
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation.

Observation in the natural sciences is an act or instance of noticing or perceiving and the acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the perception and recording of data via the use of scientific instruments. The term may also refer to any data collected during the scientific activity. Observations can be qualitative, that is, the absence or presence of a property is noted and the observed phenomenon described, or quantitative if a numerical value is attached to the observed phenomenon by counting or measuring.

Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat (Atmospheric). When blocked by clouds or reflected off other objects, sunlight is diffused. Sources estimate a global average of between 164 watts to 340 watts per square meter over a 24-hour day; this figure is estimated by NASA to be about a quarter of Earth's average total solar irradiance.
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.

A rain gauge is an instrument used by meteorologists and hydrologists to gather and measure the amount of liquid precipitation over a predefined area, over a period of time. It is used to determine the depth of precipitation that occurs over a unit area and measure rainfall amount.

An archaeological site is a place in which evidence of past activity is preserved, and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use.

A barograph is a barometer that records the barometric pressure over time in graphical form. This instrument is also used to make a continuous recording of atmospheric pressure. The pressure-sensitive element, a partially evacuated metal cylinder, is linked to a pen arm in such a way that the vertical displacement of the pen is proportional to the changes in the atmospheric pressure.
This glossary of climate change is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to climate change, global warming, and related topics.

A data logger is an electronic device that records data over time or about location either with a built-in instrument or sensor or via external instruments and sensors. Increasingly, but not entirely, they are based on a digital processor, and called digital data loggers (DDL). They generally are small, battery-powered, portable, and equipped with a microprocessor, internal memory for data storage, and sensors. Some data loggers interface with a personal computer and use software to activate the data logger and view and analyze the collected data, while others have a local interface device and can be used as a stand-alone device.

Armagh Observatory is an astronomical research institute in Armagh, Northern Ireland. Around 25 astronomers are based at the observatory, studying stellar astrophysics, the Sun, Solar System astronomy and Earth's climate.

The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. It is primarily used in daily and hourly forecasts aimed at the general public. The UV index is designed as an open-ended linear scale, directly proportional to the intensity of UV radiation, and adjusting for wavelength based on what causes human skin to sunburn. The purpose of the UV index is to help people effectively protect themselves from UV radiation, which has health benefits in moderation but in excess causes sunburn, skin aging, DNA damage, skin cancer, immunosuppression, and eye damage, such as cataracts.

The Campbell–Stokes recorder is a type of sunshine recorder. It was invented by John Francis Campbell in 1853 and modified in 1879 by Sir George Gabriel Stokes. The original design by Campbell consisted of large ball lens set into a wooden bowl with the sun burning a trace on the bowl. Stokes's refinement was to make the housing out of metal and to have a card holder set behind the sphere.
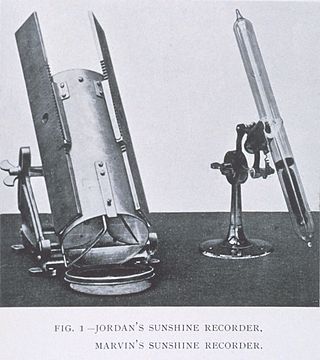
A Jordan sunshine recorder is a type of sunshine recorder invented in the 19th century by T. B. Jordan with later modifications by his son, J. B. Jordan. The device consists of a cylinder with two small apertures through which sunlight can pass. Two sheets of photosensitive paper are placed inside the cylinder and the recorder is positioned in such a way that the sunlight falling through the apertures leaves a path on the paper as the sun moves through the sky during the day. The Jordan recorder was criticized as producing less consistent results than the Campbell–Stokes recorder due to difficulty in precisely interpreting the sun paths recorded.

Meteorological instruments, including meteorological sensors, are the equipment used to find the state of the atmosphere at a given time. Each science has its own unique sets of laboratory equipment. Meteorology, however, is a science which does not use much laboratory equipment but relies more on on-site observation and remote sensing equipment. In science, an observation, or observable, is an abstract idea that can be measured and for which data can be taken. Rain was one of the first quantities to be measured historically. Two other accurately measured weather-related variables are wind and humidity. Many attempts had been made prior to the 15th century to construct adequate equipment to measure atmospheric variables.
Open Wonderland is an open-source toolkit written in Java for creating collaborative 3D virtual worlds. Within those worlds, users can communicate with high-fidelity, immersive audio, share live desktop applications and documents and conduct real business. Open Wonderland is completely extensible; developers and graphic artists can extend its functionality to create entirely new worlds including adding new features to existing worlds.

Wildlife observation is the practice of noting the occurrence or abundance of animal species at a specific location and time, either for research purposes or recreation. Common examples of this type of activity are bird watching and whale watching.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the field of Meteorology.
The University of Reading Atmospheric Observatory, is an atmospheric observatory and weather station located on the Whiteknights Campus of the University of Reading. It forms part of the university's Department of Meteorology. The site at its current location has been a centre for atmospheric research since 1970, but the weather record was originally started by the University College of Reading in 1901 at the London Road campus as a rainfall station with a near complete daily record from January 1908. Automatic meteorological observations are continually recorded at the site and available online
Sunshine duration or sunshine hours is a climatological indicator, measuring duration of sunshine in given period for a given location on Earth, typically expressed as an averaged value over several years. It is a general indicator of cloudiness of a location, and thus differs from insolation, which measures the total energy delivered by sunlight over a given period.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.
















