
Rhineland-Palatinate is a western state of Germany. It covers 19,846 km2 (7,663 sq mi) and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Koblenz, Trier, Kaiserslautern, Worms, and Neuwied. It is bordered by North Rhine-Westphalia, Saarland, Baden-Württemberg and Hesse and by France, Luxembourg and Belgium.

The Palatinate, or the Rhenish Palatinate (Rheinpfalz), is a historical region of Germany. The Palatinate occupies most of the southern quarter of the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate (Rheinland-Pfalz), covering an area of 2,105 square miles (5,450 km2) with about 1.4 million inhabitants. Its residents are known as Palatines (Pfälzer).
A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface in contact with a thermal mass of air. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space.
Alzey-Worms is a district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is bounded by the district Groß-Gerau (Hesse), the city of Worms and the districts of Bad Dürkheim, Donnersbergkreis, Bad Kreuznach and Mainz-Bingen.
Kaiserslautern is a district (Kreis) in the south of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Neighboring districts are Kusel, Saarpfalz-Kreis, Donnersbergkreis, Bad Dürkheim and Südwestpfalz. The city of Kaiserslautern is almost fully enclosed by, but not belonging to the district.
Südwestpfalz is a district in the south of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Neighboring districts are Saarpfalz, the district-free city Zweibrücken, the districts Kaiserslautern and Bad Dürkheim, the district-free city Landau, Südliche Weinstraße, and the French département Bas-Rhin. The district-free city Pirmasens is surrounded by the district.

Green building refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. This requires close cooperation of the contractor, the architects, the engineers, and the client at all project stages. The Green Building practice expands and complements the classical building design concerns of economy, utility, durability, and comfort. Green building also refers to saving resources to the maximum extent, including energy saving, land saving, water saving, material saving, etc., during the whole life cycle of the building, protecting the environment and reducing pollution, providing people with healthy, comfortable and efficient use of space, and being in harmony with nature. Buildings that live in harmony; green building technology focuses on low consumption, high efficiency, economy, environmental protection, integration and optimization.’

The Environmental Campus Birkenfeld (ECB) is a branch of the Hochschule Trier in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is close to the small town of Birkenfeld in Rhineland-Palatinate, close to the border of Saarland, Luxembourg, Belgium and France. There are 1,800 students enrolled in two departments. There are a total of 59 professors teaching in both departments.
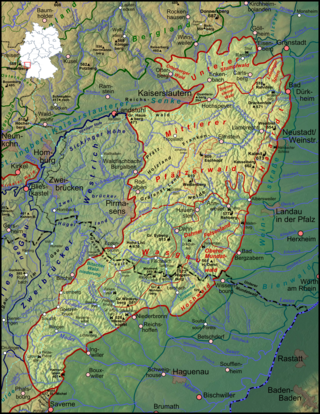
The Palatinate Forest, sometimes also called the Palatine Forest, is a low-mountain region in southwestern Germany, located in the Palatinate in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate. The forest is a designated nature park covering 1,771 km2 and its highest elevation is the Kalmit.
Renewable heat is an application of renewable energy referring to the generation of heat from renewable sources; for example, feeding radiators with water warmed by focused solar radiation rather than by a fossil fuel boiler. Renewable heat technologies include renewable biofuels, solar heating, geothermal heating, heat pumps and heat exchangers. Insulation is almost always an important factor in how renewable heating is implemented.

Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods.
The Trier University of Applied Sciences is one of the largest Universities of Applied Sciences in Rhineland-Palatinate with approximately 6000 students, around 170 professors and around 700 academic and nonacademic staff. It is spread over three campuses in Trier, Birkenfeld, and Idar-Oberstein. It is a member of the European University Association (EUA).

Biomass heating systems generate heat from biomass. The systems may use direct combustion, gasification, combined heat and power (CHP), anaerobic digestion or aerobic digestion to produce heat. Biomass heating may be fully automated or semi-automated they may be pellet-fired, or they may be combined heat and power systems.

Bärenbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Kirchberg, whose seat is in the like-named town.

A green home is a type of house designed to be environmentally sustainable. Green homes focus on the efficient use of "energy, water, and building materials". A green home may use sustainably sourced, environmentally friendly, and/or recycled building materials. This includes materials like reclaimed wood, recycled metal, and low VOC paints. Additionally, green homes often prioritize energy efficiency by incorporating features, such as high-performance insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and smart home technologies that monitor and optimize energy usage. Water conservation is another important aspect, with green homes often featuring water-saving fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and grey water recycling systems to reduce water waste. It may include sustainable energy sources such as solar or geothermal, and be sited to take maximum advantage of natural features such as sunlight and tree cover to improve energy efficiency.

The Franco-German Palatinate Forest-North Vosges Biosphere Reserve was created in 1998 as the first UNESCO trans-boundary biosphere reserve in Europe. The German part became the 12th of 16 biosphere reserves in Germany, and the French part, the 6th of 14 in France.

The Biosphere House in the village of Fischbach bei Dahn in the German state of Rhineland-Pfalz is a nature experience centre and important regional tourist attraction.

Trippstadt House is an 18th-century, baroque schloss or manor house in the eponymous village in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate.

The Saar-Hunsrück Nature Park was established in 1980 and covers an area of just under 2,000 km² in the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and the Saarland.
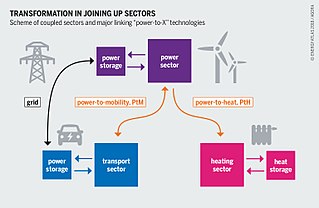
Power-to-X are electricity conversion, energy storage, and reconversion pathways from surplus renewable energy. Power-to-X conversion technologies allow for the decoupling of power from the electricity sector for use in other sectors, possibly using power that has been provided by additional investments in generation. The term is widely used in Germany and may have originated there.














