Organisations
- Cape Corps, formerly Hottentot Corps, a South African army unit
- Terre Haute Hottentots, a baseball team
Hottentot may refer to:
The Khoisan languages are a number of African languages once classified together, originally by Joseph Greenberg. Khoisan is defined as those languages that have click consonants and do not belong to other African language families. For much of the 20th century, they were thought to be genealogically related to each other, but this is no longer accepted. They are now held to comprise three distinct language families and two language isolates.

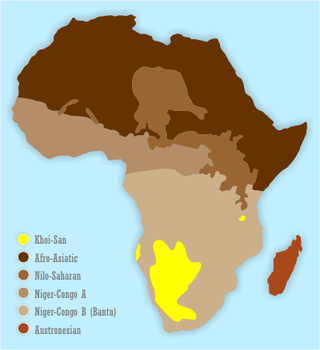
KhoisanKOY-sahn, or Khoe-Sān, is a catch-all term for the indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who traditionally speak non-Bantu languages, combining the Khoekhoen and the Sān peoples. Khoisan populations traditionally speak click languages and are considered to be the historical communities throughout Southern Africa, remaining predominant until European colonisation in areas climatically unfavorable to Bantu (sorghum-based) agriculture, such as the Cape region, through to Namibia, where Khoekhoe populations of Nama and Damara people are prevalent groups, and Botswana. Considerable mingling with Bantu-speaking groups is evidenced by prevalence of click phonemes in many especially Xhosa Southern African Bantu languages.

Khoekhoe are the traditionally nomadic pastoralist indigenous population of South Africa. They are often grouped with the hunter-gatherer San peoples. The designation "Khoekhoe" is actually a kare or praise address, not an ethnic endonym, but it has been used in the literature as an ethnic term for Khoe-speaking peoples of Southern Africa, particularly pastoralist groups, such as the !Ora, !Gona, Nama, Xiri and ǂNūkhoe nations. The Khokhoe were once known as Hottentots, a term now considered offensive.

Hottentot is a term that was historically used by Europeans to refer to the Khoekhoe, the indigenous nomadic pastoralists in South Africa.

Sarah Baartman, also spelled Sara, sometimes in the diminutive form Saartje, or Saartjie, and Bartman, Bartmann, was a Khoikhoi woman who was exhibited as a freak show attraction in 19th-century Europe under the name Hottentot Venus, a name that was later attributed to at least one other woman similarly exhibited. The women were exhibited for their steatopygic body type uncommon in Western Europe that not only was perceived as a curiosity at that time, but became subject of scientific interest as well as of erotic projection.

The San peoples, or Bushmen, are the members of any of the indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures of southern Africa, and the oldest surviving cultures of the region. Their recent ancestral territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, and South Africa.
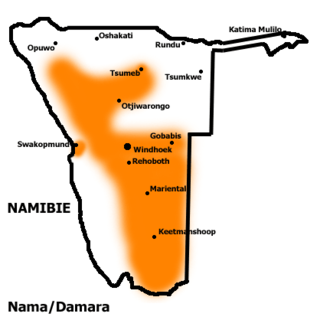
Khoekhoe, also known by the ethnic terms Nama, Damara (ǂNūkhoegowab), or Nama/Damara and formerly as Hottentot, is the most widespread of the non-Bantu languages of Southern Africa that make heavy use of click consonants and therefore were formerly classified as Khoisan, a grouping now recognized as obsolete. It belongs to the Khoe language family, and is spoken in Namibia, Botswana, and South Africa primarily by three ethnic groups: Namakhoen, ǂNūkhoen, and Haiǁomkhoen.

The Griquas are a subgroup of mixed-race heterogeneous formerly Xiri-speaking nations in South Africa with a unique origin in the early history of the Dutch Cape Colony. Like the Boers they migrated inland from the Cape and in the 19th century established several states in what is now South Africa and Namibia. The Griqua consider themselves as being South Africa’s first multiracial nation with people descended directly from Dutch settlers in the Cape, and local peoples.
ǃOrakobab or Khoemana, also known as Korana, ǃOra, or Griqua, is a moribund Khoe language of South Africa.

Namaqualand is an arid region of Namibia and South Africa, extending along the west coast over 1,000 km (600 mi) and covering a total area of 440,000 km2 (170,000 sq mi). It is divided by the lower course of the Orange River into two portions – Little Namaqualand to the south and Great Namaqualand to the north.

Nama are an African ethnic group of South Africa, Namibia and Botswana. They traditionally speak the Nama language of the Khoe-Kwadi language family, although many Nama also speak Afrikaans. The Nama People are the largest group of the Khoikhoi people, most of whom have disappeared as a group, except for the Namas. Many of the Nama clans live in Central Namibia and the other smaller groups live in Namaqualand, which today straddles the Namibian border with South Africa.

The Tuu languages, or Taa–ǃKwilanguages, are a language family consisting of two language clusters spoken in Botswana and South Africa. The relationship between the two clusters is not doubted, but is distant. The name Tuu comes from a word common to both branches of the family for "person".
The Khoe languages are the largest of the non-Bantu language families indigenous to Southern Africa. They were once considered to be a branch of a Khoisan language family, and were known as Central Khoisan in that scenario. Though Khoisan is now rejected as a family, the name is retained as a term of convenience.

Elongated labia is a feature of certain Khoikhoi and other African women who develop, whether naturally or through artificial stretching, relatively elongated labia minora, which may hang up to four inches outside the rest of the vulva when they are standing in an upright position.

The Oorlam or Orlam people are a subtribe of the Nama people, largely assimilated after their migration from the Cape Colony to Namaqualand and Damaraland.

The Khoikhoi–Dutch Wars were a series of conflicts that took place in the latter half of the 17th century in what was known then as the Cape of Good Hope, in the area of present-day Cape Town, South Africa, between Dutch colonisers who came from the Netherlands and the local African people, the indigenous Khoikhoi.
The Prehistory of South Africa lasts from the Middle Stone Age until the 17th century. Southern Africa was first reached by Homo sapiens before 130,000 years ago, possibly before 260,000 years ago. The region remained in the Late Stone Age until the first traces of pastoralism were introduced about 2,000 years ago. The Bantu migration reached the area now South Africa around the first decade of the 3rd century, over 1800 years ago. Early Bantu kingdoms were established in the 11th century. First European contact dates to 1488, but European colonization began in the 17th century.

The Nguni people are a linguistic cultural group of Bantu cattle herders who migrated from central Africa into Southern Africa, made up of ethnic groups formed from hunter-gatherer pygmy and proto-agrarians, with offshoots in neighboring colonially-created countries in Southern Africa. Swazi people live in both South Africa and Eswatini, while Ndebele people live in both South Africa and Zimbabwe.

Samuel Daniell was a British painter of natural history and other scenes in Africa and Ceylon. He first went to Cape Colony in 1799.
Hans Christian Knudsen was a Norwegian missionary and painter. He was a pioneer Rhenish Missionary pioneer and scholar of Khoekhoe.