
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets, though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets fall generally in cold weather while hail growth is greatly inhibited during cold surface temperatures.
Diamond dust is a ground-level cloud composed of tiny ice crystals. This meteorological phenomenon is also referred to simply as ice crystals and is reported in the METAR code as IC. Diamond dust generally forms under otherwise clear or nearly clear skies, so it is sometimes referred to as clear-sky precipitation. Diamond dust is most commonly observed in Antarctica and the Arctic, but can occur anywhere with a temperature well below freezing. In the polar regions of Earth, diamond dust may persist for several days without interruption.
A winter storm is an event in which varieties of precipitation are formed that only occur at low temperatures, such as snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are low enough to allow ice to form. In temperate continental climates, these storms are not necessarily restricted to the winter season, but may occur in the late autumn and early spring as well. Very rarely, they may form in summer, though it would have to be an abnormally cold summer, such as the summer of 1816 in the Northeastern United States.

A hygrometer is an instrument used to measure the amount of humidity and water vapor in the atmosphere, in soil, or in confined spaces. Humidity measurement instruments usually rely on measurements of some other quantity such as temperature, pressure, mass, a mechanical or electrical change in a substance as moisture is absorbed. By calibration and calculation, these measured quantities can lead to a measurement of humidity. Modern electronic devices use temperature of condensation, or changes in electrical capacitance or resistance to measure humidity differences. The first crude hygrometer was invented by the Italian Renaissance polymath Leonardo da Vinci in 1480 and a more modern version was created by Swiss polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert in 1755. Later in the year 1783, Swiss physicist and Geologist, Horace Benedict De Saussure invented the first hygrometer using human hair to measure humidity.

In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor, so that the water condenses and "precipitates". Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but suspensions, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called "showers."
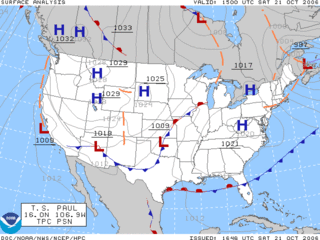
A weather map displays various meteorological features across a particular area at a particular point in time and has various symbols which all have specific meanings. Such maps have been in use since the mid-19th century and are used for research and weather forecasting purposes. Maps using isotherms show temperature gradients, which can help locate weather fronts. Isotach maps, analyzing lines of equal wind speed, on a constant pressure surface of 300 or 250 hPa show where the jet stream is located. Use of constant pressure charts at the 700 and 500 hPa level can indicate tropical cyclone motion. Two-dimensional streamlines based on wind speeds at various levels show areas of convergence and divergence in the wind field, which are helpful in determining the location of features within the wind pattern. A popular type of surface weather map is the surface weather analysis, which plots isobars to depict areas of high pressure and low pressure. Cloud codes are translated into symbols and plotted on these maps along with other meteorological data that are included in synoptic reports sent by professionally trained observers.
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by pilots in fulfillment of a part of a pre-flight weather briefing, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting.

Rime ice forms when supercooled water liquid droplets freeze onto surfaces. Meteorologists distinguish between three basic types of ice forming on vertical and horizontal surfaces by deposition of supercooled water droplets. There are also intermediate formations.
This is a list of meteorology topics. The terms relate to meteorology, the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere that focuses on weather processes and forecasting.
The Wegener–Bergeron–Findeisen process, is a process of ice crystal growth that occurs in mixed phase clouds in regions where the ambient vapor pressure falls between the saturation vapor pressure over water and the lower saturation vapor pressure over ice. This is a subsaturated environment for liquid water but a supersaturated environment for ice resulting in rapid evaporation of liquid water and rapid ice crystal growth through vapor deposition. If the number density of ice is small compared to liquid water, the ice crystals can grow large enough to fall out of the cloud, melting into rain drops if lower level temperatures are warm enough.
A pilot report or PIREP is a report of actual weather conditions encountered by an aircraft in flight. This information is usually relayed by radio to the nearest ground station, but other options also exist in some regions. The message would then be encoded and relayed to other weather offices and air traffic service units.
The December 2005 North American ice storm was a damaging winter storm that produced extensive ice damage in a large portion of the Southern United States from December 14–16, 2005, while extensive snowfall was reported across portions of the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The ice storm led to enormous and widespread power outages, and at least 7 deaths.
Frost or freezing occurs when the temperature of air falls below the freezing point of water. This is usually measured at the height of 1.2 m above the ground surface.

Automated airport weather stations are automated sensor suites which are designed to serve aviation and meteorological observing needs for safe and efficient aviation operations, weather forecasting and climatology. Automated airport weather stations have become part of the backbone of weather observing in the United States and Canada and are becoming increasingly more prevalent worldwide due to their efficiency and cost-savings.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to meteorology:

Surface weather observations are the fundamental data used for safety as well as climatological reasons to forecast weather and issue warnings worldwide. They can be taken manually, by a weather observer, by computer through the use of automated weather stations, or in a hybrid scheme using weather observers to augment the otherwise automated weather station. The ICAO defines the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA), which is the model of the standard variation of pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity with altitude in the Earth's atmosphere, and is used to reduce a station pressure to sea level pressure. Airport observations can be transmitted worldwide through the use of the METAR observing code. Personal weather stations taking automated observations can transmit their data to the United States mesonet through the Citizen Weather Observer Program (CWOP), the UK Met Office through their Weather Observations Website (WOW), or internationally through the Weather Underground Internet site. A thirty-year average of a location's weather observations is traditionally used to determine the station's climate. In the US a network of Cooperative Observers make a daily record of summary weather and sometimes water level information.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and the atmospheric sciences, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.













