
The iRobot Warrior (also described as the Warrior 700 or X700) is an unmanned robotic platform from iRobot Corporation.

The iRobot Warrior (also described as the Warrior 700 or X700) is an unmanned robotic platform from iRobot Corporation.
The 285 lb (129 kg) robot can traverse land at up to 9.3 mph (15 km/h) and is capable of carrying up to 500 lb (227 kg), including 150 lb (68 kg) in its manipulator. [1] [2] Able to climb steps and slopes at up to 45°, the next generation of remote control robotic vehicles is bigger, faster, and more capable than their smaller counterparts. [3] [ promotion? ] Initial intended uses are Explosive Ordnance Disposal, route-clearance, surveillance, enhanced security measures, scouting, reconnaissance, casualty extraction, firefighting, manipulating and welding. [3] [4]
iRobot has teamed up with Metal Storm to mount an electronically controlled firing system on a Warrior capable of firing up to 16 rounds per second. [2]
In c. 2008, iRobot announced that it received a $3.75 million contract from Army Tank-Automotive Research, Development and Engineering Center for research and development. [5]
An autonomous robot is a robot that acts without recourse to human control. The first autonomous robots environment were known as Elmer and Elsie, which were constructed in the late 1940s by W. Grey Walter. They were the first robots in history that were programmed to "think" the way biological brains do and meant to have free will. Elmer and Elsie were often labeled as tortoises because of how they were shaped and the manner in which they moved. They were capable of phototaxis which is the movement that occurs in response to light stimulus.

The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supports astronauts working in space, and services instruments and other payloads attached to the ISS and is used for external maintenance. Astronauts receive specialized training to enable them to perform these functions with the various systems of the MSS.

James Sacra Albus was an American engineer, Senior NIST Fellow and founder and former chief of the Intelligent Systems Division of the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).

Canadarm or Canadarm1 is a series of robotic arms that were used on the Space Shuttle orbiters to deploy, manoeuvre, and capture payloads. After the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, the Canadarm was always paired with the Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), which was used to inspect the exterior of the shuttle for damage to the thermal protection system.

iRobot Corporation is an American technology company that designs and builds consumer robots. It was founded in 1990 by three members of MIT's Artificial Intelligence Lab, who designed robots for space exploration and military defense. The company's products include a range of autonomous home vacuum cleaners (Roomba), floor moppers, and other autonomous cleaning devices.

Prithvi is a tactical surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP). It is deployed by India's Strategic Forces Command.
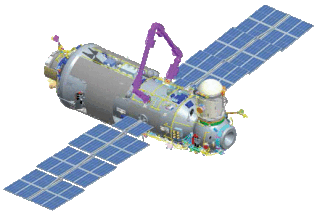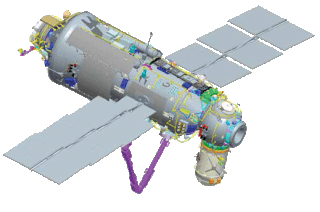
The European Robotic Arm (ERA) is a robotic arm that is attached to the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) of the International Space Station. Launched to the ISS in July 2021; it is the first robotic arm that is able to work on the Russian Segment of the station. The arm supplements the two Russian Strela cargo cranes that were originally installed on the Pirs module, but were later moved to the docking compartment Poisk and Zarya module.

An unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) is a vehicle that operates while in contact with the ground and without an onboard human presence. UGVs can be used for many applications where it may be inconvenient, dangerous, or impossible to have a human operator present. Generally, the vehicle will have a set of sensors to observe the environment, and will either autonomously make decisions about its behavior or pass the information to a human operator at a different location who will control the vehicle through teleoperation.
The Battlefield Extraction-Assist Robot (BEAR) is a remotely controlled robot developed by Vecna Robotics for use in the extraction of wounded soldiers from the battlefield with no risk to human life. The humanoid robot uses a powerful hydraulics system to carry humans and other heavy objects over long distances and rough terrain, such as stairs.

Mesa Associates' Tactical Integrated Light-Force Deployment Assembly (MATILDA) is a remote controlled surveillance and reconnaissance robot, created and designed by the 'Mesa Robotics Corporation'. It is available in many different models such as the Urban Warrior, Block II, and Scout, which feature different combinations of components for increased utility. These options include a sensor mount, manipulator arm, weapon mount, fiber optic reel, remote trailer release, and disrupter mount. When purchased the basic system includes the platform, the control unit, and battery charger.

The history of robots has its origins in the ancient world. During the industrial revolution, humans developed the structural engineering capability to control electricity so that machines could be powered with small motors. In the early 20th century, the notion of a humanoid machine was developed.

Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots. Robotics is related to the sciences of electronics, engineering, mechanics, and software.
The Chinese 8A4 class ROUV is a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROUV) used to perform various underwater tasks, ranging from oil platform service to salvage and rescue missions. The 8A4 is a member of a series of related ROUVs developed by the Shenyang Institute of Automation (SIA) in the People's Republic of China (PRC). The predecessor to the 8A4 was the RECON-IV, an improved version of the American RECON-III. The 8A4 itself is an upgraded version of the American AMETEK 2006, and the 7B8 is an improved version of the 8A4.
Sea Dragon-class remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROUVs) are a class of Chinese remotely operated vehicle (ROV) used to perform various underwater tasks such as oil platform service, salvage, and rescue missions. Following the successful development of the original Sea Dragon (海龙), a series of ROUVs based on it have been developed. The original model had a diving capability up to 3,500 meters, but subsequent models were designed to meet a variety of operating conditions.
SJT-class ROUVs are a series of Chinese remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROUVs) jointly developed by the Shenyang Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Science and the Institute of Underwater Engineering of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SHJTU). The general designer of the SJT-class of ROUVs is Zhu Jimao (朱继懋), a professor at SHJTU, who also was the general designer of the earlier Type 7103 DSRV. Many more ROUVs have been developed after the SJT series, based on experience gained from this series.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to robotics:

The Ripsaw is a series of developmental unmanned ground combat vehicles designed by Howe & Howe Technologies for evaluation by the United States Army.
The Modular Advanced Armed Robotic System (MAARS) is a robot that is being developed by Qinetiq. A member of the TALON family, it will be the successor to the armed SWORDS robot. It has a different, larger chassis than the SWORDS robot, so has little physically in common with the SWORDS and TALON

Counter-IED equipment are created primarily for military and law enforcement. They are used for standoff detection of explosives and explosive precursor components and defeating the Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) devices themselves as part of a broader counter-terrorism, counter-insurgency, or law enforcement effort.

The HAL Combat Air Teaming System (CATS) is an Indian unmanned and manned combat aircraft air teaming system being developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The system will consist of a manned fighter aircraft acting as "mothership" of the system and a set of swarming UAVs and UCAVs governed by the mothership aircraft. A twin-seated HAL Tejas is likely to be the mothership aircraft. Various other sub components of the system are currently under development and will be jointly produced by HAL, National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Newspace Research & Technologies.