Interstate 66 (I-66) is an Interstate Highway in the eastern United States. As indicated by its even route number, it runs in an east–west direction. Its western terminus is near Middletown, Virginia, at an interchange with I-81; its eastern terminus is in Washington, D.C., at an interchange with U.S. Route 29 (US 20). Much of the route parallels US 29 or State Route 55 (SR 55). I-66 has no physical or historical connection to the famous US 66 which was located in a different region of the United States.

Bailey's Crossroads is a census-designated place (CDP) in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. The population was 23,643 at the 2010 census. Bailey's Crossroads lies at the crossroads of State Route 7 and State Route 244.
Ballston is a neighborhood in Arlington County, Virginia. Located at the western end of the Rosslyn-Ballston corridor, Ballston is a major transportation hub, and boasts one of the nation's highest concentrations of scientific research agencies, including the Office of Naval Research, the Virginia Tech Advanced Research Institute, and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.

The Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway, often shortened to Shirley Highway, consists of a 17.3-mile (27.8 km) portion of Interstates 95 and 395 in the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. Shirley Highway was the first limited-access freeway in Virginia. Begun in 1941, the road was completed from U.S. Route 1 in Colchester, Virginia, just north of Woodbridge, to the 14th Street Bridge over the Potomac River between Virginia and Washington, D.C. in 1952.
The George Washington Memorial Parkway, colloquially the G.W. Parkway, is a 25-mile-long (40 km) parkway that runs along the south bank of the Potomac River from Mount Vernon, Virginia, northwest to McLean, Virginia, and is maintained by the National Park Service (NPS). It is located almost entirely within Virginia, except for a short portion of the parkway northwest of the Arlington Memorial Bridge that passes over Columbia Island within the District of Columbia.

State Route 244 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known as Columbia Pike, the state highway runs 8.25 miles (13.28 km) from SR 236 in Annandale east to SR 27 and Interstate 395 (I-395) at The Pentagon in Arlington. SR 244 is a major southwest–northeast thoroughfare in northeastern Fairfax County and eastern Arlington County, connecting Annandale with SR 7 at Bailey's Crossroads and SR 120 in the multicultural Westmont neighborhood of Arlington.

Virginia State Route 7 (VA 7) is a major primary state highway and busy commuter route in northern Virginia, United States. It travels southeast from downtown Winchester to SR 400 in downtown Alexandria. Its route largely parallels those of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail and the Potomac River. Between its western terminus and Interstate 395 (I-395), SR 7 is part of the National Highway System. In 1968, the Virginia State Highway Commission designated the road as the "Harry Flood Byrd Highway" between Alexandria and Winchester to commemorate Harry F. Byrd Sr. (1887–1966).

State Route 236 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 15.63 miles (25.15 km) from U.S. Route 29 and US 50 in Fairfax east to SR 400 in Alexandria. SR 236 is a major suburban arterial highway that connects the independent cities of Fairfax and Alexandria via Annandale in Fairfax County. The state highway is known as Main Street in City of Fairfax, Little River Turnpike in Fairfax County, where the highway meets Interstate 495 (I-495), and Duke Street in Alexandria, where the road has junctions with I-395 and US 1.

State Route 120 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known as Glebe Road, the state highway runs 9.10 miles (14.65 km) from U.S. Route 1 (US 1) in Crystal City north to SR 123 at the Chain Bridge. SR 120 is a partial circumferential highway in Arlington County that connects the southeastern and northwestern corners of the county with several urban villages along its crescent-shaped path, including Ballston. The state highway also connects all of the major highways in Virginia that radiate from Washington, including Interstate 395, I-66, US 50, and US 29. SR 120 is a part of the National Highway System for its entire length.

