
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA, RNA is found in nature as a single strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.

Ribosomes are macromolecular machines, found within all living cells, that perform biological protein synthesis. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.

In molecular biology, RNA polymerase, is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.

In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression.
The Shine–Dalgarno (SD) sequence is a ribosomal binding site in bacterial and archaeal messenger RNA, generally located around 8 bases upstream of the start codon AUG. The RNA sequence helps recruit the ribosome to the messenger RNA (mRNA) to initiate protein synthesis by aligning the ribosome with the start codon. Once recruited, tRNA may add amino acids in sequence as dictated by the codons, moving downstream from the translational start site.
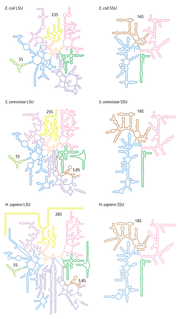
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins by mass.
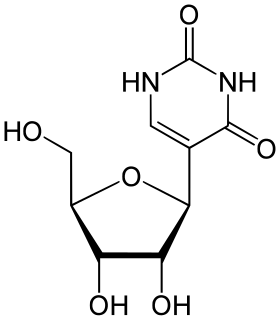
Pseudouridine is an isomer of the nucleoside uridine in which the uracil is attached via a carbon-carbon instead of a nitrogen-carbon glycosidic bond.
Bacterial translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in bacteria.
In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes.
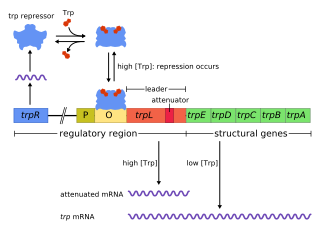
The trp operon is an operon—a group of genes that is used, or transcribed, together—that codes for the components for production of tryptophan. The trp operon is present in many bacteria, but was first characterized in Escherichia coli. The operon is regulated so that, when tryptophan is present in the environment, the genes for tryptophan synthesis are not expressed. It was an important experimental system for learning about gene regulation, and is commonly used to teach gene regulation.
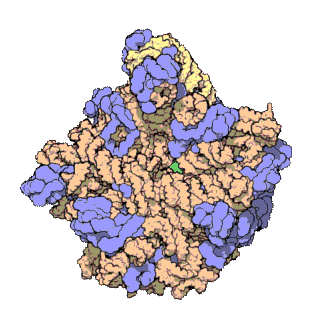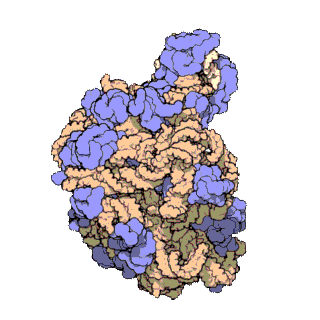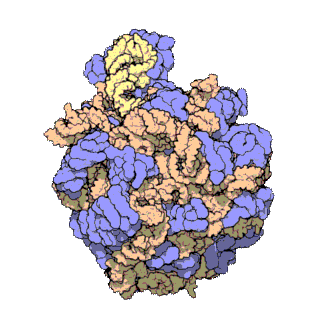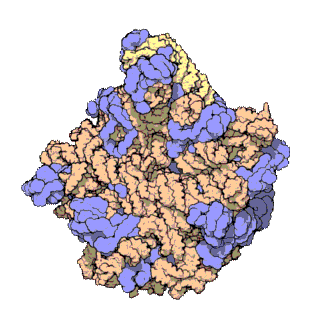
A ribosomal protein is any of the proteins that, in conjunction with rRNA, make up the ribosomal subunits involved in the cellular process of translation. E. coli, other bacteria and Archaea have a 30S small subunit and a 50S large subunit, whereas humans and yeasts have a 40S small subunit and a 60S large subunit. Equivalent subunits are frequently numbered differently between bacteria, Archaea, yeasts and humans.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochrondria as TUFM.

The 5S ribosomal RNA is an approximately 120 nucleotide-long ribosomal RNA molecule with a mass of 40 kDa. It is a structural and functional component of the large subunit of the ribosome in all domains of life, with the exception of mitochondrial ribosomes of fungi and animals. The designation 5S refers to the molecule's sedimentation velocity in an ultracentrifuge, which is measured in Svedberg units (S).

