Horizon scanning may refer to:
- Literally horizon scanning performed by technical devices like infrared horizon-scanning
- Horizon scanning, a method from futures studies
Horizon scanning may refer to:
Scan may refer to:
HSC may stand for:

In astronomy, a planisphere is a star chart analog computing instrument in the form of two adjustable disks that rotate on a common pivot. It can be adjusted to display the visible stars for any time and date. It is an instrument to assist in learning how to recognize stars and constellations. The astrolabe, an instrument that has its origins in Hellenistic astronomy, is a predecessor of the modern planisphere. The term planisphere contrasts with armillary sphere, where the celestial sphere is represented by a three-dimensional framework of rings.

New Horizons is an interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), with a team led by S. Alan Stern, the spacecraft was launched in 2006 with the primary mission to perform a flyby study of the Pluto system in 2015, and a secondary mission to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) in the decade to follow, which became a mission to 486958 Arrokoth. It is the fifth space probe to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System.
HS or Hs can stand for:

Scanner Access Now Easy (SANE) is an application programming interface (API) that provides standardized access to any raster image scanner hardware.

The Horizon class is a class of air-defence destroyers in service with the French Navy and the Italian Navy, designated as destroyers using NATO classification. The programme started as the Common New Generation Frigate (CNGF), a multi-national collaboration to produce a new generation of air-defence frigates. In Italy the class is known as the Orizzonte class, which translates to "horizon" in French and English. The UK then joined France and Italy in the Horizon-class frigate programme; however, differing national requirements, workshare arguments and delays led to the UK withdrawing on 26 April 1999 and starting its own national project, the Type 45 destroyer.

The SAMPSON is a multi-function dual-face active electronically scanned array radar produced by BAE Systems Maritime. It is the fire control radar component of the Sea Viper naval air defence system. It was previously designated PAAMS(S) to distinguish it from the PAAMS system on the Franco-Italian Horizon Class.

Horizon is an ongoing and long-running British documentary television series on BBC Two that covers science and philosophy.

A QR code is a type of matrix barcode first designed in 1994 for the automotive industry in Japan. A barcode is a machine-readable optical label that contains information about the item to which it is attached. In practice, QR codes often contain data for a locator, identifier, or tracker that points to a website or application. A QR code uses four standardized encoding modes to store data efficiently; extensions may also be used.
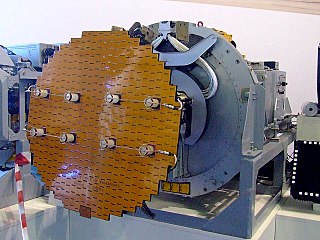
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics.

Microsoft ScanDisk, is a diagnostic utility program included in MS-DOS and Windows 9x. It checks and repairs file systems errors on a disk drive, while the system starts.

Google Books is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition (OCR), and stored in its digital database. Books are provided either by publishers and authors through the Google Books Partner Program, or by Google's library partners through the Library Project. Additionally, Google has partnered with a number of magazine publishers to digitize their archives.
The AN/SPY-3 is an active electronically scanned array radar manufactured by Raytheon and designed for both blue-water and littoral operations.

Bring Me the Horizon are a British rock band formed in Sheffield in 2004. The group consists of lead vocalist Oliver Sykes, guitarist Lee Malia, bassist Matt Kean, drummer Matt Nicholls and keyboardist Jordan Fish. They are signed to RCA Records globally and Columbia Records exclusively in the United States.

The Government Office for Science is part of the British government. This organisation advises the UK Government on policy and decision-making based on robust scientific evidence and long-term thinking. It is led by the Government Chief Scientific Adviser (GCSA), Sir Patrick Vallance who reports to the Prime Minister and Cabinet.

"I'll Go Crazy If I Don't Go Crazy Tonight" is the fifth song from U2's 2009 album No Line on the Horizon. The song was released as the album's third single in a digital format on 25 August 2009 and in a physical version released on 7 September 2009. Two music videos were made, one directed by David O'Reilly, and one by Alex Courtes.

Oliver Scott "Oli" Sykes is an English singer and songwriter, best known as the lead vocalist of the rock band Bring Me the Horizon. He also founded the apparel company Drop Dead Clothing, and created a graphic novel.

Ralph is a science instrument aboard the robotic New Horizons spacecraft, which was launched in 2006. Ralph is a visible and infrared imager and spectrometer to provide maps of relevant astronomical targets based on data from that hardware. Ralph has two major subinstruments, LEISA and MVIC. MVIC stands for Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera and is a color imaging device, while LEISA originally stood for Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array and is an infrared imaging spectrometer for spaceflight. LEISA observes 250 discrete wavelengths of infrared light from 1.25 to 2.5 micrometers. MVIC is a pushbroom scanner type of design with seven channels, including red, blue, near-infrared (NIR), and methane.
Horizon scanning (HS) or also horizon scan is a method from futures studies, sometimes regarded as a part of foresight. It is the early detection and assessment of emerging technologies or threats for mainly policy makers in a domain of choice. Such domains include agriculture, environmental studies, health care, biosecurity, and food safety.