
Authentication is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. It might involve validating personal identity documents, verifying the authenticity of a website with a digital certificate, determining the age of an artifact by carbon dating, or ensuring that a product or document is not counterfeit.
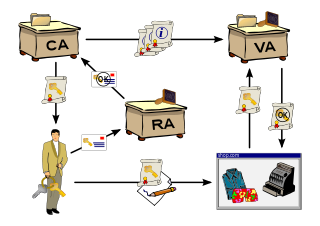
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of a PKI is to facilitate the secure electronic transfer of information for a range of network activities such as e-commerce, internet banking and confidential email. It is required for activities where simple passwords are an inadequate authentication method and more rigorous proof is required to confirm the identity of the parties involved in the communication and to validate the information being transferred.
A DataBlade is a module for the IBM Informix database server. Released in 1996, it allows creating complex, custom datatypes whilst providing the same level of integration as built-in datatypes.
FCAPS is the ISO Telecommunications Management Network model and framework for network management. FCAPS is an acronym for fault, configuration, accounting, performance, security, the management categories into which the ISO model defines network management tasks. In non-billing organizations accounting is sometimes replaced with administration.
Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems.
Identity management (IdM), also known as identity and access management, is a framework of policies and technologies to ensure that the right users have the appropriate access to technology resources. IdM systems fall under the overarching umbrellas of IT security and data management. Identity and access management systems not only identify, authenticate, and control access for individuals who will be utilizing IT resources but also the hardware and applications employees need to access.
Digital identity is the phrase referring to the data that computer systems use to identify individuals, organizations, applications, or devices. For individuals, it involves the collection of personal data that is essential for facilitating automated access to digital services, confirming one's identity on the internet, and allowing digital systems to manage interactions between different parties. It is a component of a person's social identity in the digital realm, often referred to as their online identity.
IBM Storage Protect is a data protection platform that gives enterprises a single point of control and administration for backup and recovery. It is the flagship product in the IBM Spectrum Protect family.
A friend class in C++ can access the private and protected members of the class in which it is declared as a friend. A significant use of a friend class is for a part of a data structure, represented by a class, to provide access to the main class representing that data structure. The friend class mechanism allows to extend the storage and access to the parts, while retaining proper encapsulation as seen by the users of the data structure.
Application Response Measurement (ARM) is an open standard published by the Open Group for monitoring and diagnosing performance bottlenecks within complex enterprise applications that use loosely-coupled designs or service-oriented architectures.
IBM Tivoli Identity Manager, also known as TIM, ITIM, or ISIM, is an Identity Management System product from IBM.
HCL Connections is a Web 2.0 enterprise social software application developed originally by IBM and acquired by HCL Technologies in July 2019. Connections is an enterprise-collaboration platform which aims to helps teams work more efficiently. Connections is part of HCL collaboration suite which also includes Notes / Domino, Sametime, Portal and Connections.
Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password.
Tape labels are identifiers given to volumes of magnetic tape.

OpenAM is an open-source access management, entitlements and federation server platform. Now it is supported by Open Identity Platform Community.
Encentuate, Inc., was a privately held company that was started in Singapore in 2002, but eventually based in Redwood City, California before it was acquired by IBM in 2008. It developed an identity and access management software product focused on enterprise single sign-on and integration of strong authentication technology.
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is a set of specifications that encompasses the XML-format for security tokens containing assertions to pass information about a user and protocols and profiles to implement authentication and authorization scenarios. This article has a focus on software and services in the category of identity management infrastructure, which enable building Web-SSO solutions using the SAML protocol in an interoperable fashion. Software and services that are only SAML-enabled do not go here.
A whole new range of techniques has been developed to identify people since the 1960s from the measurement and analysis of parts of their bodies to DNA profiles. Forms of identification are used to ensure that citizens are eligible for rights to benefits and to vote without fear of impersonation while private individuals have used seals and signatures for centuries to lay claim to real and personal estate. Generally, the amount of proof of identity that is required to gain access to something is proportionate to the value of what is being sought. It is estimated that only 4% of online transactions use methods other than simple passwords. Security of systems resources generally follows a three-step process of identification, authentication and authorization. Today, a high level of trust is as critical to eCommerce transactions as it is to traditional face-to-face transactions.
A trusted execution environment (TEE) is a secure area of a main processor. It helps code and data loaded inside it to be protected with respect to confidentiality and integrity. Data integrity prevents unauthorized entities from outside the TEE from altering data, while code integrity prevents code in the TEE from being replaced or modified by unauthorized entities, which may also be the computer owner itself as in certain DRM schemes described in SGX. This is done by implementing unique, immutable, and confidential architectural security such as Intel Software Guard Extensions which offers hardware-based memory encryption that isolates specific application code and data in memory. Intel SGX allows user-level code to allocate private regions of memory, called enclaves, which are designed to be protected from processes running at higher privilege levels. A TEE as an isolated execution environment provides security features such as isolated execution, integrity of applications executing with the TEE, along with confidentiality of their assets. In general terms, the TEE offers an execution space that provides a higher level of security for trusted applications running on the device than a rich operating system (OS) and more functionality than a 'secure element' (SE).
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a type of identity management and branch of cybersecurity that focuses on the control, monitoring, and protection of privileged accounts within an organization. Accounts with privileged status grant users enhanced permissions, making them prime targets for attackers due to their extensive access to vital systems and sensitive data.


