Related Research Articles
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that develops from experiencing a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on a person's life or well-being. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress to trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in the way a person thinks and feels, and an increase in the fight-or-flight response. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event and can include triggers such as misophonia. Young children are less likely to show distress, but instead may express their memories through play. A person with PTSD is at a higher risk of suicide and intentional self-harm.

In medicine, traumatology is the study of wounds and injuries caused by accidents or violence to a person, and the surgical therapy and repair of the damage. Traumatology is a branch of medicine. It is often considered a subset of surgery and in countries without the specialty of trauma surgery it is most often a sub-specialty to orthopedic surgery. Traumatology may also be known as accident surgery.

Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.

An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. Injuries to humans can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or overexertion. Injuries can occur in any part of the body, and different symptoms are associated with different injuries.
Psychological trauma is an emotional response caused by severe distressing events that are outside the normal range of human experiences. It must be understood by the affected person as directly threatening the affected person or their loved ones generally with death, severe bodily injury, or sexual violence; indirect exposure, such as from watching television news, may be extremely distressing and can produce an involuntary and possibly overwhelming physiological stress response, but does not produce trauma per se. Examples of distressing events include violence, rape, or a terrorist attack.

A blast injury is a complex type of physical trauma resulting from direct or indirect exposure to an explosion. Blast injuries occur with the detonation of high-order explosives as well as the deflagration of low order explosives. These injuries are compounded when the explosion occurs in a confined space.
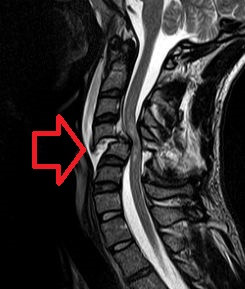
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.
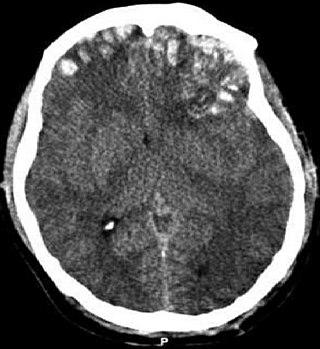
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumatic brain injury. TBI can also be characterized based on mechanism or other features. Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death.
Closed-head injury is a type of traumatic brain injury in which the skull and dura mater remain intact. Closed-head injuries are the leading cause of death in children under 4 years old and the most common cause of physical disability and cognitive impairment in young people. Overall, closed-head injuries and other forms of mild traumatic brain injury account for about 75% of the estimated 1.7 million brain injuries that occur annually in the United States. Brain injuries such as closed-head injuries may result in lifelong physical, cognitive, or psychological impairment and, thus, are of utmost concern with regards to public health.
Post-concussion syndrome (PCS), also known as persisting symptoms after concussion, is a set of symptoms that may continue for weeks, months, or years after a concussion. PCS is medically classified as a mild traumatic brain injury (TBI). About 35% of people with concussion experience persistent or prolonged symptoms 3 to 6 months after injury. Prolonged concussion is defined as having concussion symptoms for over four weeks following the first accident in youth and for weeks or months in adults.

Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease linked to repeated trauma to the head. The encephalopathy symptoms can include behavioral problems, mood problems, and problems with thinking. The disease often gets worse over time and can result in dementia.
Polytrauma and multiple trauma are medical terms describing the condition of a person who has been subjected to multiple traumatic injuries, such as a serious head injury in addition to a serious burn. The term is defined via an Injury Severity Score (ISS) equal to or greater than 16. It has become a commonly applied term by US military physicians in describing the seriously injured soldiers returning from Operation Iraqi Freedom in Iraq and Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan. The term is generic, however, and has been in use for a long time for any case involving multiple trauma.

The Madigan Army Medical Center, located on Joint Base Lewis-McChord just outside Lakewood, Washington, is a key component of the Madigan Healthcare System and one of the largest military hospitals on the West Coast of the United States.
Memory and trauma is the deleterious effects that physical or psychological trauma has on memory.

