
Ithaca College is a private college in Ithaca, New York. It was founded by William Egbert in 1892 as a conservatory of music. Ithaca College is known for its media-related programs and entertainment programs within the Roy H. Park School of Communications and the Ithaca College School of Music, Theatre, and Dance. The college has a liberal arts focus, and offers several pre-professional programs, along with some graduate programs.
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.
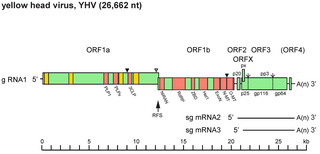
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.

Chrysoviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Members of the family are called chrysoviruses.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.

Ithaca College Television (ICTV) is Ithaca College's student-run television station. It's the largest student-run organization on Ithaca's campus. Founded in 1958 as the country's first student-run cable television station, ICTV provides original, student-produced programming to approximately 26,000 households in Tompkins County, New York through Spectrum Cable. Additionally, ICTV offers a livestream of its programming on its website, ICTV.org, along with on-demand episodes from past and present shows.

Iflaviridae is a family of positive sense RNA viruses insect-infecting viruses. Some of the insects commonly infected by iflaviruses include aphids, leafhoppers, flies, bees, ants, silkworms and wasps. The name "Ifla" is derived from the name "Infectious flacherie virus", a member species. There is one genus (Iflavirus) and 16 species in this family.

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.

TVi was a Ukrainian TV channel that began broadcasting in 2008; it was widely seen as Ukraine's only independent TV channel. It was known for its critical coverage of the Ukrainian government, particularly of President Viktor Yanukovych.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Bottigliavirus is the only genus in the family Ampullaviridae and contains 3 species. Ampullaviridae infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.
Starlight Media is the largest Ukrainian broadcasting group, composed of six television stations and nine other media and advertising companies. It was founded 11 November 2009 in Kyiv. In 2013 its market share was 30.17% and in 2014 - 27.85% of the 14-49 audience. Its market share in 2012 was 34% for the audience aged 14–49 and in 2014 - 32%. In 2015 the group's share of the audience of 14-49 year olds was 27.33%. Its margin over its closest competitor is 46%, and for middle and upper income Ukrainians — 54%.

Bamfordvirae is a kingdom of viruses. This kingdom is recognized for its use of double jelly roll major capsid proteins. It was formerly known as the PRD1-adenovirus lineage. The kingdom is named after Dennis H. Bamford who first promoted the evolutionary unity of all viruses encoding double jelly-roll major capsid proteins.
Lenarviricota is a phylum of RNA viruses that includes all positive-strand RNA viruses that infect prokaryotes. Some members also infect eukaryotes. Most of these viruses do not have capsids, except for the genus Ourmiavirus. The name of the group is a syllabic abbreviation of the names of founding member families "Leviviridae and Narnaviridae" with the suffix -viricota, denoting a virus phylum.
Pisoniviricetes is a class of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect eukaryotes. A characteristic of the group is a conserved 3C-like protease from the PA clan of proteases for processing the translated polyprotein. The name of the group is a portmanteau of member orders "picornavirales, sobelivirales, nidovirales" and -viricetes which is the suffix for a virus class.

Adnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes archaeal viruses that have a filamentous virion and a linear, double-stranded DNA genome. The genome exists in A-form (A-DNA) and encodes a dimeric major capsid protein (MCP) that contains the SIRV2 fold, a type of alpha-helix bundle containing four helices. The virion consists of the genome encased in capsid proteins to form a helical nucleoprotein complex. For some viruses, this helix is surrounded by a lipid membrane called an envelope. Some contain an additional protein layer between the nucleoprotein helix and the envelope. Complete virions are long and thin and may be flexible or a stiff like a rod.

United News, Telemarathon or UA together is a joint information telethon which was launched on February 24, 2022, at the start of Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine. It began broadcasting at the start of the invasion on February 24, 2022, as #UAtogether and broadcast on Rada TV, the official television channel of the Verkhovna Rada.














