
Beginning on August 7, 1961, a series of social psychology experiments were conducted by Yale University psychologist Stanley Milgram, who intended to measure the willingness of study participants to obey an authority figure who instructed them to perform acts conflicting with their personal conscience. Participants were led to believe that they were assisting an unrelated experiment, in which they had to administer electric shocks to a "learner". These sham or fake electric shocks gradually increased to levels that would have been fatal had they been real.

Stanley Milgram was an American social psychologist, best known for his controversial experiments on obedience conducted in the 1960s during his professorship at Yale.

Informed consent is a principle in medical ethics, medical law and media studies, that a patient must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about their medical care. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatments, alternative treatments, the patient's role in treatment, and their right to refuse treatment. In most systems, healthcare providers have a legal and ethical responsibility to ensure that a patient's consent is informed. This principle applies more broadly than healthcare intervention, for example to conduct research and to disclose a person's medical information.

A prescription, often abbreviated ℞ or Rx, is a formal communication from a physician or other registered healthcare professional to a pharmacist, authorizing them to dispense a specific prescription drug for a specific patient. Historically, it was a physician's instruction to an apothecary listing the materials to be compounded into a treatment—the symbol ℞ comes from the first word of a medieval prescription, Latin recipere, that gave the list of the materials to be compounded.

Twilight sleep is an amnesic state characterized by insensitivity to pain with or without the loss of consciousness, induced by an injection of morphine and scopolamine, with the purpose of pain management during childbirth. The obstetric method originated in Germany and gained large popularity in New York City in the early 20th century.
Obedience, in human behavior, is a form of "social influence in which a person yields to explicit instructions or orders from an authority figure". Obedience is generally distinguished from compliance, which some authors define as behavior influenced by peers while others use it as a more general term for positive responses to another individual's request, and from conformity, which is behavior intended to match that of the majority. Depending on context, obedience can be seen as moral, immoral, or amoral. For example, in psychological research, individuals are usually confronted with immoral demands designed to elicit an internal conflict. If individuals still choose to submit to the demand, they are acting obediently.

Human subject research is systematic, scientific investigation that can be either interventional or observational and involves human beings as research subjects, commonly known as test subjects. Human subject research can be either medical (clinical) research or non-medical research. Systematic investigation incorporates both the collection and analysis of data in order to answer a specific question. Medical human subject research often involves analysis of biological specimens, epidemiological and behavioral studies and medical chart review studies. On the other hand, human subject research in the social sciences often involves surveys which consist of questions to a particular group of people. Survey methodology includes questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups.
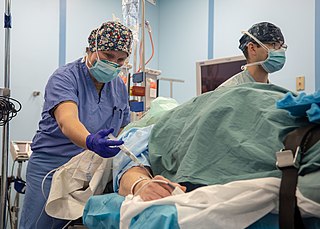
A nurse anesthetist is an advanced practice nurse who administers anesthesia for surgery or other medical procedures. Nurse anesthetists (NA's) administer or participate in administration of anesthesia services in 107 countries, working with or without anesthesiologists. Because of different historical backgrounds, anesthetist responsibilities and roles vary widely between countries. Depending on the locality, their role may be limited to intraoperative care during anesthesia itself or may also extend before and after. The International Federation of Nurse Anesthetists was established in 1989 as a forum for developing standards of education, practice, and a code of ethics.

A Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA) is a type of advanced practice nurse who administers anesthesia in the United States. CRNAs account for approximately half of the anesthesia providers in the United States and are the main providers (80%) of anesthesia in rural America. Historically, nurse anesthetists have been providing anesthesia care to patients for over 150 years since the American Civil War and the CRNA credential came into existence in 1956. CRNA schools issue a doctorate of nursing anesthesia degree to nurses who have completed a program in anesthesia, which is 3 years in length.

Hildegard E. Peplau was an American nurse and the first published nursing theorist since Florence Nightingale. She created the middle-range nursing theory of interpersonal relations, which helped to revolutionize the scholarly work of nurses. As a primary contributor to mental health law reform, she led the way towards humane treatment of patients with behavior and personality disorders.
In the statistical theory of the design of experiments, blocking is the arranging of experimental units that are similar to one another in groups (blocks) based on one or more variables. These variables are chosen carefully to minimize the impact of their variability on the observed outcomes. There are different ways that blocking can be implemented, resulting in different confounding effects. However, the different methods share the same purpose: to control variability introduced by specific factors that could influence the outcome of an experiment. The roots of blocking originated from the statistician, Ronald Fisher, following his development of ANOVA.
A Medication Administration Record, commonly referred to as a drug chart, is the report that serves as a legal record of the drugs administered to a patient at a facility by a health care professional. The MAR is a part of a patient's permanent record on their medical chart. The health care professional signs off on the record at the time that the drug or device is administered.

Matron is the job title of a very senior or the chief nurse in several countries, including the United Kingdom, and other Commonwealth countries and former colonies.

Emergency nursing is a specialty within the field of professional nursing focusing on the care of patients who require prompt medical attention to avoid long-term disability or death. In addition to addressing "true emergencies," emergency nurses increasingly care for people who are unwilling or unable to get primary medical care elsewhere and come to emergency departments for help. In fact, only a small percentage of emergency department (ED) patients have emergency conditions such as a stroke, heart attack or major trauma. Emergency nurses also tend to patients with acute alcohol and/or drug intoxication, psychiatric and behavioral problems and those who have been raped.

Clinical pharmacy is the branch of pharmacy in which clinical pharmacists provide direct patient care that optimizes the use of medication and promotes health, wellness, and disease prevention. Clinical pharmacists care for patients in all health care settings but the clinical pharmacy movement initially began inside hospitals and clinics. Clinical pharmacists often work in collaboration with physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other healthcare professionals. Clinical pharmacists can enter into a formal collaborative practice agreement with another healthcare provider, generally one or more physicians, that allows pharmacists to prescribe medications and order laboratory tests.

Obedience to Authority: An Experimental View is a 1974 book by social psychologist Stanley Milgram concerning a series of experiments on obedience to authority figures he conducted in the early 1960s. This book provides an in-depth look into his methods, theories and conclusions.

Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alleviation of suffering through compassionate presence". Nurses practice in many specialties with varying levels of certification and responsibility. Nurses comprise the largest component of most healthcare environments. Shortages of qualified nurses are found in many countries.

Chicago Hospital for Women and Children, renamed Mary Thompson Hospital after its founder's death in 1895, was established in 1865 and provided medical care to indigent women and children as well as clinical training to women doctors. It was founded by Mary Harris Thompson, who received her degree in Boston in 1863 from the New England Female Medical College, the first medical school for women.
Authority bias is the tendency to attribute greater accuracy to the opinion of an authority figure and be more influenced by that opinion. An individual is more influenced by the opinion of this authority figure, believing their views to be more credible, and hence place greater emphasis on the authority figure's viewpoint and are more likely to obey them. This concept is considered one of the social cognitive biases or collective cognitive biases.














