
In computing, an expansion card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer's motherboard to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard.

PCI Express, officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism, and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization.

CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994.

ExpressCard, initially called NEWCARD, is an interface to connect peripheral devices to a computer, usually a laptop computer. The ExpressCard technical standard specifies the design of slots built into the computer and of expansion cards to insert in the slots. The cards contain electronic circuits and sometimes connectors for external devices. The ExpressCard standard replaces the PC Card standards.
PCI-X, short for Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI local bus for higher bandwidth demanded mostly by servers and workstations. It uses a modified protocol to support higher clock speeds, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation. PCI-X 2.0 added speeds up to 533 MHz, with a reduction in electrical signal levels.

Altix is a line of server computers and supercomputers produced by Silicon Graphics, based on Intel processors. It succeeded the MIPS/IRIX-based Origin 3000 servers.
HPE Integrity is a series of server computers produced by Hewlett Packard Enterprise since 2003, based on the Itanium processor. The Integrity brand name was inherited by HP from Tandem Computers via Compaq.
Input/output operations per second is an input/output performance measurement used to characterize computer storage devices like hard disk drives (HDD), solid state drives (SSD), and storage area networks (SAN). Like benchmarks, IOPS numbers published by storage device manufacturers do not directly relate to real-world application performance.

The IBM BladeCenter was IBM's blade server architecture, until it was replaced by Flex System in 2012. The x86 division was later sold to Lenovo in 2014.

A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It is also sometimes called a semiconductor storage device, a solid-state device or a solid-state disk, even though SSDs lack the physical spinning disks and movable read–write heads used in hard disk drives (HDDs) and floppy disks.

BladeSystem is a line of blade server machines from Hewlett Packard Enterprise that was introduced in June 2006.

Fusion-io, Inc. was a computer hardware and software systems company based in Cottonwood Heights, Utah, that designed and manufactured products using flash memory technology. The Fusion ioMemory was marketed for applications such as databases, virtualization, cloud computing, big data. Their ioDrive product was considered around 2011 to be one of the fastest storage devices on the market.

The Intel X25-M was a line of Serial ATA interface solid-state drives developed by Intel for personal computers, announced in late 2008. The SSD was a multi-level-cell solid-state drive available in a 2.5" form factor, came in 80 GB and 160 GB capacities and utilized NAND flash memory on a 50 nm process. The second-generation SSD which was called the "X25-M G2". The X25-M G2 was also available in a 2.5" form factor and 80 GB and 160 GB capacities, but with NAND flash memory on a more efficient 34 nm process.

The Dell blade server products are built around their M1000e enclosure that can hold their server blades, an embedded EqualLogic iSCSI storage area network and I/O modules including Ethernet, Fibre Channel and InfiniBand switches.
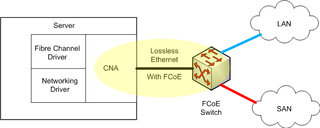
A converged network adapter (CNA), also called a converged network interface controller (C-NIC), is a computer input/output device that combines the functionality of a host bus adapter (HBA) with a network interface controller (NIC). In other words, it "converges" access to, respectively, a storage area network and a general-purpose computer network.

The ThinkStation is a line of professional workstations from Lenovo. They are designed to be used for high-end computing and CAD tasks and primarily compete with other enterprise workstation lines, such as Dell's Precision, HP's Z line, and Apple's Mac Pro line.

SATA Express is a computer bus interface that supports both Serial ATA (SATA) and PCI Express (PCIe) storage devices, initially standardized in the SATA 3.2 specification. The SATA Express connector used on the host side is backward compatible with the standard SATA data connector, while it also provides two PCI Express lanes as a pure PCI Express connection to the storage device.
Virtium Solid State Storage and Memory is a privately held American maker of semiconductor memory and solid-state disk (SSD) products for data storage in industrial/machine-to-machine designs; embedded systems, including small-footprint designs; and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) applications. Primary markets the company focuses on are defense, industrial systems, network communications, and transportation. The name Virtium is derived from the word virtue.
IBM FlashCore Modules (FCM) are solid state technology computer data storage modules using PCI Express attachment and the NVMe command set. The raw storage capacities are 4.8 TB, 9.6 TB, 19.2 TB and 38.4 TB. The FlashCore modules support hardware self-encryption and real-time inline hardware data compression without performance impact. They are used in selected arrays from the IBM FlashSystem family.














