
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation, as HVAC&R or HVACR or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

A heat pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a source of heat to what is called a thermal reservoir. Heat pumps move thermal energy in the opposite direction of spontaneous heat transfer, by absorbing heat from a cold space and releasing it to a warmer one. A heat pump uses external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink. The most common design of a heat pump involves four main components – a condenser, an expansion valve, an evaporator and a compressor. The heat transfer medium circulated through these components is called refrigerant.

The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by the German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system.

Solar water heating (SWH) is the conversion of sunlight into heat for water heating using a solar thermal collector. A variety of configurations is available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for residential and some industrial applications.
The coefficient of performance or COP of a heat pump, refrigerator or air conditioning system is a ratio of useful heating or cooling provided to work required. Higher COPs equate to lower operating costs. The COP usually exceeds 1, especially in heat pumps, because, instead of just converting work to heat, it pumps additional heat from a heat source to where the heat is required. For complete systems, COP calculations should include energy consumption of all power consuming auxiliaries. COP is highly dependent on operating conditions, especially absolute temperature and relative temperature between sink and system, and is often graphed or averaged against expected conditions. Performance of Absorption refrigerator chillers is typically much lower, as they are not heat pumps relying on compression, but instead rely on chemical reactions driven by heat.

An oceanic climate, also known as a maritime climate, marine climate, marine west coast climate or temperate oceanic climate, is the Köppen classification of climate typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, and generally features cool summers and cool but not cold winters, with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates are defined as having a monthly mean temperature below 22 °C (72 °F) in the warmest month, and above 0 °C (32 °F). This climate type is often caused by the onshore flow from the cool, high latitude oceans that are found west of their location.
An evaporative cooler is a device that cools air through the evaporation of water. Evaporative cooling differs from typical air conditioning systems, which use vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycles. Evaporative cooling uses the fact that water will absorb a relatively large amount of heat in order to evaporate. The temperature of dry air can be dropped significantly through the phase transition of liquid water to water vapor (evaporation). This can cool air using much less energy than refrigeration. In extremely dry climates, evaporative cooling of air has the added benefit of conditioning the air with more moisture for the comfort of building occupants.

A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot summers and cold winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year. The definition of this climate regarding temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below −3 °C (26.6 °F) and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above 10 °C (50 °F). In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The Dfb, Dwb and Dsb subtypes are also known as hemiboreal.
The efficiency of air conditioners is often rated by the seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) which is defined by the Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute in its 2008 standard AHRI 210/240, Performance Rating of Unitary Air-Conditioning and Air-Source Heat Pump Equipment. A similar standard is the European seasonal energy efficiency ratio (ESEER).

Reflective surfaces can deliver high solar reflectance and high thermal emittance. Reflective surfaces are a form of geoengineering.
Renewable heat is an application of renewable energy and it refers to the renewable generation of heat, rather than electrical power. Renewable heat technologies include renewable biofuels, solar heating, geothermal heating, heat pumps and heat exchangers to recover lost heat. Significant attention is also applied to insulation.
Solar air conditioning refers to any air conditioning (cooling) system that uses solar power.
An air source heat pump (ASHP) is a system that transfers heat from outside to inside a building, or vice versa. Under the principles of vapor compression refrigeration, an ASHP uses a refrigerant system involving a compressor and a condenser to absorb heat at one place and release it at another. They can be used as a space heater or cooler, and are sometimes called "reverse-cycle air conditioners".

Building insulation is any object in a building used as insulation for any purpose. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation. Often an insulation material will be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once.

A geothermal heat pump (GHP) or ground source heat pump (GSHP) is a central heating and/or cooling system that transfers heat to or from the ground.

Air conditioning is the process of removing heat and moisture from the interior of an occupied space to improve the comfort of occupants. Air conditioning can be used in both domestic and commercial environments. This process is most commonly used to achieve a more comfortable interior environment, typically for humans and other animals; however, air conditioning is also used to cool and dehumidify rooms filled with heat-producing electronic devices, such as computer servers, power amplifiers, and to display and store some delicate products, such as artwork.
Thermal comfort is the condition of mind that expresses satisfaction with the thermal environment and is assessed by subjective evaluation. The human body can be viewed as a heat engine where food is the input energy. The human body will release excess heat into the environment, so the body can continue to operate. The heat transfer is proportional to temperature difference. In cold environments, the body loses more heat to the environment and in hot environments the body does not release enough heat. Both the hot and cold scenarios lead to discomfort. Maintaining this standard of thermal comfort for occupants of buildings or other enclosures is one of the important goals of HVAC design engineers.
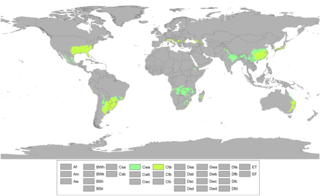
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cold to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 35° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates.

The United States is the second-largest single consumer of energy in the world. The U.S. Department of Energy categorizes national energy use in four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial, and industrial.
The climate in Spain varies across continental Spain. Spain is the most climatically diverse country in Europe with 13 different Köppen climates, excluding the Canary Islands, and is within the 10 most climatically diverse countries in the world. Five main climatic zones can be distinguished, according to the country's Köppen-Geiger climate classification and orographic conditions:
1.Design Standard for Energy Efficiency of Residential Buildings in Hot Summer and Cold Winter Zone JCJ 134—2001











