
Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

Redlichiida is an order of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Species assigned to the order Redlichiida are among the first trilobites to appear in the fossil record, about halfway during the Lower Cambrian. Due to the difficulty to relate sediments in different areas, there remains some discussion, but among the earliest are Fallotaspis, and Lemdadella, both belonging to this order. The first representatives of the orders Corynexochida and Ptychopariida also appear very early on and may prove to be even earlier than any redlichiid species. In terms of anatomical comparison, the earliest redlichiid species are probably ancestral to all other trilobite orders and share many primitive characters. The last redlichiid trilobites died out before the end of the Middle Cambrian.

A nerve net consists of interconnected neurons lacking a brain or any form of cephalization. While organisms with bilateral body symmetry are normally associated with a condensation of neurons or, in more advanced forms, a central nervous system, organisms with radial symmetry are associated with nerve nets, and are found in members of the Ctenophora, Cnidaria, and Echinodermata phyla, all of which are found in marine environments. In the Xenacoelomorpha, a phylum of bilaterally symmetrical animals, members of the subphylum Xenoturbellida also possess a nerve net. Nerve nets can provide animals with the ability to sense objects through the use of the sensory neurons within the nerve net.

Dalmanites is a genus of trilobite in the order Phacopida. They lived from the Late Ordovician to Middle Devonian.
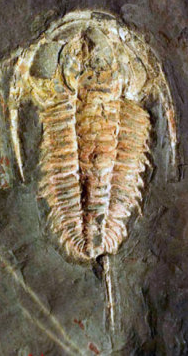
Redlichiina is a suborder of the order Redlichiida of Trilobites. The suborder contains three superfamilies: Emuelloidea, Redlichioidea and Paradoxidoidea. These trilobites are some of the oldest trilobites known. They originated at the beginning of the Cambrian Period and disappeared at the end of the middle Cambrian.
Morphallaxis is the regeneration of specific tissue in a variety of organisms due to loss or death of the existing tissue. The word comes from the Greek allazein, (αλλάζειν) which means to change.

Terataspis is a comparatively huge, 60 centimetre long lichid trilobite genus from the Early Devonian, about 397 million years ago. It lived in a shallow sea in what is now New York State and Ontario. No whole specimens have been found, only disarticulated fragments of its exoskeleton, but enough fragments have been found to allow researchers to form reconstructions of the whole animal. The genus only contains one species, T. grandis.

Tubularia is a genus of hydroids resembling furry pink tufts or balls at the end of long strings, spawning the common name as either the pink-mouthed or pink-hearted hydroid.

Olenoides was a trilobite from the Cambrian period. Its fossils are found well-preserved in the Burgess Shale in Canada. It grew up to 10 cm long.

The (pan)arthropod head problem is a long-standing zoological dispute concerning the segmental composition of the heads of the various arthropod groups, and how they are evolutionarily related to each other. While the dispute has historically centered on the exact make-up of the insect head, it has been widened to include other living arthropods, such as chelicerates, myriapods, and crustaceans, as well as fossil forms, such as the many arthropods known from exceptionally preserved Cambrian faunas. While the topic has classically been based on insect embryology, in recent years a great deal of developmental molecular data has become available. Dozens of more or less distinct solutions to the problem, dating back to at least 1897, have been published, including several in the 2000s.

In anatomy, a suture is a fairly rigid joint between two or more hard elements of an organism, with or without significant overlap of the elements.

Conica are a cnidarian suborder of the Leptomedusae. They make up the bulk of their order; their internal relationships are not well resolved, and most of the roughly 30 families are not yet assigned to a superfamily.
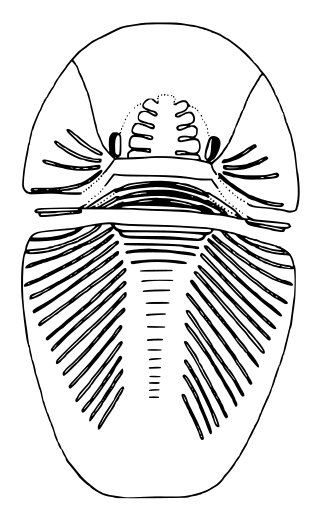
Phytophilaspis is a phosphatized genus of trilobite-like arthropod with eyes, found in association with algal remains. It dwelt in well-lit, shallow waters.
The cephalon is the head section of an arthropod. It is a tagma, i.e., a specialized grouping of arthropod segments. The word cephalon derives from the Greek κεφαλή (kephalē), meaning "head".

The hypostome is the hard mouthpart of trilobites found on the ventral side of the cephalon (head). The hypostome can be classified into three types based on whether they are permanently attached to the rostrum or not and whether they are aligned to the anterior dorsal tip of the glabella.

Emucarididae is an extinct family of soft-shelled trilobite-like arthropods (nektaspids) from the Lower Cambrian of South Australia and South China. It contains only two genera – Emucaris and Kangacaris. Two species were described in 2010 from specimens recovered from Emu Bay Shale Lagerstätte, one species in 2012 from the Maotianshan Shales. It is classified under the order Nektaspida, and is a sister-group to the families Liwiidae and Naraoiidae.

Odontochile is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Dalmanitidae.

Librostoma is a subclass of trilobites defined by having a natant hypostome, which is a hypostome that is free from the anterior doublure and aligned with the anterior of the glabella, this is unlike a conterminant hypostome, which is attached to the exoskeleton.

The subcapitulum, also known as infracapitulum, hypognathum or hipognatum, refers to the ventral part of the gnathosoma or the fusion of the palpal coxae and the labrum complex present in some arthropods on which the mouth, pedipalps, mouthparts and pharynx are generally located. It is delimited by the subcapitular apodeme, which separates it from the cheliceral frame.
















