Related Research Articles
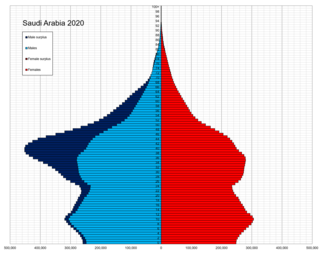
Saudi Arabia is the fourth largest state in the Arab world, with a reported population of 32,175,224 as of 2022. 41.6% of inhabitants are immigrants. Saudi Arabia has experienced a population explosion in the last 40 years, and continues to grow at a rate of 1.62% per year.

The economy of Saudi Arabia is the largest in the Middle East and the eighteenth largest in the world. A permanent and founding member of OPEC, Saudi Arabia is also a member of the G20 forum as one of the world's largest economies.

The United Arab Emirates, or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East. It is located at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula and shares borders with Oman and Saudi Arabia, while having maritime borders in the Persian Gulf with Qatar and Iran. Abu Dhabi is the nation's capital, while Dubai, the most populated city, is an international hub.

The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council, is a regional, intergovernmental, political, and economic union comprising Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The council's main headquarters is located in Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia. The Charter of the GCC was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution.

Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about 2,150,000 km2 (830,000 sq mi), making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Arab world, and the largest in West Asia and the Middle East. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to the south. Bahrain is an island country off its east coast. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt and Israel. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of its terrain consists of arid desert, lowland, steppe, and mountains. Its capital and largest city is Riyadh. The country is home to Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam.

Public education—from primary education through college—is open to every Saudi citizen. The second largest governmental spending in Saudi Arabia goes for education. Saudi Arabia spends 8.8% of its gross domestic product on education, which is nearly double the global average of 4.6%. Islamic studies are part of the education system alongside scientific and social studies that vary from educational institution to another.

Saudization, officially the Saudi nationalization scheme and also known as Nitaqat, is a policy that is implemented in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia by the Ministry of Labor and Social Development, which requires companies and enterprises to fill their workforce with Saudi nationals up to certain levels.
Multiple forms of media including books, newspapers, magazines, films, television, and content published on the Internet are censored in Saudi Arabia.

Energy in Saudi Arabia involves petroleum and natural gas production, consumption, and exports, and electricity production. Saudi Arabia is the world's leading oil producer and exporter. Saudi Arabia's economy is petroleum-based; oil accounts for 90% of the country's exports and nearly 75% of government revenue. The oil industry produces about 45% of Saudi Arabia's gross domestic product, against 40% from the private sector. Saudi Arabia has per capita GDP of $20,700. The economy is still very dependent on oil despite diversification, in particular in the petrochemical sector.
This article covers the best practices and needs for reform in entrepreneurship policies in Saudi Arabia.

Arab News is an English-language daily newspaper published in Saudi Arabia. It is published from Riyadh. The target audiences of the paper, which is published in broadsheet format, are businessmen, executives and diplomats.
The e-Government in Saudi Arabia was established as per Royal Decree No. 7/B/33181 dated 7 September 2003. The e-Government was created by the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology. In 2005, the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology created the e-Government Program Yesser with the ministry of finance and the Communications and Information Technology Commission. The portal offers around 2500 services for people of Saudi Arabia. The main goal of the service is to facilitate the transactions of citizens, residents and visitors by providing a quick and sufficient assistance. Moreover, Yesser contributes to encouraging governmental agencies in achieving a sustainable progress by improving efficiency and capacity.

Adel Fakeih is a Saudi Arabian engineer and the former mayor of Jeddah. He was the minister of labor from August 2010 to April 2015, minister of health between April 2014 and December 2014, and minister of economy and planning between 2015 and 2017. He has been in detention since November 2017.

The Ministry of Health, commonly abbreviated to MoH, is the ministry overseeing the health care and health policy of Saudi Arabia. The ministry is tasked with formulating strategies to ensure public health in the country, while also managing crucial health infrastructure.
Television in Saudi Arabia was introduced in 1965, but is now dominated by just five major companies: Middle East Broadcasting Center, SM Enterprise TV, Lebanese Broadcasting Corporation, Rotana and Saudi TV. Together, they control 80% of the pan-Arab broadcasting market. Saudi Arabia is a major market for pan-Arab satellite and pay-TV. Saudi investors are behind the major networks MBC, which is based in Dubai, and Emirates based OSN. The Saudi government estimated that in 2000 the average Saudi spent 50% to 100% more time watching television than his or her European or US counterpart. On average, 2.7 hours are spent daily watching TV in Saudi Arabia.

Foreign workers in Saudi Arabia, estimated to number about 9 million as of April 2013, began migrating to the country soon after oil was discovered in the late 1930s. Initially, the main influx was composed of Arab and Western technical, professional and administrative personnel, but subsequently substantial numbers came from Southeast Asia.

Female participation and advancement in majority Muslim countries, or nations in which more than 50% of the population identifies as an adherent of the Islamic faith, have traditionally been areas of controversy. Several Western nations, such as the United States and Western Europe, have criticised majority Muslim nations for the lack of involvement and opportunity for women in the private sector.
Disability in Saudi Arabia is seen through the lens of Islamic Sharia, through cultural norms and also through legislation. As an Islamic society that follows the Qur'an and the Sunnah, disability is often seen through the lens of religion. Islam teaches that people with disabilities are to be treated with respect and equality. However, Saudi Arabia tends to view disability through the medical model, rather than the social model. In addition, there are few studies relating to people with disabilities in Saudi Arabia compared to other countries.
The Human Resources Development Fund (HRDF) is a Saudi governmental authority that was established by a royal decree in July 2000. It falls under the Saudi Ministry of Labor and Social Development.

The Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development is a government ministry in Saudi Arabia was established in 2019 after merging Ministry of Labour and Social Development with Ministry of Civil Service. It is responsible for providing the community with development, support, and protection. The Ministry is also in charge of labor affairs and its related issues and policies. The current Minister is Ahmed al-Rajhi who was appointed in June 2018.
According to the Global Competitiveness Report 2019, compared to the previous year, the Kingdom advanced 13 ranks in the labor and production market efficiency index. Also, it advanced 17 ranks from 2018 in both the “Small and Medium Enterprises Finance” and “Availability of venture capital” respectively, moving up 5 ranks in human capital skills, innovation ability and business dynamics.
The Ministry was able to gain EFQM certificate from the European Foundation for Quality Management EFQM as the first entity in the Kingdom. It obtained this certificate in the year 2021 after it was able to successfully comply with the standards of the European Institutional Excellence Model through several areas, including: developing an electronic friendly settlement system, Raising the efficiency of spending and rationalizing consumption in the field of unified transport, and unifying methods of communication with the ministry's beneficiaries through the unified call center.
References
- ↑ "Saudi jobless rate down to 11.7%: Nitaqat pays off". Arab News . 16 February 2015.
- ↑ "Hafiz: Inspiration for job seekers". Arab News. 15 May 2012.