The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid. It served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Built c. 2600 BC, over a period of about 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only wonder that has remained largely intact. It is the most famous monument of the Giza pyramid complex, which is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Memphis and its Necropolis". It is situated at the northeastern end of the line of the three main pyramids at Giza.

Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on his achievements as a painter, he has also become known for his notebooks, in which he made drawings and notes on a variety of subjects, including anatomy, astronomy, botany, cartography, painting, and palaeontology. Leonardo is widely regarded to have been a genius who epitomised the Renaissance humanist ideal, and his collective works comprise a contribution to later generations of artists matched only by that of his younger contemporary Michelangelo.

The Codex Leicester is a collection of scientific writings by Leonardo da Vinci. The codex is named after Thomas Coke, Earl of Leicester, who purchased it in 1717. The codex provides an insight into the mind of the Renaissance artist, scientist and thinker, as well as an exceptional illustration of the link between art and science and the creativity of the scientific process.

Francesco Melzi, or Francesco de Melzi (1491–1567), was an Italian painter born into a family of the Milanese nobility in Lombardy. He became a pupil of Leonardo da Vinci and remained as his closest professional assistant throughout his career. After da Vinci's death he became the literary executor of all da Vinci's papers, editing them into a manuscript on painting he published as Trattato della Pittura [Treatise on Painting] or a compilation entitled the Codex Urbinas.

The Adoration of the Magi is an unfinished early painting by the Italian Renaissance artist Leonardo da Vinci. Leonardo was given the commission by the Augustinian monks of San Donato in Scopeto in Florence in 1481, but he departed for Milan the following year, leaving the painting unfinished. It has been in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence since 1670.

Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance painter and polymath who achieved legendary fame and iconic status within his own lifetime. His renown primarily rests upon his brilliant achievements as a painter, the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, being two of the most famous artworks ever created, but also upon his diverse skills as a scientist and inventor. He became so highly valued during his lifetime that the King of France bore him home like a trophy of war, supported him in his old age and, according to legend, cradled his head as he died.

Egyptian pyramid construction techniques are the controversial subject of many hypotheses. These techniques seem to have developed over time; later pyramids were not constructed in the same way as earlier ones. Most of the construction hypotheses are based on the belief that huge stones were carved from quarries with copper chisels, and these blocks were then dragged and lifted into position. Disagreements chiefly concern the methods used to move and place the stones.

The Italian polymath Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) left thousands of pages of writings and drawings, but rarely made any references to his personal life. The resulting uncertainty, combined with mythologized anecdotes from his lifetime, has resulted in much speculation and interest in Leonardo's personal life. Particularly, his personal relationships, philosophy, religion, vegetarianism, left-handedness and appearance.

Renaissance technology was the set of European artifacts and inventions which spread through the Renaissance period, roughly the 14th century through the 16th century. The era is marked by profound technical advancements such as the printing press, linear perspective in drawing, patent law, double shell domes and bastion fortresses. Sketchbooks from artisans of the period give a deep insight into the mechanical technology then known and applied.

Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) was an Italian polymath, regarded as the epitome of the "Renaissance Man", displaying skills in numerous diverse areas of study. While most famous for his paintings such as the Mona Lisa and the Last Supper, Leonardo is also renowned in the fields of civil engineering, chemistry, geology, geometry, hydrodynamics, mathematics, mechanical engineering, optics, physics, pyrotechnics, and zoology.
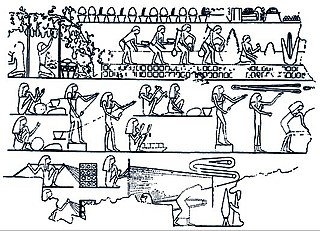
Ancient Egyptian technology describes devices and technologies invented or used in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope trusses to stiffen the beam of ships. Egyptian paper, made from papyrus, and pottery were mass-produced and exported throughout the Mediterranean Basin. The wheel was used for a number of purposes, but chariots only came into use after the Second Intermediate Period. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime technology including ships and lighthouses.

The Codex Atlanticus is a 12-volume, bound set of drawings and writings by Leonardo da Vinci, the largest single set. Its name indicates the large paper used to preserve original Leonardo notebook pages, which was used for atlases. It comprises 1,119 leaves dating from 1478 to 1519, the contents covering a great variety of subjects, from flight to weaponry to musical instruments and from mathematics to botany. This codex was gathered in the late 16th century by the sculptor Pompeo Leoni, who dismembered some of Leonardo's notebooks in its formation. It is now in the Biblioteca Ambrosiana in Milan.

Codex on the Flight of Birds is a relatively short codex from c. 1505 by Leonardo da Vinci.

Mario Taddei is an Italian academic. He is an expert in multimedia and edutainment for museums, a Leonardo da Vinci devotee and scholar, and an expert in the codexes and machines of da Vinci and ancient books of technology.

The portrait of a man in red chalk in the Royal Library of Turin is widely, though not universally, accepted as a self-portrait of Leonardo da Vinci. It is thought that Leonardo da Vinci drew this self-portrait at about the age of 60. The portrait has been extensively reproduced and has become an iconic representation of Leonardo as a polymath or "Renaissance Man". Despite this, some historians and scholars disagree as to the true identity of the sitter.

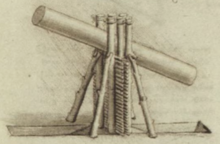
Leonardo's crossbow designs are a series of shooting weapon schematics designed by Leonardo da Vinci that are in the Codex Atlanticus. One version, a self-spanning infantry weapon called the Rapid Fire Crossbow, is found on sheets 143r, 153r, and 155r. The other is the Giant Crossbow design intended to be a mounted siege weapon found on sheet 149a in the Codex.
Ancient Egyptian trade developed with the gradual creation of land and sea trade routes connecting the ancient Egyptian civilization with ancient India, the Fertile Crescent, Arabia and Sub-Saharan Africa.

The Madrid Codices I–II, are two manuscripts by Leonardo da Vinci which were discovered in the Biblioteca Nacional de España in Madrid in 1965 by Dr. Jules Piccus, Language Professor at the University of Massachusetts. The Madrid Codices I was finished during 1490 and 1499, and II from 1503 to 1505.

Leonardo's world map is the name assigned to a unique world map drawn using the "octant projection" and found loosely inserted among a Codex of Leonardo da Vinci preserved in Windsor. It features an early use of the toponym America and incorporates information from the travels of Amerigo Vespucci, published in 1503 and 1505. Additionally, the map depicts the Arctic as an ocean and Antarctica as a continent of about the correct size.
Augusto Marinoni was professor of romance philology at the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore of Milan, a member of the Commissione Vinciana and the Accademia dei Lincei. He is considered one of the greatest scholars of Leonardo da Vinci.