Related Research Articles
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a sequence of numbers that represent samples of a continuous variable in a domain such as time, space, or frequency. In digital electronics, a digital signal is represented as a pulse train, which is typically generated by the switching of a transistor.
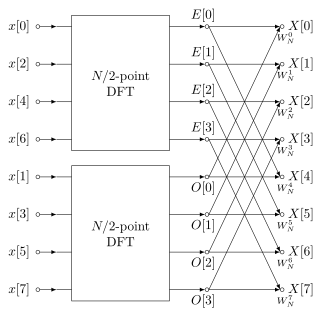
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of sparse factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the complexity of computing the DFT from , which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to , where n is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where n may be in the thousands or millions. In the presence of round-off error, many FFT algorithms are much more accurate than evaluating the DFT definition directly or indirectly. There are many different FFT algorithms based on a wide range of published theories, from simple complex-number arithmetic to group theory and number theory.
In telecommunication, a convolutional code is a type of error-correcting code that generates parity symbols via the sliding application of a boolean polynomial function to a data stream. The sliding application represents the 'convolution' of the encoder over the data, which gives rise to the term 'convolutional coding'. The sliding nature of the convolutional codes facilitates trellis decoding using a time-invariant trellis. Time invariant trellis decoding allows convolutional codes to be maximum-likelihood soft-decision decoded with reasonable complexity.
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It allows a much wider range of algorithms to be applied to the input data and can avoid problems such as the build-up of noise and distortion during processing. Since images are defined over two dimensions digital image processing may be modeled in the form of multidimensional systems. The generation and development of digital image processing are mainly affected by three factors: first, the development of computers; second, the development of mathematics ; third, the demand for a wide range of applications in environment, agriculture, military, industry and medical science has increased.

Télécom Paris is a French public institution for higher education and engineering research. Located in Palaiseau, it is also a member of the Institut Polytechnique de Paris and the Institut Mines-Télécom. In 2021 it was the sixth highest ranked French university in the World University Rankings, and the 7th best small university worldwide. In the QS Ranking, Télécom Paris is the 64th best university worldwide in Computer Science.

Andrew James Viterbi is an Italian Jewish–American electrical engineer and businessman who co-founded Qualcomm Inc. and invented the Viterbi algorithm. He is the Presidential Chair Professor of Electrical Engineering at the University of Southern California's Viterbi School of Engineering, which was named in his honor in 2004 in recognition of his $52 million gift.

David John Wheeler was a computer scientist and professor of computer science at the University of Cambridge.
Lawrence R. Rabiner is an electrical engineer working in the fields of digital signal processing and speech processing; in particular in digital signal processing for automatic speech recognition. He has worked on systems for AT&T Corporation for speech recognition.
Shmuel Winograd was an Israeli-American computer scientist, noted for his contributions to computational complexity. He has proved several major results regarding the computational aspects of arithmetic; his contributions include the Coppersmith–Winograd algorithm and an algorithm for the fast Fourier transform which transforms it into a problem of computing convolutions which can be solved with another Winograd's algorithm.
László "Les" Bélády was a Hungarian computer scientist notable for devising the Bélády's Min theoretical memory caching algorithm in 1966 while working at IBM Research. He also demonstrated the existence of a Bélády's anomaly. During the 1980s, he was the editor-in-chief of the IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering.
Richard E. Blahut, former chair of the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, is best known for his work in information theory. He received his PhD Electrical Engineering from Cornell University in 1972.

Bernard Widrow is a U.S. professor of electrical engineering at Stanford University. He is the co-inventor of the Widrow–Hoff least mean squares filter (LMS) adaptive algorithm with his then doctoral student Ted Hoff. The LMS algorithm led to the ADALINE and MADALINE artificial neural networks and to the backpropagation technique. He made other fundamental contributions to the development of signal processing in the fields of geophysics, adaptive antennas, and adaptive filtering. A summary of his work is.

Martin Vetterli is the president of École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland, succeeding Patrick Aebischer. He's a professor of engineering and was formerly the president of the National Research Council of the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Ali H. Sayed is the dean of engineering at EPFL, where he teaches and conducts research on Adaptation, Learning, Statistical Signal Processing, and Signal Processing for Communications. He is the Director of the EPFL Adaptive Systems Laboratory. He has authored several books on estimation and filtering theories, including the textbook Adaptive Filters, published by Wiley & Sons in 2008. Professor Sayed received the degrees of Engineer and Master of Science in Electrical Engineering from the University of São Paulo, Brazil, in 1987 and 1989, respectively, and the Doctor of Philosophy degree in electrical engineering from Stanford University in 1992.

Hisashi Kobayashi was the Sherman Fairchild University Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, emeritus at Princeton University in Princeton, New Jersey. His fields of expertise included applied probability; queueing theory; system modeling and performance analysis; digital communication and networks; network architecture; investigation of the Riemann hypothesis; and stochastic modeling of an infectious disease. He was a Senior Distinguished Researcher at the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Japan from September 2008 to March 2016.

Sundaraja Sitharama Iyengar is an Indian-born American computer scientist and the Distinguished University Professor, Ryder Professor and Director of Computer Science at Florida International University, Miami, Florida, USA. He also founded and directs the Robotics Research Laboratory at Louisiana State University (LSU). He has been a visiting professor or scientist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Naval Research Laboratory, and has been awarded the Satish Dhawan Visiting Chaired Professorship at the Indian Institute of Science, the Homi Bhaba Visiting Chaired Professor (IGCAR), and a professorship at the University of Paris (Sorbonne).
Edward H. Sussenguth Jr. was an American engineer and former IBM employee, known best for his work on Systems Network Architecture (SNA). He was also a contributor to the architecture of IBM's Advanced Computer System (ACS).

Boi Volkert Faltings is a Swiss professor of artificial intelligence at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne.
Patrick Flandrin is a French physicist, research director at CNRS researcher at École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, and member of the French Academy of Sciences.

Éric Moulines is a French researcher in statistical learning and signal processing. He received the silver medal from the CNRS in 2010, the France Télécom prize awarded in collaboration with the French Academy of Sciences in 2011. He was appointed a Fellow of the European Association for Signal Processing in 2012 and of the Institute of Mathematical Statistics in 2016. He is General Engineer of the Corps des Mines (X81).