State Route 123 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 29.27 miles (47.11 km) from U.S. Route 1 in Woodbridge north to the Chain Bridge across the Potomac River into Washington from Arlington. It goes by four local names. From its southern terminus to the Occoquan River Bridge, it is known as Gordon Boulevard. From the Occoquan River Bridge to the city of Fairfax it is known as Ox Road. From Fairfax until it enters the Town of Vienna, it is known as Chain Bridge Road. Then, as it passes through the Town of Vienna, it is known as Maple Avenue. After leaving the Town of Vienna, the name reverts to Chain Bridge Road, and continues this way until the intersection with I-495 in Tysons. Between Tysons and the George Washington Memorial Parkway, it is known as Dolley Madison Boulevard. After crossing over the George Washington Memorial Parkway, the name once again reverts to Chain Bridge Road and continues this way until the end of the road, at Chain Bridge. SR 123 is a partial circumferential highway in Northern Virginia that connects Woodbridge in eastern Prince William County with the independent city of Fairfax and the Fairfax County communities of Vienna, Tysons, and McLean, the last being the home of the National Counterterrorism Center and the Central Intelligence Agency. The state highway also connects all of the major highways that radiate from Washington, including Interstate 95, I-66, US 29, US 50, SR 267, and the George Washington Memorial Parkway. Furthermore, SR 123 crosses another pair of circumferential highways, I-495 and the Fairfax County Parkway, and SR 7, a major northwest–southeast highway through Northern Virginia. The state highway is a part of the National Highway System for its entire length.
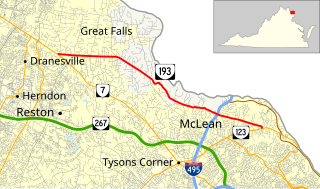
State Route 193 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known as Georgetown Pike, the state highway runs 11.79 mi (18.97 km) from SR 7 in Dranesville east to SR 123 in Langley. SR 193 passes through Great Falls and meets Interstate 495 (I-495) in McLean. The state highway was designated the first Virginia Byway for its scenic value in 1974.

Buildings, sites, districts, and objects in Virginia listed on the National Register of Historic Places:

The earliest electric railway, or streetcar line, in Northern Virginia opened in 1892. At their peak, when merged into a single interurban system, the successors of this and several other lines ran between downtown Washington, D.C., Rosslyn and Arlington Junction – in present-day Crystal City – and out to Mount Vernon, Fairfax City and Nauck.
U.S. Route 50 is a transcontinental highway which stretches from Ocean City, Maryland to West Sacramento, California. In the U.S. state of Virginia, US 50 extends 86 miles (138 km) from the border with Washington, D.C. at a Potomac River crossing at Rosslyn in Arlington County to the West Virginia state line near Gore in Frederick County.
State Route 613 in Fairfax County, Virginia is a secondary state highway. The designation includes several distinct suburban surface routes within the county. These routes were once mostly connected, but changes in road alignment, new road construction, and annexations by the independent city of Alexandria have separated them. These routes are signed only sporadically as 613 and local residents usually refer to these routes by their names.
U.S. Route 1 (US 1) is a major north–south U.S. Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. In the U.S. state of Virginia, US 1 runs north–south through South Hill, Petersburg, Richmond, Fredericksburg, and Alexandria on its way from North Carolina to the 14th Street Bridge into the District of Columbia. It is completely paralleled by Interstate Highways in Virginia – Interstate 85 (I-85) south of Petersburg, I-95 north to Alexandria, and I-395 into the District of Columbia – and now serves mainly local traffic. At its north end, on the approach to the 14th Street Bridge, US 1 is concurrent with I-395; the rest of US 1 is on surface roads.

State Route 237 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 13.07 miles (21.03 km) from SR 236 in Fairfax east to U.S. Route 50 in Arlington. SR 237 connects Fairfax and Arlington with Falls Church. Between Fairfax and Falls Church, the state highway mostly runs concurrently with US 29. East of Falls Church, SR 237 parallels Interstate 66 (I-66) and connects several of Arlington's urban villages.

State Route 309 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known for most of its length as Old Dominion Drive, which was once the right of way of the Great Falls Division of the Washington and Old Dominion Railroad, the state highway runs 5.33 miles (8.58 km) from SR 123 in McLean east to U.S. Route 29 in Arlington.

Washington Boulevard is a major arterial road in Arlington County, Virginia and Washington, DC. The western portion is designated State Route 237, the eastern portion is State Route 27 and the center is an arterial road with no designation. A short portion of the road enters the District of Columbia on Columbia Island, providing a connection between SR 27 and the Arlington Memorial Bridge.

Arlington Boulevard is a major arterial road in Arlington County, Fairfax County, and the independent City of Fairfax in Northern Virginia in metropolitan Washington, DC, United States. It is designated U.S. Route 50 (US 50) for its entire length and is part of the National Highway System.