Shell shock is a term that originated during World War I to describe the type of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) that many soldiers experienced during the war, before PTSD was officially recognized. It is a reaction to the intensity of the bombardment and fighting that produced helplessness, which could manifest as panic, fear, flight, or an inability to reason, sleep, walk, or talk.
The Defense Centers of Excellence for Psychological Health and Traumatic Brain Injury (DCoE) is a United States Department of Defense (DoD) organization that provides guidance across DoD programs related to psychological health (PH) and traumatic brain injury (TBI) issues. The organization's official mission is to "improve the lives of our nation’s service members, families and veterans by advancing excellence in psychological health and traumatic brain injury prevention and care."
PTSD or post-traumatic stress disorder, is a psychiatric disorder characterised by intrusive thoughts and memories, dreams or flashbacks of the event; avoidance of people, places and activities that remind the individual of the event; ongoing negative beliefs about oneself or the world, mood changes and persistent feelings of anger, guilt or fear; alterations in arousal such as increased irritability, angry outbursts, being hypervigilant, or having difficulty with concentration and sleep.

Richard Allan Bryant is an Australian medical scientist. He is Scientia Professor of Psychology at the University of New South Wales (UNSW) and director of the UNSW Traumatic Stress Clinic, based at UNSW and Westmead Institute for Medical Research. His main areas of research are posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and prolonged grief disorder. On 13 June 2016 he was appointed a Companion of the Order of Australia (AC), for eminent service to medical research in the field of psychotraumatology, as a psychologist and author, to the study of Indigenous mental health, as an advisor to a range of government and international organisations, and to professional societies.
The Gray Team, currently evolved into the Grey Team, and more formally known as the Joint Neurosciences Inspection Team, was the name given to a series of special inspection units commissioned by the Joint Chiefs of Staff to serve as mechanism to help improve the care of American forces serving in Iraq and Afghanistan. Their missions were particularly focused on the "invisible wounds of war" such as traumatic brain injury or post traumatic stress.
Operational stress injury or OSI is a non-clinical, non-medical term referring to a persistent psychological difficulty caused by traumatic experiences or prolonged high stress or fatigue during service as a military member or first responder. The term does not replace any individual diagnoses or disorders, but rather describes a category of mental health concerns linked to the particular challenges that these military members or first responders encounter in their service. There is not yet a single fixed definition. The term was first conceptualized within the Canadian Armed Forces to help foster understanding of the broader mental health challenges faced by military members who have been impacted by traumatic experiences and who face difficulty as a result. OSI encompasses a number of the diagnoses found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) classification system, with the common thread being a linkage to the operational experiences of the afflicted. The term has gained traction outside of the military community as an appropriate way to describe similar challenges suffered by those whose work regularly exposes them to trauma, particularly front line emergency first responders such as but not limited to police, firefighters, paramedics, correctional officers, and emergency dispatchers. The term, at present mostly used within Canada, is increasingly significant in the development of legislation, policy, treatments and benefits in the military and first responder communities.
References
- 1 2 3 Worth, Robert F. (2016-06-10). "What if PTSD Is More Physical Than Psychological?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331 . Retrieved 2016-06-14.
- 1 2 Matthews, Mark (February 2009). "Brain injury sleuth". American Society for Engineering Education. 18 (6). JSTOR 24163095.
- ↑ "Shell Shock Revisited: Solving the Puzzle of Blast Trauma". Science. 319 (5862). January 25, 2008. JSTOR i20053168.
- ↑ "U of Alberta building 'blast lab' to study brain injuries in soldiers". Edmonton Sun. Retrieved 2016-06-11.
- ↑ Staff. "Woman of Vision: Dr. Ibolja Cernak has dedicated her career to helping soldiers". Global News. Global News. Retrieved 2016-06-11.