
Information and communication technologies for development (ICT4D) refers to the application of information and communication technologies (ICT) toward social, economic, and political development, with a particular emphasis on helping poor and marginalized people and communities. It aims to help in international development by bridging the digital divide and providing equitable access to technologies. ICT4D is grounded in the notions of "development", "growth", "progress" and "globalization" and is often interpreted as the use of technology to deliver a greater good. Another similar term used in the literature is "digital development". ICT4D draws on theories and frameworks from many disciplines, including sociology, economics, development studies, library, information science, and communication studies.

Computer Aid International is a not-for-profit organisation active in the field of Information and Communication Technologies for Development. A registered charity, Computer Aid was founded in 1996 to bridge the digital divide by providing refurbished PCs from the UK to educational and non-profit organisations in developing countries.
Information and communication technology in agriculture, also known as e-agriculture, focuses on the enhancement of agricultural and rural development through improved information and communication processes. More specifically, e-agriculture involves the conceptualization, design, development, evaluation and application of innovative ways to use information and communication technologies (ICTs) in the rural domain, with a primary focus on agriculture. ICT includes devices, networks, mobiles, services and applications; these range from innovative Internet-era technologies and sensors to other pre-existing aids such as fixed telephones, televisions, radios and satellites. Provisions of standards, norms, methodologies, and tools as well as development of individual and institutional capacities, and policy support are all key components of e-agriculture.
Media Lab Asia (MLAsia) was founded in 2001 as a not-for-profit research entity as a result of cooperation between the MIT Media Lab and the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology of the Government of India. The objectives of MLAsia are to bring the benefits of Information and communications technology (ICT) to the people in Asia and around the world.

BOSCO-Uganda is a private, non-profit effort to put wireless internet and VoIP telephony into the internally displaced persons camps of northern Uganda, in cooperation with the Archdiocese of Gulu. BOSCO collaborated with Inveneo to place their low-power PCs powered by solar panels in the Catechist Training Center and the Caritas Office in Gulu, as well as at schools, hospitals, colleges and Churches in the Pabbo, Alero, Lacor, Coope, Jen'Geri, Unyama, and Pagak IDP camps. The organization aims to use ICT to help end the isolation of communities in rural northern Uganda as well as improve education, economics, human rights documentation, health care and rural development.
ASCAMM Foundation is a Technology Center located near Barcelona, at the Vallès Technology Park. the origin of this Foundation was the Catalan Association of Enterprises Mould-Makers and Die-Makers, in Catalan: Associació Catalana d'Empreses constructores de Motlles i Matrius.

The Agora Center is a separate institute at the University of Jyväskylä in Central Finland. By its nature, the Agora Center is interdisciplinary and networked. Its purpose is to conduct, coordinate, and administrate top-level research and development that relates to the knowledge society and which places emphasis on the human perspective. The research and development is conducted in the form of fixed-period projects in cooperation with the University of Jyväskylä’s other faculties and separate institutes, businesses, the public sector and other relevant parties. The Agora Center also promotes researcher training through its various research projects. One of the core missions of the Agora Center is to effectively combine research and development with education. The project staff includes a high number of students and post-graduate students.
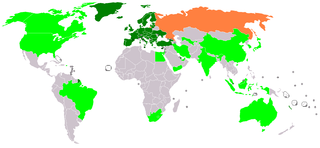
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, headquartered in Sophia-Antipolis, France, with worldwide projection. ETSI produces globally-applicable standards for Information and Communications Technologies (ICT), including fixed, mobile, radio, converged, broadcast and internet technologies.
The European Distance and E-Learning Network, abbreviated EDEN and originally named the European Distance Education Network - established in 1991, is an international educational association open to institutions and individuals dealing with e-learning, open education, and distance education. EDEN is a not-for-profit organisation, registered as a limited company under English law.
The Istituto Superiore Mario Boella (ISMB) was a center for applied research in the fields of telecommunication engineering and information and communication technologies located in Turin, Italy.
The Inclusive Design Research Centre (IDRC) is a research and development centre at OCAD University in Toronto, Canada. The centre defines inclusive design as that which "considers the full range of human diversity with respect to ability, language, culture, gender, age and other forms of human difference." The research centre is directed by Jutta Treviranus. In 2011 the centre launched a Master of Design in Inclusive Design.

The State Fund for Development of İnformation Technologies, operating under the Ministry of Communications and High Technologies of the Republic of Azerbaijan, is an Azerbaijan state organization that stimulates and finances innovation and development in the field of information and communication technology (ICT).
The VRVis Zentrum für Virtual Reality und Visualisierung (VRVis) is the largest independent research center in the area of Visual Computing in Austria, and one of the largest in Europe. It is one of currently 22 centrally funded COMET – Competence Centers for Excellent Technologies of Austria. The VRVis Center is located in Ares Tower in Vienna.
Science and Technology is Jordan's fastest-growing economic sector. This growth is occurring across multiple industries, including information and communications technology (ICTs), solar and wind energy and nuclear technology.

European Alliance for Innovation (EAI) is an international professional community and a nonprofit organization. The goal of EAI is to empower the global ICT research and innovation community, and to promote cooperation between European and International ICT communities.
New ICT is an open, customer-driven ecosystem which is proposed by the information technology company Huawei. In simple terms, the new ICT fully converges IT and CT technologies to offer large-scale communication, storage, and processing capabilities. The new ICT works as a flexible, agile platform to adapt to ever-changing business goals, system environments, and application configurations. The new ICT era has three compelling characteristics: business-driven development, agile innovation, and a new ecosystem.
Science and technology in Kazakhstan outlines government policies to develop science, technology and innovation in Kazakhstan.










