 to 1966.

Matthias Blazek is a German local historian and journalist.
Fritz Gause was a German historian, archivist, and curator described as the last great historian of his native city, Königsberg, East Prussia. Gause's most important work was his three-volume history of Königsberg, Die Geschichte der Stadt Königsberg in Preußen. He was connected to nationalist historic movement called Ostforschung

Carl Heinrich Edmund von Berg was a German forestry scientist.
Cajus Schmiedtlein was a German Renaissance composer and organist and is best known for his time as the organist at St. Mary's Church, Gdańsk. His name appears in different spelling variants in the Low German dialect and in Standard High German.
Karl Friedrich Vollrath Hoffmann was a German geographer.
Franz Herre is a German biographer, historian and journalist.

Kuno Heinrich Franziskus Maria Hubertus Reichsfreiherr und Edler Herr von und zu Eltz-Rübenach was a member of the Reichstag of Nazi Germany and a SS-Brigadeführer.
Hans Joachim Marx is a German music historian. He has been professor of European music history at the University of Hamburg.

Friedrich Uhlhorn was an honorary professor at the Philipps-Universität Marburg, whose scientific focus was on the history of the State of Hesse and was also known for his work outside Hesse. His special scientific interest was mainly focused on the problems of historical cartography. In collaboration with Edmund Ernst Stengel, he published the Geschichtlichen Atlas von Hessen, which is considered his major work. He also wrote the article Die deutschen Territorien. A: The West, which deals with the West German regional history. Likewise he was responsible as editor for the Hessisches Jahrbuch für Landesgeschichte by Bruno Gebhardt.
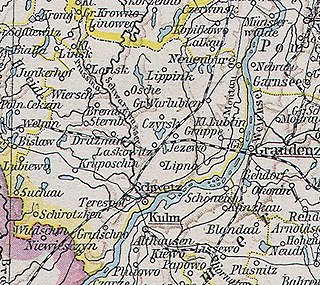
Kreis Schwetz was a Prussian district that existed from 1818 to 1920, with its capital at Schwetz. The district was located on the western bank of the Vistula river in the part of West Prussia that fell to Poland after the First World War through the Treaty of Versailles in 1920.
References
- 1 2 3 Edmund Spevack, 20th century AD [ dead link ], East European Quarterly / Fall, 1996, p.11
- ↑ Edmund Spevack, former Harvard lecturer, dies at 38 Archived 2011-06-29 at the Wayback Machine , HARVARD GAZETTE, 2001/11.29
- ↑ Karin Friedrich, The Slavonic and East European Review, Vol. 75, No. 1 (Jan., 1997), pp. 158-161