
The American Meteorological Society (AMS) is a scientific and professional organization in the United States promoting and disseminating information about the atmospheric, oceanic, and hydrologic sciences. Its mission is to advance the atmospheric and related sciences, technologies, applications, and services for the benefit of society.

The Royal Meteorological Society is a long-established institution that promotes academic and public engagement in weather and climate science. Fellows of the Society must possess relevant qualifications, but Associate Fellows can be lay enthusiasts. Its Quarterly Journal is one of the world's leading sources of original research in the atmospheric sciences. The chief executive officer is Liz Bentley.

Edward Norton Lorenz was an American mathematician and meteorologist who established the theoretical basis of weather and climate predictability, as well as the basis for computer-aided atmospheric physics and meteorology. He is best known as the founder of modern chaos theory, a branch of mathematics focusing on the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions.

Henry Melson Stommel was a major contributor to the field of physical oceanography. Beginning in the 1940s, he advanced theories about global ocean circulation patterns and the behavior of the Gulf Stream that form the basis of physical oceanography today. Widely recognized as one of the most influential and productive oceanographers of his time, Stommel was both a groundbreaking theoretician and an astute, seagoing observer.
The William Bowie Medal is awarded annually by the American Geophysical Union for "outstanding contributions to fundamental geophysics and for unselfish cooperation in research". The award is the highest honor given by the AGU and is named in honor of William Bowie, one of the co-founders of the Union.

Susan Solomon is an American atmospheric chemist, working for most of her career at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). In 2011, Solomon joined the faculty at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where she serves as the Ellen Swallow Richards Professor of Atmospheric Chemistry & Climate Science. Solomon, with her colleagues, was the first to propose the chlorofluorocarbon free radical reaction mechanism that is the cause of the Antarctic ozone hole. Her most recent book, Solvable: how we healed the earth, and how we can do it again (2024) focuses on solutions to current problems, as do books by data scientist Hannah Ritchie, marine biologist, Ayana Elizabeth Johnson and climate scientist Katharine Hayhoe.
Carl Wunsch was the Cecil and Ida Green Professor of Physical Oceanography at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, until he retired in 2013. He is known for his early work in internal waves and more recently for research into the effects of ocean circulation on climate.

Boundary currents are ocean currents with dynamics determined by the presence of a coastline, and fall into two distinct categories: western boundary currents and eastern boundary currents.
Sverdrup Gold Medal Award – is the American Meteorological Society's award granted to researchers who make outstanding contributions to the scientific knowledge of interactions between the oceans and the atmosphere.
Lynne Talley is a physical oceanographer at Scripps Institution of Oceanography known for her research into the large-scale circulation of water masses in the global ocean.
John Crossley Swallow FRS was an English oceanographer who invented the Swallow float, a scientific drifting bottle based on the messages in bottles that shipwrecked sailors hoped would reach inhabited shores, summoning assistance.
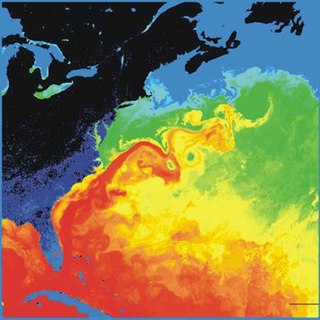
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around 40°0′N30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.
The POLYGON experiment was a pioneer experiment in oceanography conducted in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean during the 1970s. The experiment, led by Leonid Brekhovskikh, was the first to establish the existence of so-called mesoscale eddies, eddies at the 100 km (60 mi) and 100-day scale, which triggered the "mesoscale revolution". The existence of mesoscale eddies was predicted by Henry Stommel in the 1960s, but there was no way to observe them with traditional sampling methods.
Harry Leonard Bryden, FRS is an American physical oceanographer, professor at University of Southampton, and staff at the National Oceanography Centre, Southampton. He is best known for his work in ocean circulation and in the role of the ocean in the Earth's climate.
Venkatachalam Ramaswamy is the Director of the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research (OAR), studying climate modeling and climate change. "A leading climate scientist", his work is cited as supporting evidence for significant stratospheric climate change. He focuses in particular on radiative transfer models and the hydrologic cycle in the atmosphere. He has actively supported the development of supercomputing approaches that enable researchers to achieve higher resolution and greater complexity in climate models. As a lead author involved in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Ramaswamy's contributions was recognised by the joint award of the 2007 Nobel Peace Prize to the IPCC.
Charles Henry Brian (Bill) Priestley, was a British meteorologist who spent much of his career at the CSIRO in Australia.
Amy Bower is an American physical oceanographer at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She is known for her research on ocean circulation and for being one of the few blind oceanographers.
Glenn Richard Flierl is Professor of Oceanography at the Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts. In 1970, he received his B.A. in Physics from Oberlin College and in 1975 his Ph.D. in Physics from Harvard University. Advised by Allan Richard Robinson, he graduated with the dissertation "Gulf Stream Meandering, Ring Formation and Ring Propagation". He joined the faculty at MIT in 1976.
George Veronis was an American geophysicist.






