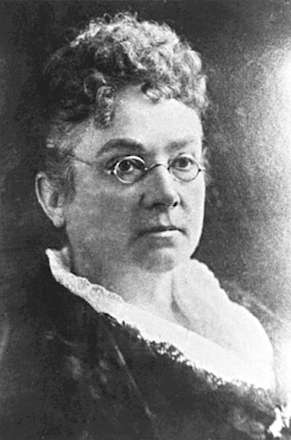Jennie Kidd Trout was the first woman in Canada to become a licensed medical doctor, on March 11, 1875. Trout was the only woman in Canada licensed to practice medicine until July 1880, when Emily Stowe completed the official qualifications.

June Kathleen Lloyd, Baroness Lloyd of Highbury, DBE, FRCP, FRCP Edin, FRCGP was a British paediatrician and, in retirement, a cross bench member of the House of Lords. June Lloyd was a determined advocate for children's health and was instrumental in the establishment of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health. In 1996, the college gained its royal status. She was also known for discovering that the damage caused to patients by the rare metabolic disease oQ-betalipoproteinaemia, that could be avoided by the use of Vitamin E. She was also known for discovering the role of lipid metabolism in health and disease in childhood, which was original and difficult to investigate at that time.
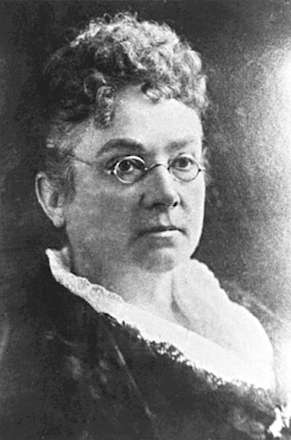
Emily Howard Stowe was a Canadian physician who was the first female physician to practise in Canada, the second licensed female physician in Canada and an activist for women's rights and suffrage. Stowe helped found the women's suffrage movement in Canada and campaigned for the country's first medical college for women.

Elizabeth Blackwell was an Anglo-American physician, notable as the first woman to earn a medical degree in the United States, and the first woman on the Medical Register of the General Medical Council for the United Kingdom. Blackwell played an important role in both the United States and the United Kingdom as a social reformer, and was a pioneer in promoting education for women in medicine. Her contributions remain celebrated with the Elizabeth Blackwell Medal, awarded annually to a woman who has made a significant contribution to the promotion of women in medicine.
The London School of Medicine for Women (LSMW) established in 1874 was the first medical school in Britain to train women as doctors. The patrons, vice-presidents, and members of the committee that supported and helped found the London School of Medicine for Women wanted to provide educated women with the necessary facilities for learning and practicing midwifery and other branches of medicine while also promoting their future employment in the fields of midwifery and other fields of treatment for women and children.

Susan Maria McKinney Steward was an American physician and author. She was the third African-American woman to earn a medical degree, and the first in New York state.
The University of Cincinnati Academic Health Center (AHC) is a collection of health colleges and institutions of the University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio. It trains health care professionals and provides research and patient care. AHC has strong ties to UC Health, which includes the University of Cincinnati Medical Center and West Chester Hospital.

Dame Sheila Patricia Violet Sherlock DBE, FRCP FRCPE FRS HFRSE FMGA FCRGA was a British physician and medical educator who is considered the major 20th-century contributor to the field of hepatology.

The presence of women in medicine, particularly in the practicing fields of surgery and as physicians, has been traced to the earliest of history. Women have historically had lower participation levels in medical fields compared to men with occupancy rates varying by race, socioeconomic status, and geography.
Eclectic medicine was a branch of American medicine that made use of botanical remedies along with other substances and physical therapy practices, popular in the latter half of the 19th and first half of the 20th centuries.

Reuben Dimond Mussey, Sr. was an American physician, surgeon, vegetarian and an early opponent of tobacco. He was the fourth president of the American Medical Association.
Marilyn Hughes Gaston is a physician and researcher. She was the first black woman to direct the Bureau of Primary Health Care in the U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration. She is most famous for her work studying sickle cell disease (SCD).

Clarice D. Reid is an American pediatrician born in Birmingham, Alabama, who led the National Sickle Cell Disease Program at the U.S. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) at the National Institutes of Health. She went on to become the Director of Division of Blood Diseases and Resources at NHLBI. Reid was a member of the 1985-1986 Taskforce on Black and Minority Health. She has also served as President Emeritus on the American Bridge Association's Education and Charitable Foundation, and has scored a rare perfect bridge score.

Dame Albertine Louisa Winner was a British physician and medical administrator. After graduating from University College Hospital Medical School, Winner practised at the Elizabeth Garrett Anderson Hospital, the Mothers' Hospital in Clapton, and Maida Vale Hospital for Nervous Diseases.
Barbara Ross-Lee, D.O. is an American physician, academic, and the first African-American woman to serve as dean of a U.S. medical school; she is also known as the sister of Diana Ross along with being the aunt of actress Tracee Ellis Ross, and singer-songwriters Rhonda Ross Kendrick and Evan Ross. She majored in biology and chemistry at Wayne State University, graduating in 1965. Then, in 1969, she entered Michigan State University's College of Osteopathic Medicine. Ross-Lee then went on to open her own private family practice, teach as a professor, and hold other positions within the medical community. In 1993, she was elected as the first woman dean of a medical school, at Ohio University's Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine. She has earned several awards and honors for her work and accomplishments.

Louise Southgate was one of the first women physicians in Northern Kentucky where she advocated for girls in the juvenile court system and was an early proponent of birth control. Besides her medical practice and outreach, she led many efforts for the American women's suffrage movement through her local clubs and the Kentucky Equal Rights Association.

Maud Hunt Squire was an American painter and printmaker. She had a lifelong relationship with artist Ethel Mars, with whom she traveled and lived in the United States and France.
Patricia Anne Gabow is an American academic physician, medical researcher, healthcare executive, author and lecturer. Specializing in nephrology, she joined the department of medicine, division of renal diseases, at the University of Colorado School of Medicine in 1973, advancing to a full professorship in 1987; she is presently Professor Emerita. She was the principal investigator on the National Institutes of Health Human Polycystic Kidney Disease research grant, which ran from 1985 to 1999, and defined the clinical manifestations and genetics of the disease in adults and children.

Harriet Pearson Dustan (1920–1999) was an American physician who is known for her pioneering contributions to effective detection and treatment of hypertension. She was the first woman to serve on the Board of Governors of the American Board of Internal Medicine.

Bertha Lund Glaeser was an American physician. She served as Professor of Pediatrics at the Woman's Medical College of Cincinnati.