Related Research Articles

Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon but life-threatening complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature; this often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.

Thyroid neoplasm is a neoplasm or tumor of the thyroid. It can be a benign tumor such as thyroid adenoma, or it can be a malignant neoplasm, such as papillary, follicular, medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer. Most patients are 25 to 65 years of age when first diagnosed; women are more affected than men. The estimated number of new cases of thyroid cancer in the United States in 2010 is 44,670 compared to only 1,690 deaths. Of all thyroid nodules discovered, only about 5 percent are cancerous, and under 3 percent of those result in fatalities.

An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure. Although adenomas are benign, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Over time adenomas may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner. Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.

Parathyroid chief cells are one of the two cell types of the parathyroid glands, along with oxyphil cells. The chief cells are much more prevalent in the parathyroid gland than the oxyphil cells. It is perceived that oxyphil cells may be derived from chief cells at puberty, as they are not present at birth like chief cells.
In medical or research imaging, an incidental imaging finding is an unanticipated finding which is not related to the original diagnostic inquiry. As with other types of incidental medical findings, they may represent a diagnostic, ethical, and philosophical dilemma because their significance is unclear. While some coincidental findings may lead to beneficial diagnoses, others may lead to overdiagnosis that results in unnecessary testing and treatment, sometimes called the "cascade effect".
An oncocytoma is a tumor made up of oncocytes, epithelial cells characterized by an excessive amount of mitochondria, resulting in an abundant acidophilic, granular cytoplasm. The cells and the tumor that they compose are often benign but sometimes may be premalignant or malignant.
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries.

A Hürthle cell is a cell in the thyroid that is often associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis as well as benign and malignant tumors. This version is a relatively rare form of differentiated thyroid cancer, accounting for only 3-10% of all differentiated thyroid cancers. Oncocytes in the thyroid are often called Hürthle cells. Although the terms oncocyte, oxyphilic cell, and Hürthle cell are used interchangeably, Hürthle cell is used only to indicate cells of thyroid follicular origin.

Toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG), also known as multinodular toxic goiter (MNTG), is an active multinodular goiter associated with hyperthyroidism.

Hürthle cell neoplasm is a rare tumor of the thyroid, typically seen in women between the ages of 70 and 80 years old. When benign, it is called a Hürthle cell adenoma, and when malignant it is called a Hürthle cell carcinoma. Hürthle cell adenoma is characterized by a mass of benign Hürthle cells. Typically such a mass is removed because it is not easy to predict whether it will transform into the malignant counterpart of Hürthle cell carcinoma, which is a subtype of follicular thyroid cancer.

The thyroid ima artery is an artery of the head and neck. It is an anatomical variant that, when present, supplies blood to the thyroid gland primarily, or the trachea, the parathyroid gland and the thymus gland in rare cases. It has also been reported to be a compensatory artery when one or both of the inferior thyroid arteries are absent, and in a few cases the only source of blood to the thyroid gland. Furthermore, it varies in origin, size, blood supply, and termination, and occurs in around 3.8% of the population and is 4.5 times more common in fetuses than in adults. Because of the variations and rarity, it may lead to surgical complications, particularly during tracheostomy and other airway managements.
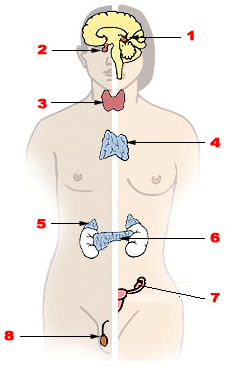
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.

A thyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the thyroid gland, that may be inactive or active as a toxic adenoma.
An endocrine gland neoplasm is a neoplasm affecting one or more glands of the endocrine system.Examples include:

Paired box gene 8, also known as PAX8, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PAX8 gene.

A parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland. It generally causes hyperparathyroidism; there are very few reports of parathyroid adenomas that were not associated with hyperparathyroidism.

A pituitary disease is a disorder primarily affecting the pituitary gland.

Parathyroid carcinoma is a rare cancer resulting in parathyroid adenoma to carcinoma progression. It forms in tissues of one or more of the parathyroid glands.
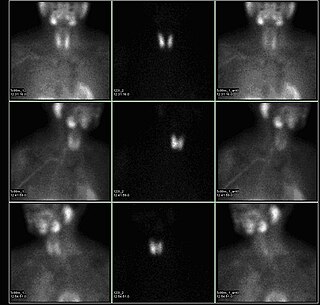
A sestamibi parathyroid scan is a procedure in nuclear medicine which is performed to localize parathyroid adenoma, which causes Hyperparathyroidism. Adequate localization of parathyroid adenoma allows the surgeon to use a minimally invasive surgical approach.
References
- ↑ Ünlütürk, U; Karaveli, G; Sak, S. D.; Erdoğan, M. F. (2011). "Hyalinizing trabecular tumor in a background of lymphocytic thyroiditis: A challenging neoplasm of the thyroid". Endocrine Practice. 17 (6): e140–3. doi:10.4158/EP11138.CR. PMID 21940281.