Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. They work by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volume, which leads to lower blood pressure and decreased oxygen demand from the heart.

Pulmonary edema is fluid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause respiratory failure. It is due to either failure of the left ventricle of the heart to remove blood adequately from the pulmonary circulation, or an injury to the lung tissue or blood vessels of the lung. Treatment is focused on three aspects: firstly improving respiratory function, secondly, treating the underlying cause, and thirdly avoiding further damage to the lung. Pulmonary edema, especially when sudden (acute), can lead to respiratory failure or cardiac arrest due to hypoxia. It is a cardinal feature of congestive heart failure. The term edema is from the Greek οἴδημα, from οἰδέω.

Bradykinin is a peptide that promotes inflammation. It causes arterioles to dilate (enlarge) via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and makes veins constrict, via prostaglandin F2, thereby leading to leakage into capillary beds, due to the increased pressure in the capillaries. Bradykinin is a physiologically and pharmacologically active peptide of the kinin group of proteins, consisting of nine amino acids.
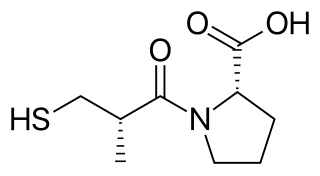
Captopril, sold under the brand name Capoten among others, is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and some types of congestive heart failure.

Angiotensin-converting enzyme, or ACE, is a central component of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. Therefore, ACE indirectly increases blood pressure by causing blood vessels to constrict. ACE inhibitors are widely used as pharmaceutical drugs for treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
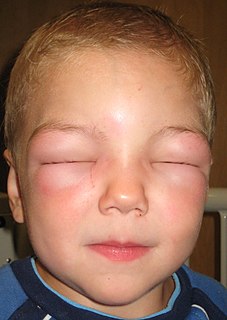
Angioedema is an area of swelling of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are swelling within the upper skin. Onset is typically over minutes to hours.
The kinin–kallikrein system or simply kinin system is a poorly understood hormonal system with limited available research. It consists of blood proteins that play a role in inflammation, blood pressure control, coagulation and pain. Its important mediators bradykinin and kallidin are vasodilators and act on many cell types.

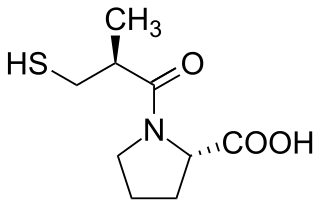
Lisinopril is a medication of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and after heart attacks. For high blood pressure it is usually a first line treatment. It is also used to prevent kidney problems in people with diabetes mellitus. Lisinopril is taken by mouth. Full effect may take up to four weeks to occur.

Ramipril, sold under the brand name Altace among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. Also used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk. It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth.
Maurício Oscar da Rocha e Silva was a Brazilian physician, biomedical scientist and pharmacologist. He discovered bradykinin, an endogenous polypeptide involved in the physiology, pharmacology and pathology of blood pressure control and many other phenomena related to the contraction of smooth muscles.
Hypervolemia, also known as fluid overload, is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood. The opposite condition is hypovolemia, which is too little fluid volume in the blood. Fluid volume excess in the intravascular compartment occurs due to an increase in total body sodium content and a consequent increase in extracellular body water. The mechanism usually stems from compromised regulatory mechanisms for sodium handling as seen in congestive heart failure (CHF), kidney failure, and liver failure. It may also be caused by excessive intake of sodium from foods, intravenous (IV) solutions and blood transfusions, medications, or diagnostic contrast dyes. Treatment typically includes administration of diuretics and limit the intake of water, fluids, sodium, and salt.
Kallikreins are a subgroup of serine proteases, enzymes capable of cleaving peptide bonds in proteins. In humans, plasma kallikrein (KLKB1) has no known paralogue, while tissue kallikrein-related peptidases (KLKs) encode a family of fifteen closely related serine proteases. These genes are localised to chromosome 19q13, forming the largest contiguous cluster of proteases within the human genome. Kallikreins are responsible for the coordination of various physiological functions including blood pressure, semen liquefaction and skin desquamation.
Kininogens are precursor proteins for kinins, biologically active polypeptides involved in blood coagulation, vasodilation, smooth muscle contraction, inflammatory regulation, and the regulation of the cardiovascular and renal systems.

Icatibant, sold under the brand name Firazyr, is a medication for the symptomatic treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adults with C1-esterase-inhibitor deficiency. It is not effective in angioedema caused by medication from the ACE inhibitor class.

Mephentermine is a cardiac stimulant. It was formerly used in Wyamine nasal decongestant inhalers and before that as a stimulant in psychiatry.
The discovery of an orally inactive peptide from snake venom established the important role of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors in regulating blood pressure. This led to the development of Captopril, the first ACE inhibitor. When the adverse effects of Captopril became apparent new derivates were designed. Then after the discovery of two active sites of ACE: N-domain and C-domain, the development of domain-specific ACE inhibitors began.
An acute hemolytic transfusion reaction (AHTR), also called immediate hemolytic transfusion reaction, is a life-threatening reaction to receiving a blood transfusion. AHTRs occur within 24 hours of the transfusion and can be triggered by a few milliliters of blood. The reaction is triggered by pre-formed host antibodies destroying donor red blood cells. AHTR typically occurs when there is an ABO blood group incompatibility, and is most severe when type A donor blood is given to a type O recipient.

Sacubitril/valsartan, sold under the brand name Entresto among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for use in heart failure. It consists of the neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril and the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan. It is recommended for use as a replacement for an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker in people with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.

Sacubitril is an antihypertensive drug used in combination with valsartan. The combination drug sacubitril/valsartan, known during trials as LCZ696 and marketed under the brand name Entresto, is a treatment for heart failure. It was approved under the FDA's priority review process for use in heart failure on July 7, 2015.











