
HLA-B is a human gene that provides instructions for making a protein that plays a critical role in the immune system. HLA-B is part of a family of genes called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex. The HLA complex helps the immune system distinguish the body's own proteins from proteins made by foreign invaders such as viruses and bacteria.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRA gene. HLA-DRA encodes the alpha subunit of HLA-DR. Unlike the alpha chains of other Human MHC class II molecules, the alpha subunit is practically invariable. However it can pair with, in any individual, the beta chain from 3 different DR beta loci, DRB1, and two of any DRB3, DRB4, or DRB5 alleles. Thus there is the potential that any given individual can form 4 different HLA-DR isoforms.
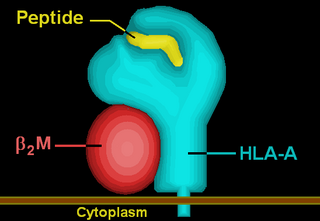
HLA-A is a group of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) that are coded for by the HLA-A locus, which is located at human chromosome 6p21.3. HLA is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen specific to humans. HLA-A is one of three major types of human MHC class I cell surface receptors. The others are HLA-B and HLA-C. The receptor is a heterodimer, and is composed of a heavy α chain and smaller β chain. The α chain is encoded by a variant HLA-A gene, and the β chain (β2-microglobulin) is an invariant β2 microglobulin molecule. The β2 microglobulin protein is coded for by a separate region of the human genome.
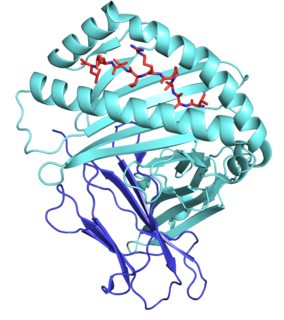
HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain E (HLA-E) also known as MHC class I antigen E is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-E gene. The human HLA-E is a non-classical MHC class I molecule that is characterized by a limited polymorphism and a lower cell surface expression than its classical paralogues. The functional homolog in mice is called Qa-1b, officially known as H2-T23.
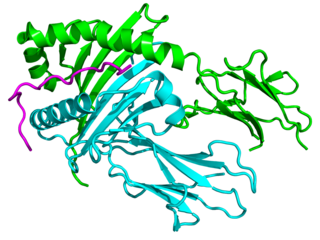
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1, also known as HLA-DQB1, is a human gene and also denotes the genetic locus that contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

Transporter associated with Antigen Processing 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAP1 gene.

Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DP(W2) beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DPB1 gene.
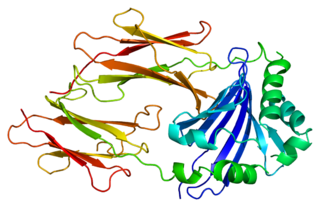
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DM beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DMB gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DM alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DMA gene.

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR2DL1 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DOA gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DOB gene.

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR3DL2 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DQ(6) alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQA2 gene. Also known as HLA-DXA or DAAP-381D23.2, it is part of the human leucocyte antigen system.

Olfactory receptor 2H2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR2H2 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase 19 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STK19 gene.

TAP2 is a gene in humans that encodes the protein Antigen peptide transporter 2.

Protein BAT4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAT4 gene.

Complement component 4B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C4B gene.













