Related Research Articles
IEEE 802.15 is a working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802 standards committee which specifies Wireless Specialty Networks (WSN) standards. The working group was formerly known as Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks.

IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, and specifies the set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand and are the world's most widely used wireless computer networking standards. IEEE 802.11 is used in most home and office networks to allow laptops, printers, smartphones, and other devices to communicate with each other and access the Internet without connecting wires. IEEE 802.11 is also a basis for vehicle-based communication networks with IEEE 802.11p.

Configuration management (CM) is a systems engineering process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product's performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. The CM process is widely used by military engineering organizations to manage changes throughout the system lifecycle of complex systems, such as weapon systems, military vehicles, and information systems. Outside the military, the CM process is also used with IT service management as defined by ITIL, and with other domain models in the civil engineering and other industrial engineering segments such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings.
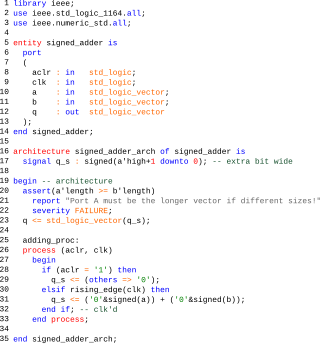
The VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL) is a hardware description language (HDL) that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gates, for design entry, documentation, and verification purposes. Since 1987, VHDL has been standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as IEEE Std 1076; the latest version of which is IEEE Std 1076-2019. To model analog and mixed-signal systems, an IEEE-standardized HDL based on VHDL called VHDL-AMS has been developed.

