Auditory illusions are illusions of real sound or outside stimulus. These false perceptions are the equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the stimulus, or sounds that should not be possible given the circumstance on how they were created.

Binaural recording is a method of recording sound that uses two microphones, arranged with the intent to create a 3D stereo sound sensation for the listener of actually being in the room with the performers or instruments. This effect is often created using a technique known as dummy head recording, wherein a mannequin head is fitted with a microphone in each ear. Binaural recording is intended for replay using headphones and will not translate properly over stereo speakers. This idea of a three-dimensional or "internal" form of sound has also translated into useful advancement of technology in many things such as stethoscopes creating "in-head" acoustics and IMAX movies being able to create a three-dimensional acoustic experience.
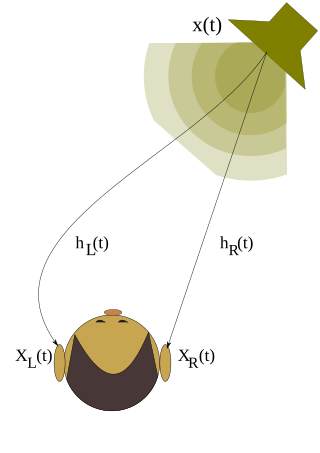
A head-related transfer function (HRTF) is a response that characterizes how an ear receives a sound from a point in space. As sound strikes the listener, the size and shape of the head, ears, ear canal, density of the head, size and shape of nasal and oral cavities, all transform the sound and affect how it is perceived, boosting some frequencies and attenuating others. Generally speaking, the HRTF boosts frequencies from 2–5 kHz with a primary resonance of +17 dB at 2,700 Hz. But the response curve is more complex than a single bump, affects a broad frequency spectrum, and varies significantly from person to person.

Obscured by Clouds is the seventh studio album by the English progressive rock band Pink Floyd, released on 2 June 1972 by Harvest and Capitol Records. It serves as the soundtrack for the French film La Vallée, by Barbet Schroeder. It was recorded in two sessions in France, while Pink Floyd were in the midst of touring, and produced by the band.
3D audio effects are a group of sound effects that manipulate the sound produced by stereo speakers, surround-sound speakers, speaker-arrays, or headphones. This frequently involves the virtual placement of sound sources anywhere in three-dimensional space, including behind, above or below the listener.
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance.
Virtual acoustic space (VAS), also known as virtual auditory space, is a technique in which sounds presented over headphones appear to originate from any desired direction in space. The illusion of a virtual sound source outside the listener's head is created.

The interaural time difference when concerning humans or animals, is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. It is important in the localization of sounds, as it provides a cue to the direction or angle of the sound source from the head. If a signal arrives at the head from one side, the signal has further to travel to reach the far ear than the near ear. This pathlength difference results in a time difference between the sound's arrivals at the ears, which is detected and aids the process of identifying the direction of sound source.
Binaural fusion or binaural integration is a cognitive process that involves the combination of different auditory information presented binaurally, or to each ear. In humans, this process is essential in understanding speech as one ear may pick up more information about the speech stimuli than the other.

Dreams Less Sweet is the second studio album by English experimental band Psychic TV, released in 1983. It was the last Psychic TV album to feature co-founder Peter "Sleazy" Christopherson.
Computational auditory scene analysis (CASA) is the study of auditory scene analysis by computational means. In essence, CASA systems are "machine listening" systems that aim to separate mixtures of sound sources in the same way that human listeners do. CASA differs from the field of blind signal separation in that it is based on the mechanisms of the human auditory system, and thus uses no more than two microphone recordings of an acoustic environment. It is related to the cocktail party problem.
Ambiophonics is a method in the public domain that employs digital signal processing (DSP) and two loudspeakers directly in front of the listener in order to improve reproduction of stereophonic and 5.1 surround sound for music, movies, and games in home theaters, gaming PCs, workstations, or studio monitoring applications. First implemented using mechanical means in 1986, today a number of hardware and VST plug-in makers offer Ambiophonic DSP. Ambiophonics eliminates crosstalk inherent in the conventional stereo triangle speaker placement, and thereby generates a speaker-binaural soundfield that emulates headphone-binaural sound, and creates for the listener improved perception of reality of recorded auditory scenes. A second speaker pair can be added in back in order to enable 360° surround sound reproduction. Additional surround speakers may be used for hall ambience, including height, if desired.

William M. Hartmann is a noted physicist, psychoacoustician, author, and former president of the Acoustical Society of America. His major contributions in psychoacoustics are in pitch perception, binaural hearing, and sound localization. Working with junior colleagues, he discovered several major pitch effects: the binaural edge pitch, the binaural coherence edge pitch, the pitch shifts of mistuned harmonics, and the harmonic unmasking effect. His textbook, Signals, Sound and Sensation, is widely used in courses on psychoacoustics. He is currently a professor of physics at Michigan State University.
3D sound localization refers to an acoustic technology that is used to locate the source of a sound in a three-dimensional space. The source location is usually determined by the direction of the incoming sound waves and the distance between the source and sensors. It involves the structure arrangement design of the sensors and signal processing techniques.
Perceptual-based 3D sound localization is the application of knowledge of the human auditory system to develop 3D sound localization technology.
3D sound is most commonly defined as the daily human experience of sounds. The sounds arrive to the ears from every direction and varying distances, which contribute to the three-dimensional aural image humans hear. Scientists and engineers who work with 3D sound work to accurately synthesize the complexity of real-world sounds.
Apparent source width (ASW) is the audible impression of a spatially extended sound source. This psychoacoustic impression results from the sound radiation characteristics of the source and the properties of the acoustic space into which it is radiating. Wide source widths are desired by listeners of music because these are associated with the sound of acoustic music, opera, classical music, and historically informed performance. Research concerning ASW comes from the field of room acoustics, architectural acoustics and auralization, as well as musical acoustics, psychoacoustics and systematic musicology.
Binaural unmasking is phenomenon of auditory perception discovered by Ira Hirsh. In binaural unmasking, the brain combines information from the two ears in order to improve signal detection and identification in noise. The phenomenon is most commonly observed when there is a difference between the interaural phase of the signal and the interaural phase of the noise. When such a difference is present there is an improvement in masking threshold compared to a reference situation in which the interaural phases are the same, or when the stimulus has been presented monaurally. Those two cases usually give very similar thresholds. The size of the improvement is known as the "binaural masking level difference" (BMLD), or simply as the "masking level difference".
Transaural Stereo is a technology suite of analog circuits and digital signal processing algorithms related to the field of sound playback for audio communication and entertainment. It is based on the concept of crosstalk cancellation but in some versions can embody other processes such as binaural synthesis and equalization.