The signal recognition particle RNA, is part of the signal recognition particle (SRP) ribonucleoprotein complex. SRP recognizes the signal peptide and binds to the ribosome, halting protein synthesis. SRP-receptor is a protein that is embedded in a membrane, and which contains a transmembrane pore. When the SRP-ribosome complex binds to SRP-receptor, SRP releases the ribosome and drifts away. The ribosome resumes protein synthesis, but now the protein is moving through the SRP-receptor transmembrane pore.

The prokaryotic small ribosomal subunit, or 30S subunit, is the smaller subunit of the 70S ribosome found in prokaryotes. It is a complex of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 19 proteins. This complex is implicated in the binding of transfer RNA to messenger RNA (mRNA). The small subunit is responsible for the binding and the reading of the mRNA during translation. The small subunit, both the rRNA and its proteins, complexes with the large 50S subunit to form the 70S prokaryotic ribosome in prokaryotic cells. This 70S ribosome is then used to translate mRNA into proteins.

EF-G is a prokaryotic elongation factor involved in protein translation. As a GTPase, EF-G catalyzes the movement (translocation) of transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) through the ribosome.
EF-Ts is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors. It is found in human mitochrondria as TSFM. It is similar to eukaryotic EF-1B.
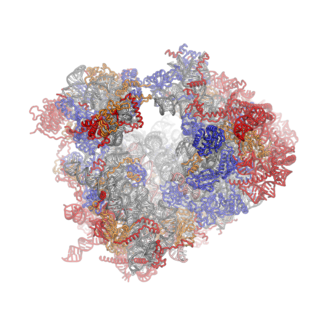
Ribosomes are a large and complex molecular machine that catalyzes the synthesis of proteins, referred to as translation. The ribosome selects aminoacylated transfer RNAs (tRNAs) based on the sequence of a protein-encoding messenger RNA (mRNA) and covalently links the amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes from all organisms share a highly conserved catalytic center. However, the ribosomes of eukaryotes are much larger than prokaryotic ribosomes and subject to more complex regulation and biogenesis pathways. Eukaryotic ribosomes are also known as 80S ribosomes, referring to their sedimentation coefficients in Svedberg units, because they sediment faster than the prokaryotic (70S) ribosomes. Eukaryotic ribosomes have two unequal subunits, designated small subunit (40S) and large subunit (60S) according to their sedimentation coefficients. Both subunits contain dozens of ribosomal proteins arranged on a scaffold composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The small subunit monitors the complementarity between tRNA anticodon and mRNA, while the large subunit catalyzes peptide bond formation.
The P-site is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. The other two sites are the A-site (aminoacyl), which is the first binding site in the ribosome, and the E-site (exit), the third. During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain. When a stop codon is reached, the peptidyl-tRNA bond of the tRNA located in the P-site is cleaved releasing the newly synthesized protein. During the translocation step of the elongation phase, the mRNA is advanced by one codon, coupled to movement of the tRNAs from the ribosomal A to P and P to E sites, catalyzed by elongation factor EF-G.

In molecular biology, the CRM domain is an approximately 100-amino acid RNA-binding domain. The name CRM has been suggested to reflect the functions established for four characterised members of the family: Zea mays (Maize) CRS1, CAF1 and CAF2 proteins and the Escherichia coli protein YhbY. Proteins containing the CRM domain are found in eubacteria, archaea, and plants. The CRM domain is represented as a stand-alone protein in archaea and bacteria, and in single- and multi-domain proteins in plants. It has been suggested that prokaryotic CRM proteins existed as ribosome-associated proteins prior to the divergence of archaea and bacteria, and that they were co-opted in the plant lineage as RNA binding modules by incorporation into diverse protein contexts. Plant CRM domains are predicted to reside not only in the chloroplast, but also in the mitochondrion and the nucleo/cytoplasmic compartment. The diversity of the CRM domain family in plants suggests a diverse set of RNA targets.















