
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction, or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. While reconstructive surgery aims to reconstruct a part of the body or improve its functioning, cosmetic surgery aims to improve the appearance of it. A comprehensive definition of plastic surgery has never been established, because it has no distinct anatomical object and thus overlaps with practically all other surgical specialties. An essential feature of plastic surgery is that it involves the treatment of conditions that require or may require tissue relocation skills.

A scar is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation.
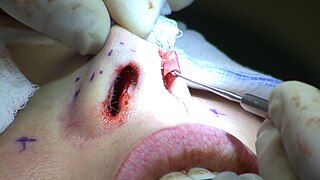
Rhinoplasty, commonly called nose job, medically called nasal reconstruction is a plastic surgery procedure for altering and reconstructing the nose. There are two types of plastic surgery used – reconstructive surgery that restores the form and functions of the nose and cosmetic surgery that changes the appearance of the nose. Reconstructive surgery seeks to resolve nasal injuries caused by various traumas including blunt, and penetrating trauma and trauma caused by blast injury. Reconstructive surgery can also treat birth defects, breathing problems, and failed primary rhinoplasties. Rhinoplasty may remove a bump, narrow nostril width, change the angle between the nose and the mouth, or address injuries, birth defects, or other problems that affect breathing, such as a deviated nasal septum or a sinus condition. Surgery only on the septum is called a septoplasty.

Abdominoplasty or "tummy tuck" is a cosmetic surgery procedure used to make the abdomen thinner and more firm. The surgery involves the removal of excess skin and fat from the middle and lower abdomen in order to tighten the muscle and fascia of the abdominal wall. This type of surgery is usually sought by patients with loose or sagging tissues, that develop after pregnancy or major weight loss.

Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft.
Otoplasty is a procedure for correcting the deformities and defects of the pinna, whether these defects are congenital conditions or caused by trauma. Otoplastic surgeons may reshape, move, or augment the cartilaginous support framework of the pinna to correct these defects.

Blepharoplasty is the plastic surgery operation for correcting defects, deformities, and disfigurations of the eyelids; and for aesthetically modifying the eye region of the face. With the excision and the removal, or the repositioning of excess tissues, such as skin and adipocyte fat, and the reinforcement of the corresponding muscle and tendon tissues, the blepharoplasty procedure resolves functional and cosmetic problems of the periorbita, which is the area from the eyebrow to the upper portion of the cheek. The procedure is more common among women, who accounted for approximately 85% of blepharoplasty procedures in 2014 in the US and 88% of such procedures in the UK.

An umbilical hernia is a health condition where the abdominal wall behind the navel is damaged. It may cause the navel to bulge outwards—the bulge consisting of abdominal fat from the greater omentum or occasionally parts of the small intestine. The bulge can often be pressed back through the hole in the abdominal wall, and may "pop out" when coughing or otherwise acting to increase intra-abdominal pressure. Treatment is surgical, and surgery may be performed for cosmetic as well as health-related reasons.
An incisional hernia is a type of hernia caused by an incompletely-healed surgical wound. Since median incisions in the abdomen are frequent for abdominal exploratory surgery, ventral incisional hernias are often also classified as ventral hernias due to their location. Not all ventral hernias are from incisions, as some may be caused by other trauma or congenital problems.
Mastopexy is the plastic surgery mammoplasty procedure for raising sagging breasts upon the chest of the woman, by changing and modifying the size, contour, and elevation of the breasts. In a breast-lift surgery to re-establish an aesthetically proportionate bust for the woman, the critical corrective consideration is the tissue viability of the nipple-areola complex (NAC), to ensure the functional sensitivity of the breasts for lactation and breast-feeding.

The vertical mattress stitch, often called vertical Donati stitch, is a suture type used to close skin wounds. The advantages of the vertical mattress suture are that it provides closure for both deep and superficial layers, and also allows perfect eversion and vertical opposition of the superficial skin edges. Its disadvantage is a relatively high propensity to dig into skin and cause prominent stitch mark scars.

Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. It is commonly performed by dermatologists. Skin biopsies are also done by family physicians, internists, surgeons, and other specialties. However, performed incorrectly, and without appropriate clinical information, a pathologist's interpretation of a skin biopsy can be severely limited, and therefore doctors and patients may forgo traditional biopsy techniques and instead choose Mohs surgery.

A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated.
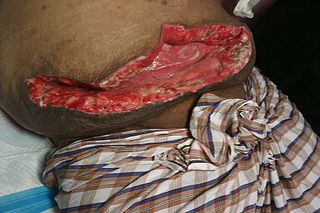
Wound dehiscence is a surgical complication in which a wound ruptures along a surgical incision. Risk factors include age, collagen disorder such as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, diabetes, obesity, poor knotting or grabbing of stitches, and trauma to the wound after surgery.
In medicine, the term cheesewiring or cheesewire effect describes any process in which cells or intercellular matrix are dissected or extruded either by the material being pressed through a taut element, or by the tension of a taut element pulling through tissue. The procedure is typically conducted in a surgical setting.
The corner stitch is a common suture technique. It used to close wounds that are angled or Y-shaped without appreciably compromising blood supply to the wound tip.
The Mustardé technique is an otoplastic surgery (otoplasty) for pinning protruding ears. The method belongs together with the Stenström and Converse methods to the traditional otoplasties. It is antihelix plastic surgery performed with the suturing technique.
The Converse technique, together with the Mustardé technique and Stenström technique, belongs to the standard methods of traditional otoplasty. Numerous variations for pinning ears have been derived from them.

A ladder stitch, or mattress stitch, is a stitch which can be used to invisibly close seams from the outside of the garment or item. It is primarily used to close seams on stuffed items, such as pillows, mattresses, down coats or stuffed toys, where, after the stuffing is added, there is no access to the back of the fabric. It can also be used to repair split seams on these items or garments, or to alter clothing.
June K. Robinson is an American dermatologist, academic and researcher. She is a Research Professor of Dermatology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine.













