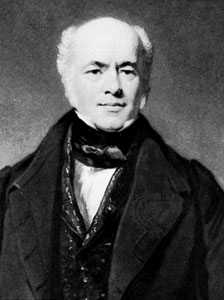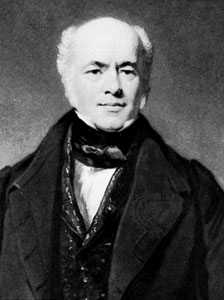
Francis Baily was an English astronomer. He is most famous for his observations of "Baily's beads" during a total eclipse of the Sun. Baily was also a major figure in the early history of the Royal Astronomical Society, as one of the founders and as the president four times.

Naunton Wayne, was a Welsh character actor, born in Pontypridd, Glamorgan, Wales. He was educated at Clifton College. His name was changed by deed poll in 1933.

The BMJ is a weekly peer-reviewed medical journal, published by BMJ Group, which in turn is wholly-owned by the British Medical Association (BMA). The BMJ has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Previously called the British Medical Journal, the title was officially shortened to BMJ in 1988, and then changed to The BMJ in 2014. The journal is published by BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, a subsidiary of the British Medical Association (BMA). The current editor-in-chief of The BMJ is Kamran Abbasi, who was appointed in January 2022.

Porth is a town and a community in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, within the historic county boundaries of Glamorgan, Wales. Lying in the Rhondda Valley, it is regarded as the gateway connecting the Rhondda Fawr and Rhondda Fach valleys due to both valleys meeting at Porth. The Welsh word "porth" means "gate". Porth is a predominantly English-speaking community.

Sir Gilbert Blane of Blanefield, 1st Baronet FRSE FRS MRCP was a Scottish physician who instituted health reform in the Royal Navy. He saw action against both the French and Spanish fleets, and later served as a Commissioner on the Sick and Wounded Board of the Admiralty. He was President of the Medical and Chirurgical Society of London in 1813.
The British Medical Association (BMA) is a registered trade union and professional body for doctors in the United Kingdom. It does not regulate or certify doctors, a responsibility which lies with the General Medical Council. The BMA has a range of representative and scientific committees and is recognised by National Health Service (NHS) employers alongside the Hospital Consultants and Specialists Association as one of two national contract negotiators for doctors.

Sir Austin Bradford Hill was an English epidemiologist who pioneered the modern randomised clinical trial and, together with Richard Doll, demonstrated the connection between cigarette smoking and lung cancer. Hill is widely known for pioneering the "Bradford Hill" criteria for determining a causal association.
Sir Alexander Armstrong was an Irish naval surgeon, explorer, naturalist and author. After obtaining a medical degree he joined the Royal Navy and was stationed on board HMS Investigator, tasked with finding the lost expedition of explorer Sir John Franklin. Investigator was trapped in the ice at Mercy Bay in 1851 and Armstrong spent several winters in the Arctic before he returned to London.
Major-General Sir David Bruce, was a Scottish pathologist and microbiologist who made some of the key contributions in tropical medicine. In 1887, he discovered a bacterium, now called Brucella, that caused what was known as Malta fever. In 1894, he discovered a protozoan parasite, named Trypanosoma brucei, as the causative pathogen of nagana.

William Henry Welch was an American physician, pathologist, bacteriologist, and medical-school administrator. He was one of the "Big Four" founding professors at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. He was the first dean of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and was also the founder of the Johns Hopkins School of Hygiene and Public Health, the first school of public health in the country. Welch was more known for his cogent summations of current scientific work, than his own scientific research. The Johns Hopkins medical school library is also named after Welch. In his lifetime, he was called the "Dean of American Medicine" and received various awards and honors throughout his lifetime and posthumously.

Sir Alexander Ogston MD CM LLD was a British surgeon, famous for his discovery of Staphylococcus.

Sir George Newman was an English public health physician, Quaker, the first Chief Medical Officer to the Ministry of Health in England, and wrote a seminal treatise on the social problems causing infant mortality.

Marcus Dillistone is a British film director.

Sir Thomas Lewis was a Welsh cardiologist. He coined the term "clinical science" and is also known for the Lewis P Factor.

The Medical Society of London is one of the oldest surviving medical societies in the United Kingdom.

Captain Albert Richard Behnke Jr. USN (ret.) was an American physician, who was principally responsible for developing the U.S. Naval Medical Research Institute. Behnke separated the symptoms of Arterial Gas Embolism (AGE) from those of decompression sickness and suggested the use of oxygen in recompression therapy.
Julian Edmund Davies is a British-born microbiologist and Professor Emeritus in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at the University of British Columbia.

Herbert Ritchie Spencer was professor of obstetrics at University College London.

James Samuel Risien Russell was a Guyanese-British physician, neurologist, professor of medicine, and professor of medical jurisprudence.

The Tynewydd Colliery disaster occurred on 11 April 1877, when water from a nearby closed colliery flooded the Newydd Colliery in Porth and 14 miners became trapped, of which five died. For his efforts in the rescue, Henry Naunton Davies received the first BMA Gold Medal.