IEEE 488 is a short-range digital communications 8-bit parallel multi-master interface bus specification developed by Hewlett-Packard as HP-IB. It subsequently became the subject of several standards, and is generically known as GPIB.
IEEE 802.1Q, often referred to as Dot1q, is the networking standard that supports virtual local area networking (VLANs) on an IEEE 802.3 Ethernet network. The standard defines a system of VLAN tagging for Ethernet frames and the accompanying procedures to be used by bridges and switches in handling such frames. The standard also contains provisions for a quality-of-service prioritization scheme commonly known as IEEE 802.1p and defines the Generic Attribute Registration Protocol.
A test plan is a document detailing the objectives, resources, and processes for a specific test session for a software or hardware product. The plan typically contains a detailed understanding of the eventual workflow.
IEEE P1363 is an Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standardization project for public-key cryptography. It includes specifications for:
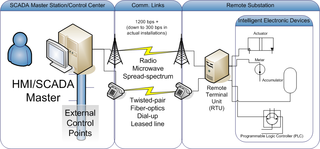
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.
IEEE 802.11n-2009, or 802.11n, is a wireless-networking standard that uses multiple antennas to increase data rates. The Wi-Fi Alliance has also retroactively labelled the technology for the standard as Wi-Fi 4. It standardized support for multiple-input multiple-output, frame aggregation, and security improvements, among other features, and can be used in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands.
The IEEE Standard for Radix-Independent Floating-Point Arithmetic, was the first Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) international standard for floating-point arithmetic with radices other than 2, including radix 10. IEEE 854 did not specify any data formats, whereas IEEE 754-1985 did specify formats for binary floating point. IEEE 754-1985 and IEEE 854-1987 were both superseded in 2008 by IEEE 754-2008, which specifies floating-point arithmetic for both radix 2 (binary) and radix 10 (decimal), and specifies two alternative formats for radix 10 floating-point values, and even more so with IEEE 754-2019. IEEE 754-2008 also had many other updates to the IEEE floating-point standardisation.
The IEEE Std 1901-2010 is a standard for high speed communication devices via electric power lines, often called broadband over power lines (BPL). The standard uses transmission frequencies below 100 MHz. This standard is usable by all classes of BPL devices, including BPL devices used for the connection to Internet access services as well as BPL devices used within buildings for local area networks, smart energy applications, transportation platforms (vehicle), and other data distribution applications.
IEEE 802.11y-2008 is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard that enables data transfer equipment to operate using the 802.11a protocol on a co-primary basis in the 3650 to 3700 MHz band except when near a grandfathered satellite earth station. IEEE 802.11y is only being allowed as a licensed band. It was approved for publication by the IEEE on September 26, 2008.
Instrument control consists of connecting a desktop instrument to a computer and taking measurements.
IEEE 802.1AE is a network security standard that operates at the medium access control layer and defines connectionless data confidentiality and integrity for media access independent protocols. It is standardized by the IEEE 802.1 working group.
IEEE 802.11 – or more correctly IEEE 802.11-1997 or IEEE 802.11-1999 – refer to the original version of the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking standard released in 1997 and clarified in 1999. Most of the protocols described by this early version are rarely used today.
IEEE 754-2008 is a revision of the IEEE 754 standard for floating-point arithmetic. It was published in August 2008 and is a significant revision to, and replaces, the IEEE 754-1985 standard. The 2008 revision extended the previous standard where it was necessary, added decimal arithmetic and formats, tightened up certain areas of the original standard which were left undefined, and merged in IEEE 854 . In a few cases, where stricter definitions of binary floating-point arithmetic might be performance-incompatible with some existing implementation, they were made optional. In 2019, it was updated with a minor revision IEEE 754-2019.
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. It is most commonly known by the name FireWire (Apple), though other brand names exist such as i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx.
ISO 10007 "Quality management — Guidelines for configuration management" is the ISO standard that gives guidance on the use of configuration management within an organization. "It is applicable to the support of products from concept to disposal." The standard was originally published in 1995, and was updated in 2003 and 2017. Its guidance is specifically recommended for meeting "the product identification and traceability requirements" introduced in ISO 9001:2015 and AS9100 Rev D.
IEEE 802.11k-2008 is an amendment to IEEE 802.11-2007 standard for radio resource measurement. It defines and exposes radio and network information to facilitate the management and maintenance of a mobile Wireless LAN. IEEE 802.11k was incorporated in IEEE Std 802.11-2012; see IEEE 802.11.
References
- ↑ "IEEE Standard for Environmental Assessment of Electronic Products". IEEE STD 1680-2009 (Revision of IEEE STD 1680-2006). 2010-03-05. pp. 1–17. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2010.5429925. ISBN 978-0-7381-6127-3.
- ↑ "IEEE 1680 Certifications". UL Empowering Trust®. Retrieved 2020-04-11.
- ↑ Code of Federal Regulations, Title 48, Federal Acquisition Regulations System, Chapter 1 (Pt. 1-51), Revised as of October 1, 2010 by Office of the Federal Register (U.S.) (Feb 25, 2011) ISBN 0160864925 page 516
- 1 2 Information Systems Theory: Explaining and Predicting Our Digital Society, Vol. 1 by Yogesh K. Dwivedi, Michael R. Wade and Scott L. Schneberger 2011 ISBN 1441961070 page 395
- ↑ "1680.1-2018 - IEEE Standard for Environmental and Social Responsibility Assessment of Computers and Displays". standards.ieee.org. Retrieved 2020-04-11.
- ↑ "IEEE Standard for Environmental and Social Responsibility Assessment of Computers and Displays - ANSI Blog". The ANSI Blog. 2018-04-06. Retrieved 2020-04-11.
- ↑ "1680.2-2012 - IEEE Standard for Environmental Assessment of Imaging Equipment". standards.ieee.org. Retrieved 2020-04-11.
- ↑ "IEEE Standard for Environmental Assessment of Imaging Equipment - Amendment 1". IEEE STD 1680.2a-2017 (Amendment to IEEE STD 1680.2-2012). 2017-12-22. pp. 1–19. doi: 10.1109/IEEESTD.2017.8237223 . ISBN 978-1-5044-4565-8.
- ↑ "1680.3-2012 - IEEE Standard for Environmental Assessment of Televisions". standards.ieee.org. Retrieved 2020-04-11.
https://global.ihs.com/doc_detail.cfm?document_name=NSF%20426&item_s_key=00728331