
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was a constituent of the FT 30 and later the FTSE 100 indices.

Rayon, also called viscose and commercialised in some countries as sabra silk or cactus silk, is a semi-synthetic fiber made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. Many types and grades of viscose fibers and films exist. Some imitate the feel and texture of natural fibers such as silk, wool, cotton, and linen. The types that resemble silk are often called artificial silk. It can be woven or knit to make textiles for clothing and other purposes.

Quorn is a brand of meat substitute products. Quorn originated in the UK and is sold primarily in Europe, but is available in 11 countries. The brand is owned by parent company Monde Nissin.
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants or fur from animals. They are the result of extensive research by scientists to replicate naturally occurring animal and plant fibers. In general, synthetic fibers are created by extruding fiber-forming materials through spinnerets, forming a fiber. These are called synthetic or artificial fibers. The word polymer comes from a Greek prefix "poly" which means "many" and suffix "mer" which means "single units"..

Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer that is used as an insulator in the electrical and electronics industries. It is a thermoplastic (semi-)crystalline polymer, and a type of polyester. PBT resists solvents, shrinks very little during forming, is mechanically strong, is heat-resistant up to 150 °C, and can be treated with flame retardants to make it noncombustible. It was developed by Britain's Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI).
In a reactive dye, a chromophore contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the covalent bonding that occurs during dyeing. Reactive dyeing is the most important method for coloring cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes can also be applied on wool and nylon; in the latter case they are applied under weakly acidic conditions. Reactive dyes have a low utilization degree compared to other types of dyestuff, since the functional group also bonds to water, creating hydrolysis.
Dhirubhai Ambani Knowledge CITY, often abbreviated as DAKC, is a technology park located at Kopar Khairane in Navi Mumbai, India. Spread over 56 hectares, it was completed in 2002. The city is named after the famous Indian industrialist Dhirubhai Ambani and is owned by the Reliance ADA Group and houses a 24-hour National Network Operations Centre (NNOC) along with more than 25,000 employees working primarily for the Reliance Communications division.

Cetrimide, or alkyltrimethylammonium bromide, is an antiseptic which is a mixture of three quaternary ammonium compounds: tetradonium bromide, cetrimonium bromide (CTAB), and laurtrimonium bromide. It was first discovered and developed by ICI and introduced under the brand name Cetavlon. It is used as a 1-3 % solution for cleaning roadside accident wounds. ICI also introduced Savlon, which was a combination of cetrimide and chlorhexidine. ICI later sold the Savlon brand OTC to Johnson & Johnson in May 1992. Cetrimide is used in various applications such as antiseptic agents, diagnostic test and analysis, topical formulations, and dental treatment.
Morada Limited is a textile company based in Altham, Lancashire. Morada specializes in curtains.

Lucky Core Industries Limited, formerly known as ICI Pakistan, is a Pakistani conglomerate company headquartered in Karachi. It manufactures polyester, pharmaceutical, agrochemical, soda ash, and veterinary medicine.
Crimplene is a texturised continuous fibre launched in 1959, produced by modifying Terylene. The patent was taken out by Mario Nava of Chesline and Crepes Ltd of Macclesfield, and sold to ICI Fibres. ICI licensed the product to various throwsters. The largest producer was William Tatton of Leek, and the Golborne factory was at one time capable of taking the entire output of ICI's Wilton production of Terylene.

Savlon is a brand of antibacterial personal care products with the active ingredients of cetrimide and chlorhexidine gluconate. Commonly sold as a cream, the product range also includes antiseptic sprays, sticking plasters and other antiseptic products.
Morgan Advanced Materials plc is a company which manufactures specialist products, using carbon, advanced ceramics and composites. The group is headquartered in Windsor, United Kingdom, and has 70 sites across 18 countries. It is listed as public limited company on the London Stock Exchange and is a component of the FTSE 250 Index.
John Rex Whinfield CBE was a British chemist. Together with James Tennant Dickson, Whinfield investigated polyesters and produced and patented the first polyester fibre in 1941, which they named Terylene equal to or surpassing nylon in toughness and resilience. He was born in Accrington, but moved out of town before the age of 4.
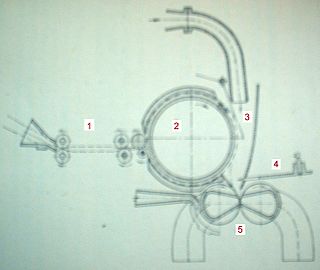
Friction spinning or DREF spinning is a textile technology that is suitable for spinning coarse counts of yarns and technical core-wrapped yarns. DREF yarns are bulky with low tensile strength, making them suitable for blankets and mop yarns. They can be spun from asbestos, carbon fibres and are capable of being made into filters for water systems. Yarns such as Rayon and Kevlar can be spun using this method. The technology was developed around 1975 by Dr. Ernst Fehrer.

The Billingham Manufacturing Plant is a large chemical works based in the Borough of Stockton-on-Tees, England. In agricultural terms, it is one of the most important factories in Britain.
British Nylon Spinners (BNS) was a British company set up in 1940 by ICI and Courtaulds to produce nylon yarn. In 1964 it was taken over by ICI after ICI had tried and failed to take over Courtaulds.
The Millhaven Fibres Plant opened September 28, 1955 as the third polyester plant in the world. It was originally built to manufacture a new type of synthetic yarn called Terylene, which is known as Dacron in the United States. Terylene polyester fibre was invented in England in 1940 and had wide application in the apparel trade and for industrial use. In 1966, Terylene underwent a name change, to Fortrel. This happened in the same year as the plant's name being changed

The Winnington Laboratory was a former chemical laboratory at Winnington, near Northwich, in Cheshire, England.
The Fibres Research Centre was a research centre of ICI in Harrogate in North Yorkshire. The site today is a redeveloped business park.









