Related Research Articles
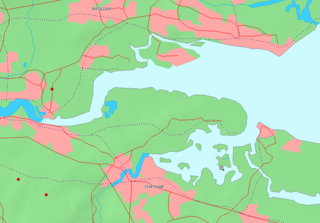
The Thames and Medway Canal is a disused canal in Kent, south east England, also known as the Gravesend and Rochester Canal. It was originally some 11 km (6.8 mi) long and cut across the neck of the Hoo peninsula, linking the River Thames at Gravesend with the River Medway at Strood. The canal was first mooted in 1778 as a shortcut for military craft from Deptford and Woolwich Dockyards on the Thames to Chatham Dockyard on the Medway, avoiding the 74 km (46 mi) journey round the peninsula and through the Thames estuary. The canal was also intended to take commercial traffic between the two rivers.

A Thames sailing barge is a type of commercial sailing boat once common on the River Thames in London. The flat-bottomed barges with a shallow draught and leeboards, were perfectly adapted to the Thames Estuary, with its shallow waters and narrow tributary rivers. The larger barges were seaworthy vessels, and were the largest sailing vessel to be handled by just two men. The average size was about 120 tons and they carried 4,200 square feet (390 m2) of canvas sail in six working sails. The mainsail was loose-footed and set up with a sprit, and was brailed to the mast when not needed. It is sheeted to a horse, as is the foresail; they require no attention when tacking. The foresail is often held back by the mate to help the vessel come about more swiftly.

The spritsail is a four-sided, fore-and-aft sail that is supported at its highest points by the mast and a diagonally running spar known as the sprit. The foot of the sail can be stretched by a boom or held loose-footed just by its sheets. A spritsail has four corners: the throat, peak, clew, and tack. The Spritsail can also be used to describe a rig that uses a spritsail.

The Commander-in-Chief, The Nore, was an operational commander of the Royal Navy. His subordinate units, establishments, and staff were sometimes informally known as the Nore Station or Nore Command. The Nore is a sandbank at the mouth of the Thames Estuary and River Medway.

SB Cambria is a preserved spritsail Thames sailing barge now used for sail training. She was the last barge to trade entirely under sail, and took her last cargo in 1970. She is now restored and owned and operated by the Cambria Trust, a registered charity under English law.

Edith May is a wooden Thames sailing barge built in Harwich, Essex, in 1906. She was used to carry various cargoes until 1952, when a diesel engine was fitted, after which she was used in various Thames Sailing Barge matches, winning several. She was a museum ship for a time, and was restored in 2010 to offer charter trips on the River Medway. Her winter moorings are at Lower Halstow, where she opens during the weekend as a tearoom.

Lady of the Lea is a spritsail Thames sailing barge, the last such barge to be built in England. She was built in 1931 to carry explosives from Waltham Abbey Royal Gunpowder Mills on the River Lea to Woolwich Arsenal on the River Thames. The barge was later sold and rebuilt. She currently operates as a private yacht and competes in Thames sailing barge matches.

SB Centaur is a wooden Thames sailing barge, built in Harwich, Essex, England in 1895. She was used to carry various cargoes, mainly grain, for the next 60 years. During the First World War she carried food and coal to the French Channel ports. During the Second World War Centaur was damaged when sailing to assist with the Dunkirk Evacuation. She did war work for the duration of the conflict.

SB Pudge is a wooden Thames sailing barge, built in Rochester, Kent, England in 1922. Her hull was pitch pine on oak frame. She was originally spritsail rigged with bowsprit. An auxiliary oil engine made by The Bergius Co.Ltd of Glasgow was installed in 1932. She was used to carry various cargoes for the London & Rochester Trading Co until 1968, when she was bought out of trade by the Thames Sailing Barge Trust. Her last cargo was pineapple juice.

SB Wyvenhoe is an 83-ton, steel Thames sailing barge. She was built by Forrest & Sons, Wivenhoe in 1898. She has the Official No. 110012.

Xylonite is one of seven Thames barges built between 1925 and 1930 for F W Horlock, Mistley. She was sold by the Horlocks in 1958 and cut down to a motor barge in 1958. Xylonite was re-rigged in the 1970s by Tim Eliff and replated on the 1980s. She has been used for sail training since 1983.
The Thames Sailing Barge Match is the second oldest sailing race in the world, beaten only by the America's Cup. It starts off Stanford-le-Hope and finishes off the Three Daws public house in Gravesend on the London River and is open to spritsail rigged Thames sailing barges, it uses the same course and rules as were used in the first match in 1863.

Reminder is one of seven Thames barges built between 1925 and 1930 for F W Horlock, Mistley.

The Phoenician is a wooden Thames sailing barge constructed in Sittingbourne in 1922. She was derigged after an accident in 1940. She left trade in 1973. In the 1980s, she was re-rigged to her original specification.

SB Decima is a steel Thames sailing barge constructed in Southampton in 1899 by J.G. Fay and Co, Southampton for E. J. Goldsmith of Grays, Essex. She is back under sail and resident on the River Darent in Dartford, Kent. She is a notable "Historic Ship".
The Golden Dustman may refer to:

Ardwina was the last wooden Thames barge to be built in Ipswich. This was in 1909. She was registered in London. She worked commercially until 1956. She was laid up after a collision and restored as a yacht conversion. She is still sailing in 2018, based at St Katherine Docks, and regularly passes under Tower Bridge.

Mirosa is a Thames barge which was built in 1892. From 1892 until 1947, she sailed under the name Ready when the name was sold to Trinity House for a lightship support vessel. Under her new name, she traded until 1955. Mirosa has never had an engine.

George Smeed is a Thames barge built in 1882 by Smeed Dean & Co. Ltd. in Murston.

Blue Mermaid is a steel-hulled Thames sailing barge constructed between 2015 and 2019. She was built specifically to operate under sail and does not carry an engine. She is a replica of Blue Mermaid. She was constructed in Devon, and she was launched on 28 May 2016 for the Sea-Change Sailing Trust. She was taken to Maldon where she was fitted out at the Downs Road Boatyard. She will operate out of the Heybridge Basin.
References
- ↑ March 1948, pp. 122–151.
- ↑ March 1948, pp. 122–167.
- Bibliography
- March, Edgar J (1948). Spritsail barges of the Thames and Medway. London: Percival Marshall.
- Roberts, Bob (2000). Coasting bargemaster : illustrated. Woodbridge: Seafarer Books. ISBN 0953818012.
- Roberts, Bob (2002). Last of the sailormen (Repr. ed.). Rendlesham, Suffolk: Seafarer Books. ISBN 0953818047.