Related Research Articles
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones.

Kidney stone disease, also known as renal calculus disease, nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material develops in the urinary tract. Renal calculi typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small calculus may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than 5 millimeters, it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back that often radiates downward to the groin. A calculus may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a renal calculus are likely to have another within ten years.

Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein, less than 150 mg/day; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy. Severe proteinuria can cause nephrotic syndrome in which there is worsening swelling of the body.

Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly, often due to high intensity exercise over a short period of time. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some of the muscle breakdown products, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and can cause acute kidney injury.

Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in the urine or other organ dysfunction, and edema. If left untreated, pre-eclampsia can result in long-term consequences for the mother, namely increased risk of cardiovascular diseases and associated complications. In more severe cases, it may be fatal for both the mother and the fetus.

Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, swelling, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of undesirable as well as lethal outcomes for both the mother and the fetus including preterm labor. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia.

Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands or as response to external stimuli. Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are caused by inappropriately normal or elevated blood calcium excreted from the bones and flowing into the blood stream in response to increased production of parathyroid hormone. In healthy people, when blood calcium levels are high, parathyroid hormone levels should be low. With long-standing hyperparathyroidism, the most common symptom is kidney stones. Other symptoms may include bone pain, weakness, depression, confusion, and increased urination. Both primary and secondary may result in osteoporosis.
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is a group of metabolic abnormalities that can occur as a complication from the treatment of cancer, where large amounts of tumor cells are killed off (lysed) from the treatment, releasing their contents into the bloodstream. This occurs most commonly after the treatment of lymphomas and leukemias and in particular when treating non-Hodgkin lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. This is a potentially fatal complication and patients at increased risk for TLS should be closely monitored while receiving chemotherapy and should receive preventive measures and treatments as necessary. TLS can also occur on its own although this is less common.

Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid–base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by consuming too little or too much electrolyte as well as excreting too little or too much electrolyte. Examples of electrolytes include calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium.

Thiazide refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first approved drug of this class, chlorothiazide, was marketed under the trade name Diuril beginning in 1958. In most countries, thiazides are the least expensive antihypertensive drugs available.
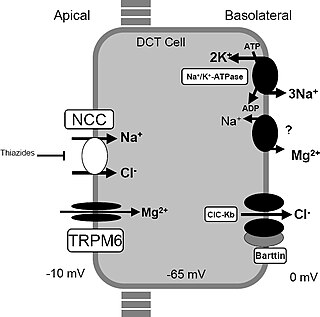
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. It is the most frequent hereditary salt-losing tubulopathy. Gitelman syndrome is caused by disease-causing variants on both alleles of the SLC12A3 gene. The SLC12A3 gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter, which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney.
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. It can result in multiple symptoms. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and nystagmus. Complications may include seizures or cardiac arrest such as from torsade de pointes. Those with low magnesium often have low potassium.

Metabolic alkalosis is an acid-base disorder in which the pH of tissue is elevated beyond the normal range (7.35–7.45). This is the result of decreased hydrogen ion concentration, leading to increased bicarbonate, or alternatively a direct result of increased bicarbonate concentrations. The condition typically cannot last long if the kidneys are functioning properly.
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, recently renamed arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R) and previously known as renal diabetes insipidus, is a form of diabetes insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. This is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of vasopressin. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an improper response of the kidney to vasopressin, leading to a decrease in the ability of the kidney to concentrate the urine by removing free water.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.
Hypercalciuria is the condition of elevated calcium in the urine. Chronic hypercalciuria may lead to impairment of renal function, nephrocalcinosis, and chronic kidney disease. Patients with hypercalciuria have kidneys that excrete higher levels of calcium than normal, for which there are many possible causes. Calcium may come from one of two paths: through the gut where higher than normal levels of calcium are absorbed by the body or mobilized from stores in the bones. After initial 24 hour urine calcium testing and additional lab testing, a bone density scan (DSX) may be performed to determine if the calcium is being obtained from the bones.

Milk-alkali syndrome (MAS), also referred to as calcium-alkali syndrome, is the third most common cause of hypercalcemia. Milk-alkali syndrome is characterized by elevated blood calcium levels, metabolic alkalosis, and acute kidney injury.

Dent's disease is a rare X-linked recessive inherited condition that affects the proximal renal tubules of the kidney. It is one cause of Fanconi syndrome, and is characterized by tubular proteinuria, excess calcium in the urine, formation of calcium kidney stones, nephrocalcinosis, and chronic kidney failure.
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) is an inherited condition that can cause hypercalcemia, a serum calcium level typically above 10.2 mg/dL; although uncommon. It is also known as familial benign hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FBHH) where there is usually a family history of hypercalcemia which is mild, a urine calcium to creatinine ratio <0.01, and urine calcium <200 mg/day (hypocalciuria).
Hypertensive disease of pregnancy, also known as maternal hypertensive disorder, is a group of high blood pressure disorders that include preeclampsia, preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension, and chronic hypertension.
References
- ↑ Kazerooni, T (2003). "Calcium to creatinine ratio in a spot sample of urine for early prediction of pre-eclampsia". International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. 80 (3): 279–283. doi:10.1016/S0020-7292(02)00382-X. PMID 12628529. S2CID 7333130.
- ↑ Cheng, Chih-Jen; Shiang, Jen-Chuan; Hsu, Yu-Juei; Yang, Sung-Sen; Lin, Shih-Hua (2007). "Hypocalciuria in Patients with Gitelman Syndrome: Role of Blood Volume". American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 49 (5): 693–700. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.02.267. PMID 17472852.