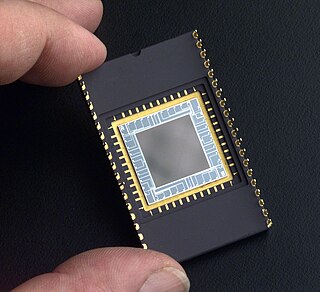
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.

Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data. This is in contrast to analog video, which represents moving visual images in the form of analog signals. Digital video comprises a series of digital images displayed in rapid succession, usually at 24, 30, or 60 frames per second. Digital video has many advantages such as easy copying, multicasting, sharing and storage.

In digital imaging, a pixel, pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software.

A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs.

XMM-Newton, also known as the High Throughput X-ray Spectroscopy Mission and the X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission, is an X-ray space observatory launched by the European Space Agency in December 1999 on an Ariane 5 rocket. It is the second cornerstone mission of ESA's Horizon 2000 programme. Named after physicist and astronomer Sir Isaac Newton, the spacecraft is tasked with investigating interstellar X-ray sources, performing narrow- and broad-range spectroscopy, and performing the first simultaneous imaging of objects in both X-ray and optical wavelengths.

Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals become easily visible against the environment, day or night. As a result, thermography is particularly useful to the military and other users of surveillance cameras.

A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos, as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film. Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other purposes.
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as pixels, each with finite, discrete quantities of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions fed as input by its spatial coordinates denoted with x, y on the x-axis and y-axis, respectively. Depending on whether the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type. By itself, the term "digital image" usually refers to raster images or bitmapped images.

The Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) is a scientific instrument for infrared astronomy, installed on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), operating from 1997 to 1999, and from 2002 to 2008. Images produced by NICMOS contain data from the near-infrared part of the light spectrum.

The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) is a third-generation axial instrument aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The initial design and scientific capabilities of ACS were defined by a team based at Johns Hopkins University. ACS was assembled and tested extensively at Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. and the Goddard Space Flight Center and underwent a final flight-ready verification at the Kennedy Space Center before integration in the cargo bay of the Columbia orbiter. It was launched on March 1, 2002, as part of Servicing Mission 3B (STS-109) and installed in HST on March 7, replacing the Faint Object Camera (FOC), the last original instrument. ACS cost US$86 million at that time.

The Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) is a camera formerly installed on the Hubble Space Telescope. The camera was built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and is roughly the size of a baby grand piano. It was installed by servicing mission 1 (STS-61) in 1993, replacing the telescope's original Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WF/PC). WFPC2 was used to image the Hubble Deep Field in 1995, the Engraved Hourglass Nebula and Egg Nebula in 1996, and the Hubble Deep Field South in 1998. During STS-125, WFPC2 was removed and replaced with the Wide Field Camera 3 as part of the mission's first spacewalk on May 14, 2009. After returning to Earth, the camera was displayed briefly at the National Air and Space Museum and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory before returning to its final home at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum.

The Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WFPC) was a camera installed on the Hubble Space Telescope launched in April 1990 and operated until December 1993. It was one of the instruments on Hubble at launch, but its functionality was severely impaired by the defects of the main mirror optics which afflicted the telescope. However, it produced uniquely valuable high resolution images of relatively bright astronomical objects, allowing for a number of discoveries to be made by HST even in its aberrated condition.

A three-CCD (3CCD) camera is a camera whose imaging system uses three separate charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each one receiving filtered red, green, or blue color ranges. Light coming in from the lens is split by a beam-splitter prism into three beams, which are then filtered to produce colored light in three color ranges or "bands". The system is employed by high quality still cameras, telecine systems, professional video cameras and some prosumer video cameras.

An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging.

An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are used as amplifiers. There are different types of APS, including the early NMOS APS and the now much more common complementary MOS (CMOS) APS, also known as the CMOS sensor. CMOS sensors are used in digital camera technologies such as cell phone cameras, web cameras, most modern digital pocket cameras, most digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs), and lensless imaging for cells.

Sony Corporation produces professional, consumer, and prosumer camcorders such as studio and broadcast, digital cinema cameras, camcorders, pan-tilt-zoom and remote cameras.

In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor.

The Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) is the Hubble Space Telescope's last and most technologically advanced instrument to take images in the visible spectrum. It was installed as a replacement for the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 during the first spacewalk of Space Shuttle mission STS-125 on May 14, 2009.

A laser beam profiler captures, displays, and records the spatial intensity profile of a laser beam at a particular plane transverse to the beam propagation path. Since there are many types of lasers—ultraviolet, visible, infrared, continuous wave, pulsed, high-power, low-power—there is an assortment of instrumentation for measuring laser beam profiles. No single laser beam profiler can handle every power level, pulse duration, repetition rate, wavelength, and beam size.
HAD CCD is the name of a technology Sony implemented on some of their CCD image sensors. There are at least six models of HAD CCD sensors.

















