
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol Z) of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (np) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons.

In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford–Bohr model of the atom, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, consists of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. It is analogous to the structure of the Solar System, but with attraction provided by electrostatic force rather than gravity, and with the electron energies quantized.

Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest element and, at standard conditions, is a gas of diatomic molecules with the formula H2. It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons.
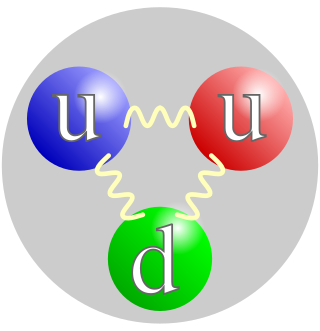
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol
p
, H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 e (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei).
Protium or hydrogen-1 is the most common isotope of the element hydrogen, with one proton, one electron, and no neutrons.
HF, Hf or hf can refer to:
In spectroscopy, the Rydberg constant, symbol for heavy atoms or for hydrogen, named after the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, is a physical constant relating to the electromagnetic spectra of an atom. The constant first arose as an empirical fitting parameter in the Rydberg formula for the hydrogen spectral series, but Niels Bohr later showed that its value could be calculated from more fundamental constants according to his model of the atom.
H2O is the chemical formula for water, meaning that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms.
RH, Rh, rH, or rh may refer to:
H2, H02, or H-2 may refer to:
A grasp generally refers to an act of taking, holding or seizing firmly with the hand.

Hydrogen (1H) has three naturally occurring isotopes, sometimes denoted 1
H
, 2
H
, and 3
H
. 1
H
and 2
H
are stable, while 3
H
has a half-life of 12.32(2) years. Heavier isotopes also exist, all of which are synthetic and have a half-life of less than one zeptosecond (10−21 s). Of these, 5
H
is the least stable, while 7
H
is the most.

The emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen has been divided into a number of spectral series, with wavelengths given by the Rydberg formula. These observed spectral lines are due to the electron making transitions between two energy levels in an atom. The classification of the series by the Rydberg formula was important in the development of quantum mechanics. The spectral series are important in astronomical spectroscopy for detecting the presence of hydrogen and calculating red shifts.
In chemistry, the hydron, informally called proton, is the cationic form of atomic hydrogen, represented with the symbol H+
. The general term "hydron", endorsed by the IUPAC, encompasses cations of hydrogen regardless of their isotopic composition: thus it refers collectively to protons (1H+) for the protium isotope, deuterons (2H+ or D+) for the deuterium isotope, and tritons (3H+ or T+) for the tritium isotope.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





