Related Research Articles

Wasatch County is a county in the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 34,788. Its county seat and largest city is Heber City. The county was named for a Ute word meaning "mountain pass" or "low place in the high mountains".

Uintah County is a county in the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2020 United States Census the population was 35,620. Its county seat and largest city is Vernal. The county was named for the portion of the Ute Indian tribe that lived in the basin.

The Wasatch Range or Wasatch Mountains is a mountain range in the western United States that runs about 160 miles (260 km) from the Utah-Idaho border south to central Utah. It is the western edge of the greater Rocky Mountains, and the eastern edge of the Great Basin region. The northern extension of the Wasatch Range, the Bear River Mountains, extends just into Idaho, constituting all of the Wasatch Range in that state.
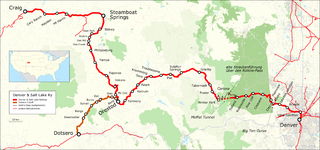
The Denver and Salt Lake Railway (D&SL) was a U.S. railroad company located in Colorado. Originally incorporated in 1902 as the Denver, Northwestern and Pacific (DN&P) Railway, it had as a goal a direct connection of Denver, Colorado, with Salt Lake City, Utah. It underwent numerous reorganizations throughout its financially troubled history and by the time the company was acquired in 1931 by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, it had advanced only as far as Craig, Colorado. After the acquisition the line was connected to the D&RGW main, and the eastern half of the line was used to give the D&RGW a more direct route to Denver. The portions of the railroad still in use today are known as the Moffat Tunnel Subdivision of Union Pacific Railroad's Central Corridor. Amtrak’s California Zephyr service from Denver to Glenwood Springs follows much of the old D&SL route.

The Uinta Mountains are an east-west trending mountain range in northeastern Utah extending a short distance into northwest Colorado and slightly into southwestern Wyoming in the United States. As a subrange of the Rocky Mountains, they are unusual for being the highest range in the contiguous United States running east to west, and lie approximately 100 miles (160 km) east of Salt Lake City. The range has peaks ranging from 11,000 to 13,528 feet, with the highest point being Kings Peak, also the highest point in Utah. The Mirror Lake Highway crosses the western half of the Uintas on its way to Wyoming. Utah State Route 44 crosses the east end of the Uintas between Vernal and Manila.

Little Cottonwood Canyon lies within the Wasatch-Cache National Forest along the eastern side of the Salt Lake Valley, roughly 15 miles from Salt Lake City, Utah. The canyon is part of Granite, a CDP and "Community Council" designated by Salt Lake County. The canyon is a glacial trough, carved by an alpine glacier during the last ice age, 15,000 to 25,000 years ago. A number of rare and endemic plant species are found in the canyon's Albion Basin. Introduced Mountain goats inhabit the surrounding mountains.
The Wasatch Back is a region in the Rocky Mountains in the U.S. state of Utah. It includes cities such as Park City, Heber City, and Morgan. The name Wasatch Back differentiates it from the Wasatch Front, which includes Utah's more populous cities such as Salt Lake City, Ogden, Layton, and Provo. The Wasatch Back sits on the eastern side of the Wasatch Range of the Rocky Mountains, while the Wasatch Front sits on the western side. Wasatch is a Ute Indian word that means "mountain pass" or "low pass over high range." The Wasatch Back is a very affluent region. Summit County is one of the wealthiest counties in the United States.

The Uinta Basin is a physiographic section of the larger Colorado Plateaus province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is also a geologic structural basin in eastern Utah, east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains. The Uinta Basin is fed by creeks and rivers flowing south from the Uinta Mountains. Many of the principal rivers flow into the Duchesne River which feeds the Green River—a tributary of the Colorado River. The Uinta Mountains form the northern border of the Uinta Basin. They contain the highest point in Utah, Kings Peak, with a summit 13,528 feet above sea level. The climate of the Uinta Basin is semi-arid, with occasionally severe winter cold.

