
Spindletop is an oil field located in the southern portion of Beaumont, Texas, in the United States. The Spindletop dome was derived from the Louann Salt evaporite layer of the Jurassic geologic period. On January 10, 1901, a well at Spindletop struck oil. The Spindletop gusher blew for 9 days at a rate estimated at 100,000 barrels (16,000 m3) of oil per day. Gulf Oil and Texaco, now part of Chevron Corporation, were formed to develop production at Spindletop. The Spindletop discovery led the United States into the oil age. Prior to Spindletop, oil was primarily used for lighting and as a lubricant. Because of the quantity of oil discovered, burning petroleum as a fuel for mass consumption suddenly became economically feasible.

The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation, and marketing of petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline (petrol). Petroleum is also the raw material for many chemical products, including pharmaceuticals, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, synthetic fragrances, and plastics. The industry is usually divided into three major components: upstream, midstream, and downstream. Upstream regards exploration and extraction of crude oil, midstream encompasses transportation and storage of crude, and downstream concerns refining crude oil into various end products.

The Iraq Petroleum Company (IPC), formerly known as the Turkish Petroleum Company (TPC), is an oil company that had a virtual monopoly on all oil exploration and production in Iraq between 1925 and 1961. It is jointly owned by some of the world's largest oil companies and headquartered in London, England.

The Trans-Arabian Pipeline (Tapline), was an oil pipeline from Qaisumah in Saudi Arabia to Sidon in Lebanon, active 1950–1976. In its heyday, it was an important factor in the global trade of petroleum, as well as in American–Middle Eastern political relations, while locally helping with the economic development of Lebanon. The pipeline was built and operated by the Trans-Arabian Pipeline Company, now a fully owned subsidiary of Aramco. It largely ceased functioning in 1983 and completely stopped operating in 1990.

The East Texas Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in east Texas. Covering 140,000 acres (57,000 ha) and parts of five counties, and having 30,340 historic and active oil wells, it is the second-largest oil field in the United States outside Alaska, and first in total volume of oil recovered since its discovery in 1930. Over 5.42 billion barrels (862,000,000 m3) of oil have been produced from it to-date. It is a component of the Mid-continent oil field, the huge region of petroleum deposits extending from Kansas to New Mexico to the Gulf of Mexico.

The Canadian petroleum industry arose in parallel with that of the United States. Because of Canada's unique geography, geology, resources and patterns of settlement, however, it developed in different ways. The evolution of the petroleum sector has been a key factor in the history of Canada, and helps illustrate how the country became quite distinct from her neighbour to the south.

Canada's early petroleum discoveries took place near population centres or along lines of penetration into the frontier.
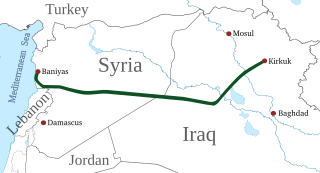
The Kirkuk–Baniyas pipeline is a currently defunct crude oil pipeline from the Kirkuk oil field in Iraq to the Syrian port of Baniyas. The pipeline went into operation in April 1952 and was formally opened in November.

Heletz is a moshav in southern Israel. Located between Ashkelon, Kiryat Gat and Sderot, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hof Ashkelon Regional Council. In 2022 it had a population of 504.

Petroleum has been a major industry in the United States since the 1859 Pennsylvania oil rush around Titusville, Pennsylvania. Commonly characterized as "Big Oil", the industry includes exploration, production, refining, transportation, and marketing of oil and natural gas products. The leading crude oil-producing areas in the United States in 2023 were Texas, followed by the offshore federal zone of the Gulf of Mexico, North Dakota and New Mexico.

Leduc No. 1 was a major crude oil discovery made near Leduc, Alberta, Canada, on February 13, 1947. It provided the geological key to Alberta's most prolific conventional oil reserves and resulted in a boom in petroleum exploration and development across Western Canada. The discovery transformed the Alberta economy; oil and gas supplanted farming as the primary industry and resulted in the province becoming one of the richest in the country. Nationally, the discovery allowed Canada to become self-sufficient within a decade and ultimately a major exporter of oil.

