Related Research Articles

AIX is a series of proprietary Unix operating systems developed and sold by IBM since 1986. The name stands for "Advanced Interactive eXecutive". Current versions are designed to work with Power ISA based server and workstation computers such as IBM's Power line.

OS/2 is a proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was initially created and developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, intended as a replacement for DOS. The first version was released in 1987; a feud between the two companies beginning in 1990 resulted in Microsoft leaving development exclusively to IBM, who continued development on their own. OS/2 Warp 4 in 1996 was the last major upgrade, after which IBM slowly halted the product as it failed to compete against Microsoft's Windows; updated versions of OS/2 were released by IBM until 2001.

Xenix is a discontinued Unix operating system for various microcomputer platforms, licensed by Microsoft from AT&T Corporation. The first version was released in 1980, and Xenix would eventually become the most common Unix variant, measured according to the number of machines on which it was installed, in the mid-to-late 1980s. The Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) later acquired exclusive rights to the software, and eventually replaced it with SCO UNIX, later known as OpenServer, with the final Xenix version released in 1991.

NetWare is a discontinued computer network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, using the IPX network protocol. The final update release was version 6.5SP8 of May 2009 and has been replaced by Open Enterprise Server.
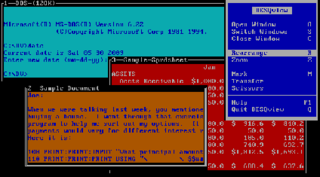
DESQview (DV) is a text mode multitasking operating environment developed by Quarterdeck Office Systems which enjoyed modest popularity in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Running on top of DOS, it allows users to run multiple programs concurrently in multiple windows.
In computing, the DOS Protected Mode Interface (DPMI) is a specification introduced in 1989 which allows a DOS program to run in protected mode, giving access to many features of the new PC processors of the time not available in real mode. It was initially developed by Microsoft for Windows 3.0, although Microsoft later turned control of the specification over to an industry committee with open membership. Almost all modern DOS extenders are based on DPMI and allow DOS programs to address all memory available in the PC and to run in protected mode.
Quarterdeck Expanded Memory Manager (QEMM) is a memory manager produced by Quarterdeck Office Systems in the late 1980s through the late 1990s. It was the most popular third-party memory manager for the MS-DOS and other DOS operating systems.

Multiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
The 3Com 3Server was a headless dedicated network-attached storage machine designed to run 3Com local area network (LAN) server software, 3+Share.
A disk compression software utility increases the amount of information that can be stored on a hard disk drive of given size. Unlike a file compression utility, which compresses only specified files—and which requires the user to designate the files to be compressed—an on-the-fly disk compression utility works automatically through resident software without the user needing to be aware of its existence. On-the-fly disk compression is therefore also known as transparent, real-time or online disk compression.
FlexOS is a discontinued modular real-time multiuser multitasking operating system (RTOS) designed for computer-integrated manufacturing, laboratory, retail and financial markets. Developed by Digital Research's Flexible Automation Business Unit in Monterey, California, in 1985.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of 16-bit x86 DOS-family disk operating systems from 1980 to present. Non-x86 operating systems named "DOS" are not part of the scope of this timeline.

Windows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, launched on May 22, 1990. It introduces a new graphical user interface (GUI) that represents applications as clickable icons, instead of the list of file names in its predecessors. Later updates expand capabilities, such as multimedia support for sound recording and playback, and support for CD-ROMs.

MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS". MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system.

DOS is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of IBM PC DOS and a rebranded version, Microsoft's MS-DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR-DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1994). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.
The ICL DRS was a range of departmental computers from International Computers Limited (ICL). Standing originally for Distributed Resource System, the full name was later dropped in favour of the abbreviation.
VM/386 is a multitasking Multi-user environment or 'control program' that took early advantage of the capabilities of Intel's 386 processor. By utilizing Virtual 8086 mode, users were able to run their existing text-based and graphical DOS software in safely separate environments. The system offered a high degree of control, with the ability to set memory limits, CPU usage and scheduling parameters, device assignments, and interrupt priorities through a virtual machine manager menu. Unique CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files could be configured for each application, and even different DOS versions. In 1991 the vendor announced intentions to support DPMI 1.0 in VM/386.
DOS Protected Mode Services (DPMS) is a set of extended DOS memory management services to allow DPMS-enabled DOS drivers to load and execute in extended memory and protected mode.
Helix Software Company, Inc. was a New York City based software company founded in October 1986. The company developed software tools and utilities for DOS and Windows. In 1993, Helix licensed some of its memory management technology to Microsoft for use in MS-DOS 6.0. Microsoft subsequently released Helix's memory management technology as part of the MEMMAKER and EMM386 DOS commands.
HeadRoom is a DOS context switching and multitasking memory manager produced by Helix Software Company in the late 1980s and early 1990s. HeadRoom managed multiple terminate-and-stay-resident programs (TSRs) and was the first TSR manager to allow sharing of address space and interrupts among TSRs in DOS. HeadRoom v1.0 was released in September 1988.
References
- ↑ "Go Where No Network Has Gone Before". PC Magazine: 65. 29 Sep 1990. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ↑ "NETROOM Adds Memory Manager, Windows Compatibility". InfoWorld: 33. 21 Jan 1991. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ↑ Derfler, Frank (29 Jan 1991). "LAN Memory Management". PC Magazine: 226. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ↑ "MicroBits". Computerworld: 41. 6 May 1991. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- ↑ "Helix brings out memory aid". Computerworld: 104. 8 Jul 1991. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- ↑ "Only NETROOM". PC Magazine: 47. 14 Jan 1992. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ↑ Simon, Barry (11 Feb 1992). "Memory Management". PC Magazine: 248. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ↑ Ayre, Rick (14 September 1993). Best Utilities. p. 134. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- ↑ Seltzer, Larry (14 May 1996). The Ultimate Utility Guide. p. 172. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- ↑ Raskin, Robin (30 March 1993). Managing Memory. p. 30. Retrieved 1 May 2015.