Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When the direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat. When it is blocked by clouds or reflects off other objects, it is experienced as diffused light. The World Meteorological Organization uses the term "sunshine duration" to mean the cumulative time during which an area receives direct irradiance from the Sun of at least 120 watts per square meter. Other sources indicate an "Average over the entire earth" of "164 Watts per square meter over a 24 hour day".

Ultraviolet (UV) designates a band of the electromagnetic spectrum with wavelength from 10 nm to 400 nm, shorter than that of visible light but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and contributes about 10% of the total light output of the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules.

Infrared astronomy is the branch of astronomy and astrophysics that studies astronomical objects visible in infrared (IR) radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 micrometers. Infrared falls in between visible radiation, which ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers, and submillimeter waves.

In ocular physiology, adaptation is the ability of the eye to adjust to various levels of light. Natural night vision, or scotopic vision, is the ability to see under low-light conditions. In humans, rod cells are exclusively responsible for night vision as cone cells are only able to function at higher illumination levels. Night vision is of much poorer quality than day vision because it is limited by a reduced resolution and therefore provides the ability to only discriminate between shades of black and white. In order for humans to transition from day to night vision they must undergo a dark adaptation period in which each eye adjusts from a high luminescence setting to a low luminescence setting. This adaptation period is different for both rod and cone cells and results from the regeneration of photopigments to restore retinal sensitivity.

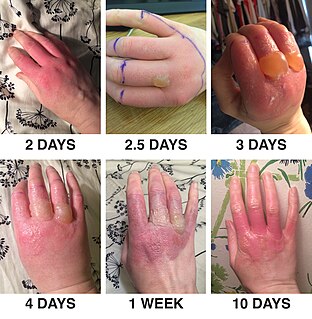
Photodermatitis, sometimes referred to as sun poisoning or photoallergy, is a form of allergic contact dermatitis in which the allergen must be activated by light to sensitize the allergic response, and to cause a rash or other systemic effects on subsequent exposure. The second and subsequent exposures produce photoallergic skin conditions which are often eczematous. It is distinct from sunburn.
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision.
The ultraviolet index or UV Index is an international standard measurement of the strength of sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. The scale was developed by Canadian scientists in 1992, then adopted and standardized by the UN's World Health Organization and World Meteorological Organization in 1994. It is primarily used in daily forecasts aimed at the general public, and is increasingly available as an hourly forecast as well.
Light sensitivity or photosensitivity refers to a notable or increased reactivity to light. Apart from vision, human beings have many physiological and psychological responses to light. In rare individuals an atypical response may result in serious discomfort, disease, or injury. Some drugs have a photosensitizing effect. Properties of natural or artificial light that may abnormally affect people include:

Polymorphous light eruption (PLE), sometimes also called polymorphic light eruption (PMLE), is a non-life-threatening and potentially distressing skin condition that is triggered by sunlight and artificial UV exposure in a genetically susceptible person, particularly in temperate climates during the spring and early summer. Due to its many clinical appearances, it is named polymorphic or polymorphous and the terms are used interchangeably. The resulting itch can cause significant suffering.

The photic sneeze reflex is a reflex condition that causes sneezing in response to numerous stimuli, such as looking at bright lights or periocular injection. The condition affects 18–35% of the population in the United States, but its exact mechanism of action is not well understood.

Sky brightness refers to the visual perception of the sky and how it scatters and diffuses light. The fact that the sky is not completely dark at night is easily visible. If light sources were removed from the night sky, only direct starlight would be visible.
Phototoxins are toxins that can cause allergic reactions in particularly susceptible individuals and which can cause dangerous photosensitivity in a much broader range of subjects.

Sun scald is the freezing of bark following high temperatures in the winter season, resulting in permanent visible damage to bark. Fruits may also be damaged. In the northern hemisphere, it is also called southwest injury.
Chronic actinic dermatitis is a condition where a subject's skin becomes inflamed due to a reaction to sunlight or artificial light. Patients often suffer from other related conditions of the skin that cause dermatitis in response to a variety of stimuli.

Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, commonly from the sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch, pain, general fatigue, and mild dizziness. An excess of UV radiation can be life-threatening in extreme cases. Excessive UV radiation is the leading cause of primarily non-malignant skin tumors.

Notobubon galbanum, re-classified from Peucedanum galbanum in 2008, commonly called the blister bush or hog's fennel, is a South African plant that is best known for its ability to cause painful blistering after contact. In Afrikaans this plant species is known as bergseldery.

Fluorescent lamps have been suggested to affect human health in various ways.
Melanizing agents are drugs that increase sensitivity to solar radiation and promote re-pigmentation of de-pigmented areas of skin. Furocoumarins stimulate melanocytes and induce their proliferation on activation by light. Melanizing agents sensitize the skin to sunlight. As a result, erythema, inflammation and pigmentation occurs.