
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial form. A monitor usually comprises the display device, circuitry, casing, and power supply. The display device in modern monitors is typically a thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) with LED backlighting having replaced cold-cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL) backlighting. Older monitors used a cathode ray tube (CRT). Monitors are connected to the computer via VGA, Digital Visual Interface (DVI), HDMI, DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) or other proprietary connectors and signals.

A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple electronic equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is 19 inches (48.3 cm) wide. The 19-inch dimension includes the edges, or "ears", that protrude on each side which allow the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws. Common uses include computer server, telecom, broadcast video, lighting, audio, and scientific lab equipment.
HP most commonly refers to:

VMEbus is a computer bus standard, originally developed for the Motorola 68000 line of CPUs, but later widely used for many applications and standardized by the IEC as ANSI/IEEE 1014-1987. It is physically based on Eurocard sizes, mechanicals and connectors, but uses its own signalling system, which Eurocard does not define. It was first developed in 1981 and continues to see widespread use today.

Pixels per inch (ppi) or pixels per centimeter (ppcm) are measurements of the pixel density (resolution) of an electronic image device, such as a computer monitor or television display, or image digitizing device such as a camera or image scanner. Horizontal and vertical density are usually the same, as most devices have square pixels, but differ on devices that have non-square pixels.

A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server needs a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole.
The VXI bus architecture is an open standard platform for automated test based upon VMEbus. VXI stands for VME eXtensions for Instrumentation, defining additional bus lines for timing and triggering as well as mechanical requirements and standard protocols for configuration, message-based communication, multi-chassis extension, and other features. In 2004, the 2eVME extension was added to the VXI bus specification, giving it a maximum data rate of 160 MB/s.

A drive bay is a standard-sized area for adding hardware to a computer. Most drive bays are fixed to the inside of a case, but some can be removed.

A cage nut or caged nut consists of a nut in a spring steel cage which wraps around the nut. The cage has two wings that when compressed allow the cage to be inserted into the square holes, for example, in the mounting rails of equipment racks. When the wings are released, they hold the nut in position behind the hole. Cage nuts conforming to this description were patented in 1952 and 1953. This design requires insertion tools to install the cage nut into the hole. Newer designs featuring a squeeze-and-release tab allow for tool-less installation.

The Acorn Eurocard systems were a series of modular microcomputer systems based on rack-mounted Eurocards developed by Acorn Computers from 1979 to 1982, aimed primarily at industrial and laboratory use, but also home enthusiasts.

Multibus is a computer bus standard used in industrial systems. It was developed by Intel Corporation and was adopted as the IEEE 796 bus.
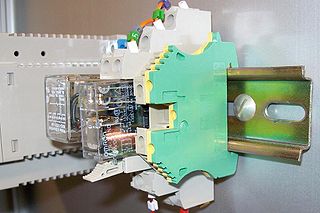
A DIN rail is a metal rail of a standard type widely used for mounting circuit breakers and industrial control equipment inside equipment racks. These products are typically made from cold rolled carbon steel sheet with a zinc-plated or chromated bright surface finish. Although metallic, they are meant only for mechanical support, and are not used as a busbar to conduct electric current, although they may provide a chassis grounding connection.

The STEbus is a non-proprietary, processor-independent, computer bus with 8 data lines and 20 address lines. It was popular for industrial control systems in the late 1980s and early 1990s before the ubiquitous IBM PC dominated this market.
A Rack rail, or rack strip, is used to mount rackable electronic hardware and 19-inch rack mount accessories within a 19-inch rack. Within a rack a minimum of two rack rails are required to mount equipment. The height of rack rail is determined by the number of rack units required for mounting the equipment.

DIN 41612 is a DIN standard for electrical connectors that are widely used in rack based electrical systems. Standardisation of the connectors is a pre-requisite for open systems, where users expect components from different suppliers to operate together. The most widely known use of DIN 41612 connectors is in the VMEbus system. They were also used by NuBus. The standard has subsequently been upgraded to international standards IEC 60603-2 and EN 60603-2.
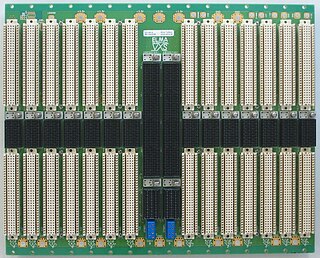
Elma Electronic is a publicly traded Swiss electronics company founded in 1960 and based in Wetzikon, Switzerland. The company has 5 product divisions: Systems Platforms, Backplanes, Enclosures & Components, Rotary Switches, and Cabinet Enclosures. The largest segment is systems packaging solutions serving the military, aerospace, homeland security, medical and industrial markets. The Elma Bustronic division develops backplanes, including VME320, which was the world's fastest VME backplane in 1997. Elma Bustronic also develops backplanes in OpenVPX, VMEbus, VME64X, CompactPCI, MicroTCA, and custom bus structures. Elma is an executive member of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG), VME International Trade Association, and member of the OpenVPX Industry Working Standards Group.
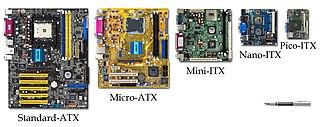
Form factor is an aspect of hardware design which defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in consumer electronics and electronic packaging. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard.















