
Corinth is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the municipality of Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It is the capital of Corinthia.

Tripoli is a city in the central part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. It is the capital of the Peloponnese region as well as of the regional unit of Arcadia. The homonymous municipality had 44,165 inhabitants in 2021.

Kalamata is the second most populous city of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece after Patras, and the largest city of the homonymous administrative region. As the capital and chief port of the Messenia regional unit, it lies along the Nedon River at the head of the Messenian Gulf.

National Road 48 is a single carriageway road in central Greece. It connects the Greek National Road 5 at Antirrio with the town Livadeia, passing through Naupactus and Delphi. The section between Antirrio and Itea is part of European route E65. The GR-48 passes through the regional units Aetolia-Acarnania, Phocis and Boeotia.
Lechaeum or Lechaion, also called Lecheae and Lecheum, was the port in ancient Corinthia on the Corinthian Gulf connected with the city of Corinth by means of the Long Walls, 12 stadia in length. The Long Walls ran nearly due north, so that the wall on the right hand was called the eastern, and the one on the left hand the western or Sicyonian. The space between them must have been considerable; since there was sufficient space for an army to be drawn up for battle. Indeed, the area was the scene of battles between Sparta and Athens in 391 BCE, leaving Spartans in command of Lechaeum, which they garrisoned with their troops. One of the earliest active ports in Europe, Lechaeum was in use as a commercial port as early as 1381 BCE.

National Road 70 is a single carriageway road in southern Greece. It connects Corinth with Argos, via Epidavros and Nafplio. It is situated in the regional units Corinthia and Argolis, in the Peloponnese peninsula. The total length is 96 kilometres (60 mi).

The Hellenic Railways Organisation or OSE is the Greek national railway company which owns, maintains and operates all railway infrastructure in Greece with the exception of Athens' rapid transit lines. Train services on these lines are run by Hellenic Train S.A., a former OSE subsidiary, Rail Cargo Logistics Goldair, Pearl and Grup Feroviar Român.
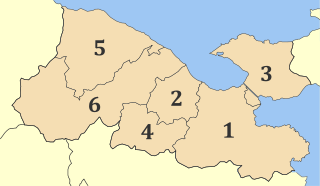
Corinthia is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Peloponnese. It is situated around the city of Corinth, in the north-eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula.

Alexandroupolis or Alexandroupoli is a city in Greece and the capital of the Evros regional unit. It is the largest city in Greek Thrace and the region of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, with a population of 71,751, and is an important port and commercial center for northeastern Greece.

Acrocorinth is a monolithic rock overlooking the ancient city of Corinth, Greece. In the estimation of George Forrest, "It is the most impressive of the acropolis of mainland Greece."

The Kalavryta massacre, or the Holocaust of Kalavryta, was the near-extermination of the male population and the total destruction of the town of Kalavryta, Axis-occupied Greece, by the 117th Jäger Division (Wehrmacht) during World War II, on 13 December 1943.

Sparta is a city and municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. It lies at the site of ancient Sparta within the Evrotas Valley. The municipality was merged with six nearby municipalities in 2011, for a total population of 32,786, of whom 17,773 lived in the city.

Corinth was a city-state (polis) on the Isthmus of Corinth, the narrow stretch of land that joins the Peloponnese peninsula to the mainland of Greece, roughly halfway between Athens and Sparta. The modern city of Corinth is located approximately 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) northeast of the ancient ruins. Since 1896, systematic archaeological investigations of the Corinth Excavations by the American School of Classical Studies at Athens have revealed large parts of the ancient city, and recent excavations conducted by the Greek Ministry of Culture have brought to light important new facets of antiquity.

Greek National Road 7 is a single carriageway with at-grade intersections in the Peloponnese region in southern Greece. It connects the cities of Corinth and Kalamata, via Nemea, Argos, Tripoli and Megalopoli. It has been succeeded in importance by the Moreas Motorway (Corinth–Kalamata), which is numbered A7.

The Museum of the Macedonian Struggle near Chromio, Kozani regional unit, Greece is an open-air museum created and landscaped over an area of 7 hectares presenting the struggles of the Greeks in Macedonia until it was united to Greece in 1912–13.

Isthmia is a Greek village and community 7.5 km (4.7 mi) southeast of Corinth. It is located in the south entry of Corinth Canal. The community spreads in the place where the Isthmian Games were held in antiquity. So, near the village important ruins of the archaeological site are kept including the Temple of Poseidon, the ancient stadium and the ancient theatre. Administratively, Isthmia belongs to Loutraki-Perachora-Agioi Theodoroi municipality and Loutraki-Perachora municipal unit.

Filoti is a semi-mountainous village of central Naxos, Greece, with a population of 1,617 residents, located at the foot of Mt. Zas, at an altitude of 400 meters, about 18.2 kilometres (11.3 mi) from the city of Naxos. It is located on the slopes of two hills and consists of three settlements, Rachidi, Klefaros and Lioiri. Its stand out is the Orthodox church of Panagia Filotitissa that is dedicated to the Assumption of the Virgin, a basilica built in 1718 in the place of an old Byzantine church. The economy of the village is mainly based on livestock products, secondarily in agriculture and tourism. It has a Primary School, a Professional High School, a Multipurpose Regional Doctor, a Citizen Service Center (KEP), a Post office, a dentist and a pharmacy.

The Ahmed III Mosque, also known as the Acrocorinth Mosque or the Ahmed Pasha Mosque, is an Ottoman mosque located in the fortress of the Acrocorinth, in the Peloponnese, Greece. Built on the site of an earlier 16th-century mosque, the monument was commissioned by Sultan Ahmed III after the Ottoman reconquest of 1715. It now lies in a mostly ruinous state, abandoned and neglected, however it did undergo some restoration work in 2000.
















