
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol ′, is a unit of angular measurement equal to 1/60 of one degree. Since one degree is 1/360 of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is 1/21600 of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near 21600 nmi. A minute of arc is π/10800 of a radian.

A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are ground, polished, or molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.

Right ascension is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the point in question above the Earth. When paired with declination, these astronomical coordinates specify the location of a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system.

A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface.
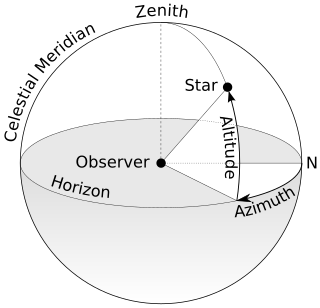
The horizontal coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane to define two angles: altitude and azimuth. Therefore, the horizontal coordinate system is sometimes called the az/el system, the alt/az system, or the alt-azimuth system, among others. In an altazimuth mount of a telescope, the instrument's two axes follow altitude and azimuth.

The zenith is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction opposite to the gravity direction at that location (nadir). The zenith is the "highest" point on the celestial sphere.

Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. These points are usually on the surface of the Earth, and they are often used to establish maps and boundaries for ownership, locations, such as the designed positions of structural components for construction or the surface location of subsurface features, or other purposes required by government or civil law, such as property sales.

An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms object and body are often used interchangeably. However, an astronomical body or celestial body is a single, tightly bound, contiguous entity, while an astronomical or celestial object is a complex, less cohesively bound structure, which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures.

A heliograph is a solar telegraph system that signals by flashes of sunlight reflected by a mirror. The flashes are produced by momentarily pivoting the mirror, or by interrupting the beam with a shutter. The heliograph was a simple but effective instrument for instantaneous optical communication over long distances during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its main uses were military, survey and forest protection work. Heliographs were standard issue in the British and Australian armies until the 1960s, and were used by the Pakistani army as late as 1975.
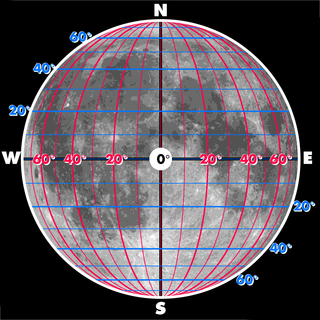
The selenographic coordinate system is used to refer to locations on the surface of Earth's moon. Any position on the lunar surface can be referenced by specifying two numerical values, which are comparable to the latitude and longitude of Earth. The longitude gives the position east or west of the Moon's prime meridian, which is the line passing from the lunar north pole through the point on the lunar surface directly facing Earth to the lunar south pole. This can be thought of as the midpoint of the visible Moon as seen from the Earth. The latitude gives the position north or south of the lunar equator. Both of these coordinates are given in degrees.

The Apollo primary guidance, navigation, and control system was a self-contained inertial guidance system that allowed Apollo spacecraft to carry out their missions when communications with Earth were interrupted, either as expected, when the spacecraft were behind the Moon, or in case of a communications failure. The Apollo command module (CM) and lunar module (LM), were each equipped with a version of PGNCS. PGNCS, and specifically its computer, were also the command center for all system inputs from the LM, including the alignment optical telescope, the radar system, the manual translation and rotation device inputs by the astronauts as well as other inputs from the LM systems.

A heliostat is a device that includes a mirror, usually a plane mirror, which turns so as to keep reflecting sunlight toward a predetermined target, compensating for the Sun's apparent motions in the sky.

Solar rotation varies with latitude. The Sun is not a solid body, but is composed of a gaseous plasma. Different latitudes rotate at different periods. The source of this differential rotation is an area of current research in solar astronomy. The rate of surface rotation is observed to be the fastest at the equator and to decrease as latitude increases. The solar rotation period is 25.67 days at the equator and 33.40 days at 75 degrees of latitude.

Heliography from helios, meaning "sun", and graphein (γράφειν), "writing") is the photographic process invented, and named thus, by Joseph Nicéphore Niépce around 1822, which he used to make the earliest known surviving photograph from nature, View from the Window at Le Gras, and the first realisation of photoresist as means to reproduce artworks through inventions of photolithography and photogravure.

A solar telescope or a solar observatory is a special-purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph.

The Stonyhurst Observatory is a functioning observatory and weather station at Stonyhurst College in Lancashire, England. Built in 1866, it replaced a nearby earlier building, built in 1838, which is now used as the Typographia Collegii.

The Gauribidanur Radio Observatory is a radio telescope observatory located at Gauribidanur, near Bengaluru. It is operated jointly by Raman Research Institute and the Indian Institute of Astrophysics. The observatory has been in operation since 1976.

The Nançay Radio Observatory, opened in 1956, is part of Paris Observatory, and also associated with the University of Orléans. It is located in the department of Cher in the Sologne region of France. The station consists of several instruments. Most iconic of these is the large decimetric radio telescope, which is one of the largest radio telescopes in the world. Long established are also the radio heliograph, a T-shaped array, and the decametric array operating at wavelengths between 3 m and 30 m.
In solar observation and imaging, coordinate systems are used to identify and communicate locations on and around the Sun. Since the Sun is gaseous in nature, there are no permanent demarcated points that can be referenced.

















