
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance.
A relational database is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using the SQL for querying and maintaining the database.
The relational model (RM) is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by English computer scientist Edgar F. Codd, where all data is represented in terms of tuples, grouped into relations. A database organized in terms of the relational model is a relational database.
Structured Query Language, abbreviated as SQL, is a domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e. data incorporating relations among entities and variables.
In database theory, relational algebra is a theory that uses algebraic structures with a well-founded semantics for modeling data, and defining queries on it. The theory was introduced by Edgar F. Codd.
A hierarchical database model is a data model in which the data are organized into a tree-like structure. The data are stored as records which are connected to one another through links. A record is a collection of fields, with each field containing only one value. The type of a record defines which fields the record contains.
A join clause in SQL – corresponding to a join operation in relational algebra – combines columns from one or more tables into a new table. Informally, a join stitches two tables and puts on the same row records with matching fields : INNER, LEFT OUTER, RIGHT OUTER, FULL OUTER and CROSS.
The SQL SELECT statement returns a result set of records, from one or more tables.
Dataphor is an open-source truly-relational database management system (RDBMS) and its accompanying user interface technologies, which together are designed to provide highly declarative software application development. The Dataphor Server has its own storage engine or it can be a virtual, or federated, DBMS, meaning that it can utilize other database engines for storage.
An SQL INSERT statement adds one or more records to any single table in a relational database.
In a database, a view is the result set of a stored query on the data, which the database users can query just as they would in a persistent database collection object. This pre-established query command is kept in the database dictionary. Unlike ordinary base tables in a relational database, a view does not form part of the physical schema: as a result set, it is a virtual table computed or collated dynamically from data in the database when access to that view is requested. Changes applied to the data in a relevant underlying table are reflected in the data shown in subsequent invocations of the view. In some NoSQL databases, views are the only way to query data.

In SQL, null or NULL is a special marker used to indicate that a data value does not exist in the database. Introduced by the creator of the relational database model, E. F. Codd, SQL null serves to fulfil the requirement that all true relational database management systems (RDBMS) support a representation of "missing information and inapplicable information". Codd also introduced the use of the lowercase Greek omega (ω) symbol to represent null in database theory. In SQL, NULL is a reserved word used to identify this marker.
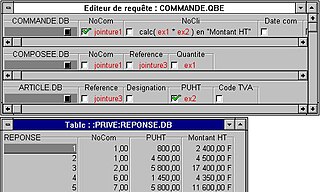
Query by Example (QBE) is a database query language for relational databases. It was devised by Moshé M. Zloof at IBM Research during the mid-1970s, in parallel to the development of SQL. It is the first graphical query language, using visual tables where the user would enter commands, example elements and conditions. Many graphical front-ends for databases use the ideas from QBE today. Originally limited only for the purpose of retrieving data, QBE was later extended to allow other operations, such as inserts, deletes and updates, as well as creation of temporary tables.
A pivot table is a table of grouped values that aggregates the individual items of a more extensive table within one or more discrete categories. This summary might include sums, averages, or other statistics, which the pivot table groups together using a chosen aggregation function applied to the grouped values.
Language Integrated Query is a Microsoft .NET Framework component that adds native data querying capabilities to .NET languages, originally released as a major part of .NET Framework 3.5 in 2007.
A hierarchical query is a type of SQL query that handles hierarchical model data. They are special cases of more general recursive fixpoint queries, which compute transitive closures.
In a SQL database query, a correlated subquery is a subquery that uses values from the outer query. Because the subquery may be evaluated once for each row processed by the outer query, it can be slow.
Strozzi NoSQL is a shell-based relational database management system initialized and developed by Carlo Strozzi that runs under Unix-like operating systems, or others with compatibility layers. Its file name NoSQL merely reflects the fact that it does not express its queries using Structured Query Language; the NoSQL RDBMS is distinct from the circa-2009 general concept of NoSQL databases, which are typically non-relational, unlike the NoSQL RDBMS. Strozzi NoSQL is released under the GNU GPL.
QUEL is a relational database query language, based on tuple relational calculus, with some similarities to SQL. It was created as a part of the Ingres DBMS effort at University of California, Berkeley, based on Codd's earlier suggested but not implemented Data Sub-Language ALPHA. QUEL was used for a short time in most products based on the freely available Ingres source code, most notably in an implementation called POSTQUEL supported by POSTGRES. As Oracle and DB2 gained market share in the early 1980s, most companies then supporting QUEL moved to SQL instead. QUEL continues to be available as a part of the Ingres DBMS, although no QUEL-specific language enhancements have been added for many years.
The syntax of the SQL programming language is defined and maintained by ISO/IEC SC 32 as part of ISO/IEC 9075. This standard is not freely available. Despite the existence of the standard, SQL code is not completely portable among different database systems without adjustments.