Offshore oil and gas in the Gulf of Mexico is a major source of oil and natural gas in the United States. The western and central Gulf of Mexico, which includes offshore Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama, is one of the major petroleum-producing areas of the United States. Oil production from US federal waters in the Gulf of Mexico reached an all-time annual high of 1.65 million barrels per day in 2017. Oil production is expected to continue the upward trend in 2018 and 2019, based on ten new oil fields which are planned to start production in those years. According to the Energy Information Administration, "Gulf of Mexico federal offshore oil production accounts for 15% of total U.S. crude oil production and federal offshore natural gas production in the Gulf accounts for 5% of total U.S. dry production."
The Az Zubair Field, also known as Az-Zubayr, is an oil field located in southern Iraq, west of Basrah. It is one of the largest fields in the world and was discovered by the Basrah Petroleum Company, an associate of the Iraq Petroleum Company, in 1949. Zubair was the first field developed by the company on a concession granted in 1938. Commercial production started in December 1951. Oil was delivered via some 70 miles of pipeline to a new loading facility at Al-Faw (Fao). The Zubair field was the third oil field in Iraq to enter production and the first in the south of the country. The even larger Rumaila oil field was discovered in 1953 some 20 miles west of Zubair.
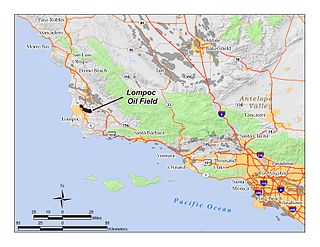
The Lompoc Oil Field is a large oil field in the Purisima Hills north of Lompoc, California, in Santa Barbara County. Discovered in 1903, two years after the discovery of the Orcutt Oil Field in the Solomon Hills, it is one of the oldest oil fields in northern Santa Barbara County, and one of the closest to exhaustion, reporting only 1.7 million barrels (270,000 m3) of recoverable oil remaining out of its original 50 million barrels (7,900,000 m3) as of the end of 2008. Its sole operator is Sentinel Peak Resources, who acquired it from Freeport-McMoRan. In 2009, the proposed decommissioning and habitat restoration of the 3,700-acre (15 km2) field was part of a controversial and so-far unsuccessful deal between Plains, several environmental groups, Santa Barbara County, and the State of California, to allow Plains to carry out new offshore oil drilling on the Tranquillon Ridge, in the Pacific Ocean about twenty miles (32 km) southwest of the Lompoc field.

The Kirkuk-Mediterranean pipeline was a mixed 10/12-inch twin crude oil pipeline from the oil fields in Kirkuk, located in the former Ottoman vilayet of Mosul in northern Iraq, through Transjordan to Haifa in mandatory Palestine ; and through Syria and a short stretch of what was to become the state of Lebanon to Tripoli. The oil arriving on the coast was shipped to European refineries until in 1939 the refinery in Haifa was completed, soon capable of processing the entire supply. For a few years before 1948 crude oil was transported from Tripoli to Haifa by tankers.
Isramco Negev 2 LP (TASE: ISRA.L) is an American Israeli publicly traded master limited partnership that holds interests in oil and gas properties in Israel. The partnership shares are traded on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange and have been a constituent of the TA-35 Index since January 2010. The partnership was founded by Isramco Inc. and other parties in 1989.

The Bahrain Petroleum Company (BAPCO) is an integrated petroleum company that is the national oil company of Bahrain.

Iraq was the world's 5th largest oil producer in 2009, and has the world's fifth largest proven petroleum reserves. Just a fraction of Iraq's known fields are in development, and Iraq may be one of the few places left where vast reserves, proven and unknown, have barely been exploited. Iraq's energy sector is heavily based upon oil, with approximately 94 percent of its energy needs met with petroleum. In addition, crude oil export revenues accounted for over two-thirds of GDP in 2009. Iraq's oil sector has suffered over the past several decades from sanctions and wars, and its oil infrastructure is in need of modernization and investment. As of June 30, 2010, the United States had allocated US$2.05 billion to the Iraqi oil and gas sector to begin this modernization, but ended its direct involvement as of the first quarter of 2008. According to reports by various U.S. government agencies, multilateral institutions and other international organizations, long-term Iraq reconstruction costs could reach $100 billion (US) or higher.
Naft Khana is an Iraqi town in Diyala Governorate, central Iraq, near the Iraqi-Iranian border. Its population were Kurdish nationality during the Iran-Iraq war. Its residents were displaced according to the Arabization policy. Nearby are oil fields containing oil wells found by British companies after the British occupation in 1924. It is considered one of the richest areas in the Diyala Governorate.















