
Embassy Row is the informal name for a section of Northwest Washington, D.C., with a high concentration of embassies, diplomatic missions, and diplomatic residences. It spans Massachusetts Avenue N.W. between 18th and 35th street, bounded by Scott Circle to the south and the United States Naval Observatory to the north; the term is often applied to nearby streets and neighborhoods that also host diplomatic buildings, such as Kalorama.

Mount Vernon is a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland, located immediately north of the city's downtown. It is named for George Washington's Mount Vernon estate in Virginia, as the site of the city's Washington Monument.

Waddy Butler Wood was an American architect of the early 20th century and resident of Washington, D.C. Although Wood designed and remodeled numerous private residences, his reputation rested primarily on his larger commissions, such as banks, commercial offices, and government buildings. His most notable works include the Woodrow Wilson House and the Main Interior Building.

Albert Irvin Cassell (1895–1969) was a prominent mid-twentieth-century African-American architect in Washington, D.C., whose work shaped many academic communities in the United States. He designed buildings for Howard University in Washington D.C., Morgan State University in Baltimore, and Virginia Union University in Richmond. Cassell also designed and built civic structures for the State of Maryland and the District of Columbia.
Thomas Dixon was a Presbyterian architect born in Wilmington, Delaware and one of the founders of the Baltimore chapter of AIA. He was the father of minister Thomas Freeman Dixon, an 1893 graduate of Princeton Theological Seminary. He partnered with his brother, James M. Dixon, from 1851 until James's death in 1863. In 1871, he partnered with another well-known Baltimore architect Charles L. Carson for some time doing business from their offices at 117 Baltimore Street as Thomas Dixon and Charles L. Carson until sometime before 1877 when the partnership was dissolved. In 1827, he was elected Honorary Academician at the National Academy of Design.

Edward Livingston Palmer Jr. was an American architect from Baltimore, Maryland, credited with the design and development of several planned neighborhoods such as Homeland, Roland Park, Guilford, Wawaset Park, and the design of many buildings within Dundalk, Maryland, which were created specifically for the workers of Bethlehem Steel

The Sixteenth Street Historic District is a 1.25-mile (2.01 km) linear historic district in Washington, D.C., that includes all structures along 16th Street NW between H Street and Florida Avenue. The district's southern boundary is bordered by Lafayette Square, just north of the White House, and Meridian Hill Park on its northern boundary. It includes an eclectic mix of architectural styles on one of the city's most historic and important numbered streets including single and multi-family residential buildings, embassies, hotels, churches, and office buildings.

U.S. Custom House is a historic custom house building located at Baltimore, Maryland, United States. It is a granite, steel-frame structure measuring 252 feet 8 inches (77.01 m) by 139 feet 6 inches (42.52 m). It is an exceptionally distinguished example of Beaux Arts architecture and was built from 1903 through late 1907 from plans by Hornblower and Marshall, a Washington, D.C. firm. The ceiling of the Call Room, located in the pavilion, was painted by Francis Davis Millet (1846–1912). It served as Baltimore's Custom House until 1953. Since that time various Federal agencies have occupied the building.
J. Harleston Parker was an American architect active in Boston, Massachusetts.
Charles L. Carson, was an architect born in Baltimore, the oldest son of Daniel Carson, a builder, and one of the founders of the Baltimore chapter of AIA. Carson had little formal training as an architect. Around 1870 he partnered with Thomas Dixon (architect) while taking drawing lessons at the Maryland Institute College of Art. Carson and Dixon worked from their offices at 117 Baltimore Street as Thomas Dixon and Charles L. Carson until sometime before 1877 when the partnership was dissolved. In 1888 he hired Joseph Evans Sperry who became his chief assistant, and later his partner and successor.

Charles L. Thompson and associates is an architectural group that was established in Arkansas since the late 1800s. It is now known as Cromwell Architects Engineers, Inc.. This article is about Thompson and associates' work as part of one architectural group, and its predecessor and descendant firms, including under names Charles L. Thompson,Thompson & Harding,Sanders & Ginocchio, and Thompson, Sanders and Ginocchio.

