
The Province of Saxony, also known as Prussian Saxony, was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.

Sangerhausen is a town in Saxony-Anhalt, central Germany, capital of the district of Mansfeld-Südharz. It is situated southeast of the Harz, approx. 35 kilometres east of Nordhausen, and 50 km (31 mi) west of Halle (Saale). About 26,000 people live in Sangerhausen (2020).
Ulrich Willerding is a professor emeritus of botany at the Göttingen University, Germany. He is also an instructor at a local high school. Willerding is one of the leading European palaeo-ethnobotanists. He has specialized in Medieval Europe but also done work on other times. One of his special interests is weeds. He has worked on bibliographies of European paleoethnobotany. Although a biologist by training, he has worked extensively with archaeologists.

Christian Ludwig Nitzsch was a German zoologist. He is best remembered for his approach to classifying birds on the basis of their feather tract distributions or pterylosis of their young.

Mansfeld, sometimes also unofficially Mansfeld-Lutherstadt, is a town in the district of Mansfeld-Südharz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany.

Bad Bocklet is a municipality in the district of Bad Kissingen in Bavaria in Germany. It is a market town and a health spa.
Ebersroda is a village and a former municipality in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 July 2009, it is part of the municipality Gleina.
Röblingen am See is a village and a former municipality in the Mansfeld-Südharz district, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the municipality Seegebiet Mansfelder Land, of which it is the administrative centre.
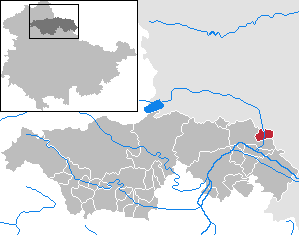
Mönchpfiffel-Nikolausrieth is a municipality on the river Helme in the district Kyffhäuserkreis, in Thuringia, Germany. The municipality was created in 1956 by the merging of the villages Monchpfiffel and Nikolausrieth.
Matilda, also known as Mathilda and Mathilde, was a German regent, and the first Princess-Abbess of Quedlinburg. She served as regent of Germany for her brother during his absence in 967, and as regent during the minority of her nephew from 984.

The Helme is a river in central Germany that is about 65 kilometres (40 mi) long and which forms a left-hand, western tributary of the Unstrut in the states of Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt.
Mansfeld Land is a region in the southwestern corner of the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. The region derives its name from the counts of Mansfeld, who ruled this region for about 1,000 years.

The Teltow and Magdeburg Wars were fought between 1239 and 1245 over possession of Barnim and Teltow in the present-day federal German state of Brandenburg. They took place in the 13th century during the course of the Eastern German Expansion. The opposing sides during the armed conflict, which took place on two fronts simultaneously, were:

Heinrich August Erhard was a German physician, archivist and historian.

Fischberg Castle was a high medieval fortification in the Felda valley that was sited on an exposed hill above the villages of Klings, Fischbach and Diedorf. Its ruins currently stand in the county of Wartburgkreis (Thuringia) - in the Anterior Rhön, part of a mountain region in central Germany.

The Friesenfeld was a Gau (territory), in modern-day north Thuringia and south Saxony-Anhalt in the area between Allstedt and Merseburg and which bordered Hassegau. Numerous places in Friesenfeld such as Erdeborn were named in the Hersfeld Tithe Register of the Hersfeld Abbey as being obliged to pay tithes.

Johannisberg is a prominent ridge of the Wöllmisse, a Muschelkalk plateau east of Jena. The steeply sloping spur of land to the Saale Valley north of the district of Alt-Lobeda bears the remains of two important fortifications from the late Bronze Age and the early Middle Ages. Due to several archaeological excavations and finds recovered since the 1870s, they are among the few investigated fortifications from these periods in Thuringia. Of particular interest in archaeological and historical research is the early medieval castle. Due to its location directly on the eastern bank of the Saale, its dating and interpretation were and are strongly linked to considerations of the political-military eastern border of the Frankish empire. It is disputed whether it was a fortification of independent Slavic rulers or whether it was built under Frankish rule. According to a recent study, it may have been built in the second half of the 9th century in connection with the establishment of the limes sorabicus under Frankish influence.

Mistislaw, also known as Mstislav, was an Elbe Slavic prince of the Nakonid lineage and ruled over the Obotrites in what is now Mecklenburg and eastern Holstein from 990/995 to 1018.