Rock Canyon is located in the Wasatch Mountains, in east Provo, Utah, United States. It is popular with rock climbers and hikers due to its unique and rugged geology as well as its proximity to Brigham Young University. The mouth of the canyon is located just behind the Provo Utah Temple.
The Central Utah Project is a US federal water project that was authorized for construction under the Colorado River Storage Project Act of April 11, 1956, as a participating project. In general, the Central Utah Project develops a portion of Utah's share of the yield of the Colorado River, as set out in the Colorado River Compact of 1922.

Provo Canyon is located in unincorporated Utah County and Wasatch County, Utah. Provo Canyon runs between Mount Timpanogos on the north and Mount Cascade on the south. The canyon extends from Orem on the west end to Heber City on the east. Provo Canyon is situated to the east of Utah Valley and grants access to the valleys and Uinta Basin regions that lie beyond the Wasatch front.

Millcreek Canyon is a canyon in the Wasatch Mountains and part of Millcreek City on the east side of the Salt Lake Valley, Utah. It is a popular recreation area both in the summer and in the winter. It was named by Brigham Young on August 22, 1847, before all of the mills that were built in and below the densely forested canyon. It is home to two restaurants and six Boy Scout Day Camps.

The Duchesne River, located in the Uintah Basin region of Utah in the western United States, is a tributary of the Green River. The watershed of the river covers the Northeastern corner of Utah. The Duchesne River is 115 miles (185 km) long, and drains a total land area of 3,790 square miles (9,800 km2).
The Uinta Basin Rail project is a proposed 100-mile (160 km) rail line to connect the shale oil rich Uinta Basin region of eastern Utah to the national rail network. Numerous proposals have been made, some as far back as 1902, that are still under consideration. The current effort is a public-private partnership between a coalition of 7 counties in Utah, the Rio Grande Pacific Corporation and Drexel Hamilton Infrastructure Partners. The railroad is also backed by the Ute Tribe who hold a 5% stake in the project. If the rail line is built it will be the first major greenfield rail line built in the United States since the Chicago and North Western’s line to the Powder River Basin was built in the early 1980s. The Surface Transportation Board approved construction of the line in December 2021, however, the approval is being challenged in court by various environmentalist groups. In 2024, the Supreme Court of the United States agreed to hear the case Seven County Infrastructure Coalition v. Eagle County, involving the approval to build the rail line.
Willow Creek is a tributary stream of the Jordan River, in Salt Lake County, Utah.
Dalton Creek is a stream in Morgan County, Utah, United States. A tributary of the Weber River, it is located within the Uinta-Wasatch-Cache National Forest and its mouth is about 1.75 miles (2.82 km) southeast of Peterson.
Davenport Creek is a stream in Cache County, Utah, United States. It is also located within the Uinta-Wasatch-Cache National Forest and its mouth is about 2 miles (3.2 km) southeast of Avon. The creek rises in the Bear River Mountains and flows briefly southwest. It then turns northwest and runs in that direction for most of its course before emptying into the South Fork Little Bear River at a point immediately west of Utah State Route 162. The main tributaries of Davenport Creek are Pole Creek, Bald Head Creek, Smith Creek, and Fish Creek.
Days Canyon is a canyon in the Wasatch Range in eastern Utah County, Utah, United States.

The White River is a 8-mile-long (13 km) southeastward flowing river in Wasatch and Utah Counties in eastern Utah. The White River is a tributary to the Price River, which is, in turn, a tributary to the Green River, and then to the Colorado River.
Hobble Creek is a census-designated place (CDP) in eastern Utah County, Utah, United States. It was first listed as a CDP prior to the 2020 census.
References
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Hobble Creek
- ↑ Strack, Don (May 30, 2019). "Salt Lake & Denver Railroad". Utah Rails.net. Retrieved November 22, 2019.
- ↑ Seven County Infrastructure Coalition (March 13, 2019), Seven County Infrastructure Coalition – Uinta Basin Railway Evaluation of Potential route alternatives (PDF), Surface Transportation Board, retrieved December 29, 2019