Related Research Articles

Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin calx "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone.

Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4·2H2O. It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk chalk. Gypsum also crystallizes as translucent crystals of selenite. It forms as an evaporite mineral and as a hydration product of anhydrite. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness defines gypsum as hardness value 2 based on scratch hardness comparison.

Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula MgSO4, consisting of magnesium cations Mg2+ (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions SO2−4. It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water but not in ethanol.

Copper(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuSO4. It forms hydrates CuSO4·nH2O, where n can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (n = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate, while its anhydrous form is white. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper, and Roman vitriol. It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The Cu(II)(H2O)4 centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains.

Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Paris, and another occurs naturally as the mineral gypsum. It has many uses in industry. All forms are white solids that are poorly soluble in water. Calcium sulfate causes permanent hardness in water.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is a white powder, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting to the dihydrate BaCl2·2H2O, which are colourless crystals with a bitter salty taste. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.

In colloidal chemistry, flocculation is a process by which colloidal particles come out of suspension to sediment in the form of floc or flake, either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended, under the form of a stable dispersion and are not truly dissolved in solution.
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.
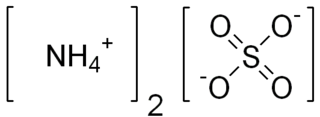
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen and 24% sulfur.
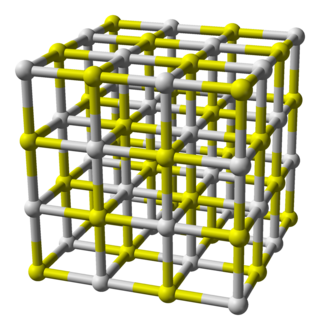
Calcium sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula CaS. This white material crystallizes in cubes like rock salt. CaS has been studied as a component in a process that would recycle gypsum, a product of flue-gas desulfurization. Like many salts containing sulfide ions, CaS typically has an odour of H2S, which results from small amount of this gas formed by hydrolysis of the salt.
Indium(III) sulfate (In2(SO4)3) is a sulfate salt of the metal indium. It is a sesquisulfate, meaning that the sulfate group occurs 11/2 times as much as the metal. It may be formed by the reaction of indium, its oxide, or its carbonate with sulfuric acid. An excess of strong acid is required, otherwise insoluble basic salts are formed. As a solid indium sulfate can be anhydrous, or take the form of a pentahydrate with five water molecules or a nonahydrate with nine molecules of water. Indium sulfate is used in the production of indium or indium containing substances. Indium sulfate also can be found in basic salts, acidic salts or double salts including indium alum.

Ettringite is a hydrous calcium aluminium sulfate mineral with formula: Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O. It is a colorless to yellow mineral crystallizing in the trigonal system. The prismatic crystals are typically colorless, turning white on partial dehydration. It is part of the ettringite-group which includes other sulfates such as thaumasite and bentorite.
Tricalcium aluminate Ca3Al2O6, often formulated as 3CaO·Al2O3 to highlight the proportions of the oxides from which it is made, is the most basic of the calcium aluminates. It does not occur in nature, but is an important mineral phase in Portland cement.

Calcium sulfite, or calcium sulphite, is a chemical compound, the calcium salt of sulfite with the formula CaSO3·x(H2O). Two crystalline forms are known, the hemihydrate and the tetrahydrate, respectively CaSO3·½(H2O) and CaSO3·4(H2O). All forms are white solids. It is most notable as the product of flue-gas desulfurization.

In chemistry, isomorphism has meanings both at the level of crystallography and at a molecular level. In crystallography, crystals are isomorphous if they have identical symmetry and if the atomic positions can be described with a set of parameters whose numerical values differ only slightly.

Concrete degradation may have many different causes. Concrete is mostly damaged by the corrosion of reinforcement bars due to the carbonatation of hardened cement paste or chloride attack under wet conditions. Chemical damage is caused by the formation of expansive products produced by chemical reactions, by aggressive chemical species present in groundwater and seawater, or by microorganisms Other damaging processes can also involve calcium leaching by water infiltration, physical phenomena initiating cracks formation and propagation, fire or radiant heat, aggregate expansion, sea water effects, leaching, and erosion by fast-flowing water.

Bassanite is a calcium sulfate mineral with formula CaSO4·1/2H2O or 2CaSO4·H2O. In other words it has half a water molecule per CaSO4 unit, hence its synonym calcium sulfate hemihydrate.
A sulfite sulfate is a chemical compound that contains both sulfite and sulfate anions [SO3]2− [SO4]2−. These compounds were discovered in the 1980s as calcium and rare earth element salts. Minerals in this class were later discovered. Minerals may have sulfite as an essential component, or have it substituted for another anion as in alloriite. The related ions [O3SOSO2]2− and [(O2SO)2SO2]2− may be produced in a reaction between sulfur dioxide and sulfate and exist in the solid form as tetramethyl ammonium salts. They have a significant partial pressure of sulfur dioxide.
Biphasic calcium sulfate is a granulated powder composed of calcium sulfate hydrate (CaSO4•2H2O) and calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO4•1/2H2O). It is used primarily as a bone grafting material in dental augmentation procedures such as socket grafting, lateral augmentation, sinus lift, cyst enucleation and more.
AFt Phases refer to the calcium Aluminate Ferrite trisubstituted, or calcium aluminate trisubstituted, phases present in hydrated cement paste (HCP) in concrete.
References
- ↑ Kent, James A. (2007-10-08). Kent and Riegel's Handbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 1096. ISBN 978-0-387-27842-1.