
Bone healing, or fracture healing, is a proliferative physiological process in which the body facilitates the repair of a bone fracture.

A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is benign and is initially in liquid form spread among the tissues including in sacs between tissues where it may coagulate and solidify before blood is reabsorbed into blood vessels. An ecchymosis is a hematoma of the skin larger than 10 mm.
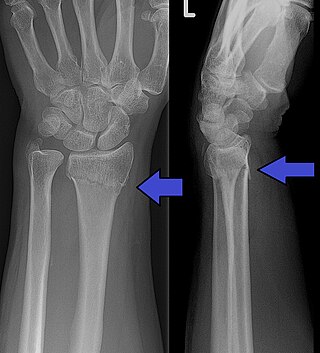
A Colles' fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backwards. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising. Complications may include damage to the median nerve.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a comminuted fracture. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.

A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.
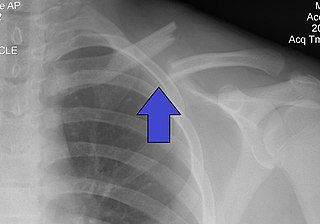
A clavicle fracture, also known as a broken collarbone, is a bone fracture of the clavicle. Symptoms typically include pain at the site of the break and a decreased ability to move the affected arm. Complications can include a collection of air in the pleural space surrounding the lung (pneumothorax), injury to the nerves or blood vessels in the area, and an unpleasant appearance.
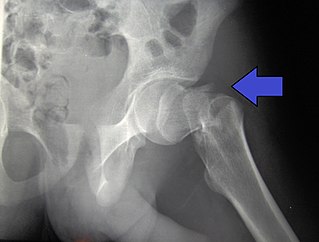
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur, at the femoral neck or (rarely) the femoral head. Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.

A periorbital hematoma, commonly called a black eye or a shiner, is bruising around the eye commonly due to an injury to the face rather than to the eye. The name refers to the dark-colored bruising which is the result of accumulated blood and fluid in the loose areolar tissue following a blow to the head. This blood tracks freely under the scalp producing a generalised swelling over the dome of the skull but cannot pass into either occipital or the temple regions because of the bony attachments of the occipitofrontalis muscle. But this fluid can, however, track forward into the eyelid because the occipitofrontalis muscle has no bony attachment anteriorly. This leads to formation of hematoma a few hours after the head injury or cranial operation. If injury is more extensive, potentially even a skull fracture, an apparent black eye can sometimes worsen and may require professional medical treatment before it will resolve. This is more likely if the area around both eyes has been injured or if there is a history of prior head injury or fracture around the eye. Though disfiguring, the vast majority of black eyes are not serious, require little or no treatment, and will resolve spontaneously within a week or two.

External fixation is a surgical treatment wherein Kirschner pins and wires are inserted and affixed into bone and then exit the body to be attached to an external apparatus composed of rings and threaded rods — the Ilizarov apparatus, the Taylor Spatial Frame, and the Octopod External Fixator — which immobilises the damaged limb to facilitate healing. As an alternative to internal fixation, wherein bone-stabilising mechanical components are surgically emplaced in the body of the patient, external fixation is used to stabilize bone tissues and soft tissues at a distance from the site of the injury.

Reduction is a surgical procedure to repair a fracture or dislocation to the correct alignment.

An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body or at the tendon by a muscular contraction that is stronger than the forces holding the bone together. Generally muscular avulsion is prevented by the neurological limitations placed on muscle contractions. Highly trained athletes can overcome this neurological inhibition of strength and produce a much greater force output capable of breaking or avulsing a bone.

A subungual hematoma is a collection of blood (hematoma) underneath a toenail or fingernail. It can be extremely painful for an injury of its size, although otherwise it is not a serious medical condition.
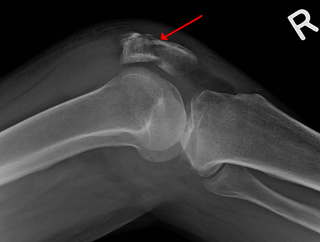
A patella fracture is a break of the kneecap. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and bruising to the front of the knee. A person may also be unable to walk. Complications may include injury to the tibia, femur, or knee ligaments.

A calcaneal fracture is a break of the calcaneus. Symptoms may include pain, bruising, trouble walking, and deformity of the heel. It may be associated with breaks of the hip or back.

Nasal septal hematoma is a condition affecting the nasal septum. It can be associated with trauma.

Bennett fracture is a type of partial broken finger involving the base of the thumb, and extends into the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint.

A humerus fracture is a break of the humerus bone in the upper arm. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and bruising. There may be a decreased ability to move the arm and the person may present holding their elbow. Complications may include injury to an artery or nerve, and compartment syndrome.

A nasal fracture, commonly referred to as a broken nose, is a fracture of one of the bones of the nose. Symptoms may include bleeding, swelling, bruising, and an inability to breathe through the nose. They may be complicated by other facial fractures or a septal hematoma.

Mandibular fracture, also known as fracture of the jaw, is a break through the mandibular bone. In about 60% of cases the break occurs in two places. It may result in a decreased ability to fully open the mouth. Often the teeth will not feel properly aligned or there may be bleeding of the gums. Mandibular fractures occur most commonly among males in their 30s.

A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. In children, many of these fractures are non-displaced and can be treated with casting. Some are angulated or displaced and are best treated with surgery. In children, most of these fractures can be treated effectively with expectation for full recovery. Some of these injuries can be complicated by poor healing or by associated blood vessel or nerve injuries with serious complications.

