Major General George B. McClellan is an equestrian statue in Washington, D.C. that honors politician and Civil War general George B. McClellan. The monument is sited on a prominent location in the Kalorama Triangle neighborhood due to efforts made by area residents. The statue was sculpted by American artist Frederick William MacMonnies, a graduate of the École des Beaux-Arts whose best known work is a statue of Nathan Hale in New York City. MacMonnies was chosen to design the statue following a lengthy competition organized by a statue commission, led by then Secretary of War William Howard Taft. The monument was dedicated in 1907, with prominent attendees at the ceremony including President Theodore Roosevelt, New York City mayor George B. McClellan Jr., politicians, generals and thousands of military personnel.

Theodore Wells Pietsch was a well-known American architect, best remembered for a large body of work in and around Baltimore, Maryland. Among his best-known buildings are Recreation Pier at Fell’s Point at 1715 Thames Street, and the SS. Philip and James Catholic Church at 2801 North Charles Street, Baltimore.
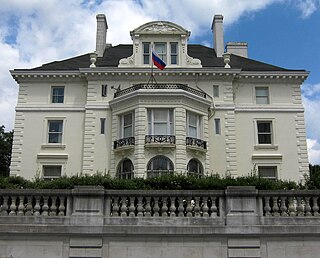
The Lothrop Mansion, also known as the Alvin Mason Lothrop House, is an historic home, located at 2001 Connecticut Avenue, Northwest, Washington, D.C., in the Kalorama Triangle neighborhood.

The Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station, also known as Pennsylvania Railroad Station, was a railroad station that was owned by the Pennsylvania Railroad and operated by the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad in Washington, D.C., from July 2, 1872 until its closure in 1907. It was located at the southern corner of 6th street NW and B Street NW, now the site of the West Building of the National Gallery of Art. It was in this train station that United States President James A. Garfield was shot by assassin Charles J. Guiteau on July 2, 1881.

George S. Cooper was an American architect and builder from Washington, D.C. During his 40-year career, he was responsible for designing around 850 properties, including homes, commercial buildings and apartment buildings, several of which are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). The 1903 book History of the City of Washington states: "It may be thought that Mr. Cooper's forte lies in the designing of apartment houses, since the handsomest in the city are a result of his genius..." and "No young man has played a more important part in the active growth and great development of Greater Washington than George S. Cooper..."

Appleton Prentiss Clark Jr. was an American architect from Washington, D.C. During his 60-year career, Clark was responsible for designing hundreds of buildings in the Washington area, including homes, hotels, churches, apartments and commercial properties. He is considered one of the city's most prominent and influential architects from the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Many of his designs are now listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP).

Albert L. Harris was an American architect who worked primarily in Washington, D.C. He was born in Wales and emigrated to the United States as a young child. He worked for architectural firms in Chicago and Baltimore and then Washington, where he also obtained an architectural degree from George Washington University. He was a part-time professor there while also working for the US Navy and then the city of Washington where he served as the city's Municipal Architect from 1921 until his death in 1933. A number of his works are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP).

The Beezer Brothers were American architects active from the late 19th-century to the Great Depression. They were twins, who practiced together in western Pennsylvania before moving to Seattle, Washington in 1907 to participate in the city's rapid growth brought on by the Klondike Gold Rush. Best known for the many Catholic churches they designed, they also worked on domestic residences and municipal buildings. Their work on the west coast, while concentrated in Seattle, can be found from Los Angeles to San Francisco to Alaska, and inland to Montana. At least one church and two buildings are individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places, and several other buildings are contributing properties to several different National Historic Districts.

Waldron Faulkner was an American architect in practice in New York City and Washington, D.C. from 1927 to until his retirement 1968. Faulkner was a sole practitioner until 1939, when he formed a partnership with Slocum Kingsbury, his long-time collaborator. Later partners of the firm included Faulkner's son, Avery C. Faulkner, who sold the firm to CannonDesign in 1982.




















