
Board games are tabletop games that typically use pieces - moved or placed on a pre-marked board and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well.

Sternhalma, commonly known as Chinese checkers or Chinese chequers, is a strategy board game of German origin that can be played by two, three, four, or six people, playing individually or with partners. The game is a modern and simplified variation of the game Halma.

Alquerque is a strategy board game that is thought to have originated in the Middle East. It is considered to be the parent of draughts and Fanorona.

Checkers, also known as draughts, is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Checkers is developed from alquerque. The term "checkers" derives from the checkered board which the game is played on, whereas "draughts" derives from the verb "to draw" or "to move".

Christian Freeling is a Dutch game designer and inventor of abstract strategy games, notably Dameo, Grand Chess, Havannah, and Hexdame.

English draughts or American checkers, also called straight checkers, or simply draughts or checkers, is a form of the strategy board game checkers. It is played on an 8×8 checkerboard with 12 pieces per side. The pieces move and capture diagonally forward, until they reach the opposite end of the board, when they are crowned and can thereafter move and capture both backward and forward.

Lasca is a draughts variant, invented by the second World Chess Champion Emanuel Lasker (1868–1941). Lasca is derived from English draughts and the Russian draughts game bashni (Towers).

Agon is a strategy game invented by Anthony Peacock of London, and first published in 1842. It is a two-player game played on a 6×6×6 hexagonal gameboard, and is notable for being the oldest known board game played on a board of hexagonal cells.

Turkish draughts is a variant of draughts (checkers) played in Turkey, Greece, Egypt, Kuwait, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and several other locations around the Mediterranean Sea and Middle East.

Russian draughts is a variant of draughts (checkers) played in Russia and some parts of the former USSR, as well as parts of Eastern Europe and Israel.

Armenian draughts, or Tama, is a variant of draughts played in Armenia. The rules are similar to Dama. Armenian draughts, however, allows for diagonal movement.

Emergo is an abstract strategy game created by Christian Freeling and Ed van Zon in 1986. It belongs to the "stacking" category of games, or column checkers, along with Bashni and Lasca. The name comes from the motto of the Dutch province of Zeeland: Luctor et emergo meaning: "I wrestle and emerge". The goal of the game is to capture all of the opponents pieces similar to checkers/draughts. Emergo, and all column checkers, differ from most draughts variants because of their unique method of capture. A opponent's piece is added to the capturing player's column rather than being removed. Men can be recaptured from an opponent later on in the game.
Czech draughts is a board game played in the territory formerly occupied by Czechoslovakia. It is governed by the Czech Draughts Federation.

Italian draughts is a variant of the draughts family played mainly in Italy and Northern Africa. It is a two-handed game played on a board consisting of sixty-four squares, thirty-two white and thirty-two black. There are twenty-four pieces: twelve white and twelve black. The board is placed so that the rightmost square on both sides of the board is black.
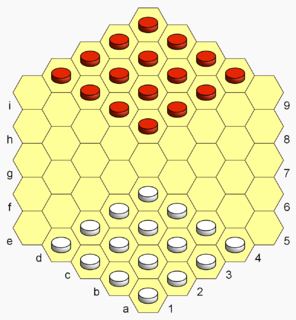
Hexdame is a strategy board game for two players invented by Christian Freeling in 1979. The game is a literal adaptation of the game international draughts to a hexagonal gameboard.

Dameo is an abstract strategy board game for two players invented by Christian Freeling in 2000. It is a variant of the game draughts and is played on an 8×8 checkered gameboard.

Canadian checkers is a variant of the strategy board game draughts. It is one of the largest draughts games, played on a 12×12 checkered board with 30 game pieces per player.
This page explains commonly used terms in board games in alphabetical order. For a list of board games, see List of board games. For terms specific to chess, see Glossary of chess. For terms related to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems.

Poddavki, also known as Giveaway checkers, Suicide checkers, Anti-checkers or Losing draughts is a draughts (checkers) game based on the rules of Russian draughts, with the variation that a player wins if they have no legal moves on their turn, either by giving up all their pieces or having them all blocked. As in most varieties of draughts, capturing is mandatory. The game is played in Russia and some parts of the former Soviet Union.

Bashni, also known as column draughts, multi-level checkers, and rarer Chinese checkers, is a variation of draughts, known in Russia since the 19th century. The game is played according to the basic rules of Russian draughts, with the main difference being that draughts being jumped over are not removed from the playing field but are instead placed under the jumping piece . The resulting towers move across the board as one piece, obeying the status of the upper draught. When a tower is jumped over, only the upper draught is removed from it. If, as a result of the combat, the top draught changes colour, ownership of the tower passes on to the opposing player. Based on Bashni, but according to the basic rules of English draughts, world chess champion Emanuel Lasker developed the draughts game "Laska" and, in 1911, published its description. Lasker described towers that can only be "double-layered": i.e. there can be no alternation of colors. He also showed that during the game the number of game pieces either remains constant or decreases. Column draughts are a subject of interest for the mathematical Sciences: combinatorics, theory of paired zero-sum games, etc.














